Ch 14 Notes - OCPS TeacherPress
... Radioactive dating is the method used to determine the age of the earth and of fossils. Clues in Rocks A fossil is any preserved evidence of an organism. Examples of fossils include bones, shells, and impressions of dead organisms left in rocks. Most organisms decompose before they have a ch ...
... Radioactive dating is the method used to determine the age of the earth and of fossils. Clues in Rocks A fossil is any preserved evidence of an organism. Examples of fossils include bones, shells, and impressions of dead organisms left in rocks. Most organisms decompose before they have a ch ...
TEST 1 FALL 2006
... 40. As the word is understood in sciences, many “theories” in geology will never become laws because__________. a. geologists cannot agree b. geologic time cannot be duplicated in the lab or field c. it is impossible to observe Earth processes d. all of these 41. Subduction zones are associated wit ...
... 40. As the word is understood in sciences, many “theories” in geology will never become laws because__________. a. geologists cannot agree b. geologic time cannot be duplicated in the lab or field c. it is impossible to observe Earth processes d. all of these 41. Subduction zones are associated wit ...
What is “magnetic reversal?”
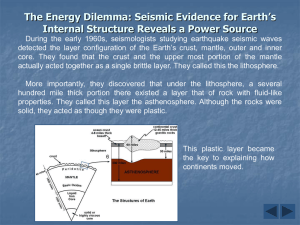
... During the early 1960s, seismologists studying earthquake seismic waves detected the layer configuration of the Earth’s crust, mantle, outer and inner core. They found that the crust and the upper most portion of the mantle actually acted together as a single brittle layer. They called this the lith ...
... During the early 1960s, seismologists studying earthquake seismic waves detected the layer configuration of the Earth’s crust, mantle, outer and inner core. They found that the crust and the upper most portion of the mantle actually acted together as a single brittle layer. They called this the lith ...
notes for geologofe - sciencepowerpoint.com
... Physical Property of Minerals- a characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance. Luster – How light is reflected from a mineral. Metallic (shiny) or non-metallic (dull) Hardness – How easily a mineral can be scratched. Color – Tells what atoms make ...
... Physical Property of Minerals- a characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance. Luster – How light is reflected from a mineral. Metallic (shiny) or non-metallic (dull) Hardness – How easily a mineral can be scratched. Color – Tells what atoms make ...
Marcie wanted to compare the lengths and masses of some different
... B. most fresh water is frozen and may be hard to reach. C. more than 6 billion people throughout the world need fresh water. D. less than three percent of the water on Earth is fresh water. ...
... B. most fresh water is frozen and may be hard to reach. C. more than 6 billion people throughout the world need fresh water. D. less than three percent of the water on Earth is fresh water. ...
Physical Geology 101*Midterm 1
... B. paleomagnetism and seafloor striping C. relative dating of rocks using Steno’s and Lyell’s principles D. counting the number of atoms of FeS in meteorites 25. The Hawaiian Islands have formed over a mantle plume/hot spot that has remained in nearly the same place for at least 80 million years. 26 ...
... B. paleomagnetism and seafloor striping C. relative dating of rocks using Steno’s and Lyell’s principles D. counting the number of atoms of FeS in meteorites 25. The Hawaiian Islands have formed over a mantle plume/hot spot that has remained in nearly the same place for at least 80 million years. 26 ...
review list 2013
... Current Plate Tectonic Theory includes Alfred Wegener’s original idea of Continental Drift and the modern idea of seafloor spreading. Continental Drift evidence: Correlation of fossils, rock structures and types, continent shapes, and climate (glacial) evidence across continents. Seafloor spre ...
... Current Plate Tectonic Theory includes Alfred Wegener’s original idea of Continental Drift and the modern idea of seafloor spreading. Continental Drift evidence: Correlation of fossils, rock structures and types, continent shapes, and climate (glacial) evidence across continents. Seafloor spre ...
File
... 7.5 – Recognize that lithospheric plates on the scale of continents and oceans continually move at rates of centimeters per year 7.6 – Describe the relationship between plate movements and earthquakes, mountain building, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading ...
... 7.5 – Recognize that lithospheric plates on the scale of continents and oceans continually move at rates of centimeters per year 7.6 – Describe the relationship between plate movements and earthquakes, mountain building, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading ...
section 1 - image identification
... Do meandering rivers make stable and unchanging boundaries between states and countries? Match the layers of the earth listed below with their corresponding positions on the diagram ...
... Do meandering rivers make stable and unchanging boundaries between states and countries? Match the layers of the earth listed below with their corresponding positions on the diagram ...
6th Grade Earth Science – Inside Earth Vocabulary 1. crust – the
... 9. compass – an instrument composed of a small, light-weight magnet called a needle, that is balanced on a frictionless bearing 10. continental drift – the hypothesis that the continents slowly move across the Earth’s surface 11. sea-floor spreading – the process by which molten material adds new cr ...
... 9. compass – an instrument composed of a small, light-weight magnet called a needle, that is balanced on a frictionless bearing 10. continental drift – the hypothesis that the continents slowly move across the Earth’s surface 11. sea-floor spreading – the process by which molten material adds new cr ...
Earth`s Interior
... Study rock samples from inside Earth. Study seismic waves from earthquakes and how they travel through different parts of Earth. ...
... Study rock samples from inside Earth. Study seismic waves from earthquakes and how they travel through different parts of Earth. ...
Pangea Location of different fossils, location of different types of
... Sonar is sound waves that bounce off the ocean floor. These sound waves show features on the ocean floor. The midocean ridge and trenches The plates moving apart along the midocean ridge have different ages of rocks. The newest rocks are along the midocean ridge where lava comes out. The o ...
... Sonar is sound waves that bounce off the ocean floor. These sound waves show features on the ocean floor. The midocean ridge and trenches The plates moving apart along the midocean ridge have different ages of rocks. The newest rocks are along the midocean ridge where lava comes out. The o ...
LANDFORMS
... The rocks of Gros Morne National Park and adjacent parts of western Newfoundland are world-renowned for the light they shed on the geological evolution of ancient mountain belts. The geology of the park illustrates the concept of plate tectonics, one of the most important ideas in modern science