Solid Earth - SchoolNova
... • Fifty years long lively debate started between "drifters" or "mobilists" (proponents of the theory) and "fixists" (opponents), during which the theory of plate tectonics was born. ...
... • Fifty years long lively debate started between "drifters" or "mobilists" (proponents of the theory) and "fixists" (opponents), during which the theory of plate tectonics was born. ...
The Layers of Earth
... Heat maintained by insulation of outer layers Powers all geologic activity ...
... Heat maintained by insulation of outer layers Powers all geologic activity ...
Geology and Mining
... pushes them apart, creating new crust as it cools and spreads • Transform plate boundary = two plates meet, slipping and grinding alongside one another – Friction spawns earthquakes along slip-strike faults ...
... pushes them apart, creating new crust as it cools and spreads • Transform plate boundary = two plates meet, slipping and grinding alongside one another – Friction spawns earthquakes along slip-strike faults ...
Geology and Mining
... The rock cycle • Rock cycle = The heating, melting, cooling, breaking and reassembling of rocks and ...
... The rock cycle • Rock cycle = The heating, melting, cooling, breaking and reassembling of rocks and ...
Earths Layers
... And what type of crust would you like with your Earth? 6. There are two types of crust ...
... And what type of crust would you like with your Earth? 6. There are two types of crust ...
Relative Age Dating and Correlation Review
... The geologic columns A, B, and C in the diagrams below represent widely spaced outcrops of sedimentary rocks. Symbols are used to indicate fossils found within each rock layer. Each rock layer represents the fossil record of a different geologic time period. ...
... The geologic columns A, B, and C in the diagrams below represent widely spaced outcrops of sedimentary rocks. Symbols are used to indicate fossils found within each rock layer. Each rock layer represents the fossil record of a different geologic time period. ...
Exemplar: Describe the theory of Plate Tectonics Claim: The theory
... at some maps. As he continued to investigate, he found similar fossils and rocks on continents separated by oceans. He proposed that the continents were drifting. Later Harry Hess discovered the mechanism that caused the movement. ...
... at some maps. As he continued to investigate, he found similar fossils and rocks on continents separated by oceans. He proposed that the continents were drifting. Later Harry Hess discovered the mechanism that caused the movement. ...
First Hour Exam, Fall, 1998
... a. they are being pushed up by mantle plumes and convection cells. b. they are composed of less-dense rocks than the oceanic crust. c. volcanoes on the continents have erupted vast thicknesses of volcanic rocks, so they're much thicker than the crust beneath the oceans. d. the continents are compose ...
... a. they are being pushed up by mantle plumes and convection cells. b. they are composed of less-dense rocks than the oceanic crust. c. volcanoes on the continents have erupted vast thicknesses of volcanic rocks, so they're much thicker than the crust beneath the oceans. d. the continents are compose ...
25.1 Notes
... - corresponds closely with plate boundaries -usually shallow EQ’s (70km or lower) occur at divergent boundaries -deep EQ’s (70km or more) occur at convergent boundaries ...
... - corresponds closely with plate boundaries -usually shallow EQ’s (70km or lower) occur at divergent boundaries -deep EQ’s (70km or more) occur at convergent boundaries ...
here
... Slieve Foye – there is a noticeable change in the appearance of the mountain at the change in geology. Both of these rocks are intrusive rather than extrusive or volcanic, meaning that they cooled and hardened from magma below the surface, but it is likely that there was volcanic activity, much like ...
... Slieve Foye – there is a noticeable change in the appearance of the mountain at the change in geology. Both of these rocks are intrusive rather than extrusive or volcanic, meaning that they cooled and hardened from magma below the surface, but it is likely that there was volcanic activity, much like ...
geology stratigraphy geological time scale
... Æ Study of the origin, structure, composition & physical history of Earth, and the processes which have led to its present state. Æ The science that deals with the dynamics and physical history of Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the physical, chemical, and biological changes that it ha ...
... Æ Study of the origin, structure, composition & physical history of Earth, and the processes which have led to its present state. Æ The science that deals with the dynamics and physical history of Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the physical, chemical, and biological changes that it ha ...
Plate tectonics theory
... PBS, Intro to Plate Tectonic Theory, http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/tectonics/intro.html, accessed ...
... PBS, Intro to Plate Tectonic Theory, http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/tectonics/intro.html, accessed ...
The Rock Cycle - The Inspired Instructor
... The buried rock is changed by extreme heat and pressure. ...
... The buried rock is changed by extreme heat and pressure. ...
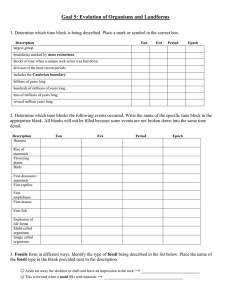
Goal 5: Evolution of Organisms and Landforms
... 4. Most fossils form in ________________________ rock. The ________________________ of fossils within this type of rock layers help scientists construct the geologic time scale. 5. Sequence the following events in the fossilization process: _______ Over time, the surrounding material builds up and t ...
... 4. Most fossils form in ________________________ rock. The ________________________ of fossils within this type of rock layers help scientists construct the geologic time scale. 5. Sequence the following events in the fossilization process: _______ Over time, the surrounding material builds up and t ...
Branches of Science
... Earth along with its rocks, minerals, and land forms, and of the history of the changes these have undergone. • The structure of a specific region of the Earth, including its rocks, soils, mountaines, fossils, and other features. ...
... Earth along with its rocks, minerals, and land forms, and of the history of the changes these have undergone. • The structure of a specific region of the Earth, including its rocks, soils, mountaines, fossils, and other features. ...
Name - oms6a
... Continental drift - The hypothesis that the continents slowly move across Earth’s surface. Pangaea - The name of the single landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago and gave rise to today’s continents. (Supercontinent – Pangaea means “All land”) Fossil - A trace of an ancient organism that ha ...
... Continental drift - The hypothesis that the continents slowly move across Earth’s surface. Pangaea - The name of the single landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago and gave rise to today’s continents. (Supercontinent – Pangaea means “All land”) Fossil - A trace of an ancient organism that ha ...
TOP 50 ASTRONOMY FACTS
... 43. The lithosphere is the earth’s crust and upper portion of the mantle. It is in the lithosphere that the tectonic plates are found. 44. The asthenosphere is the portion of the earth’s mantle that is under the lithosphere. 45. Convection is the movement of heat through liquid. 46. Convection cause ...
... 43. The lithosphere is the earth’s crust and upper portion of the mantle. It is in the lithosphere that the tectonic plates are found. 44. The asthenosphere is the portion of the earth’s mantle that is under the lithosphere. 45. Convection is the movement of heat through liquid. 46. Convection cause ...
D-1_Study_Guide_2014
... 16. What does the Richter scale measure? _________________________________________________ 17. Which earthquake waves cause the greatest amount of damage to buildings, roads, and other surface features? ____________________________________ 18. What commonly occurs along a transform boundary________ ...
... 16. What does the Richter scale measure? _________________________________________________ 17. Which earthquake waves cause the greatest amount of damage to buildings, roads, and other surface features? ____________________________________ 18. What commonly occurs along a transform boundary________ ...
Name - RCSD
... 16. What does the Richter scale measure? _________________________________________________ 17. Which earthquake waves cause the greatest amount of damage to buildings, roads, and other surface features? ____________________________________ 18. What commonly occurs along a transform boundary________ ...
... 16. What does the Richter scale measure? _________________________________________________ 17. Which earthquake waves cause the greatest amount of damage to buildings, roads, and other surface features? ____________________________________ 18. What commonly occurs along a transform boundary________ ...
12.1 Evidence for Continental Drift
... evidence for continental drift. The rocks found in Newfoundland are the same type and age as rocks found in Greenland, ...
... evidence for continental drift. The rocks found in Newfoundland are the same type and age as rocks found in Greenland, ...
5.2 Notes
... Soil forms slowly over time and has been classified into layers, giving it a soil profile: - Topsoil (dark rich soil containing humus and small grains of rock - Subsoil (lighter in color with little or no humus- contains minerals that have been leached from the topsoil). Leaching is the removal of m ...
... Soil forms slowly over time and has been classified into layers, giving it a soil profile: - Topsoil (dark rich soil containing humus and small grains of rock - Subsoil (lighter in color with little or no humus- contains minerals that have been leached from the topsoil). Leaching is the removal of m ...
Unit 2 Review and Solutions
... Creatures when they die) – Chemical (Rock formed from natural chemical processes and cementation) ...
... Creatures when they die) – Chemical (Rock formed from natural chemical processes and cementation) ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.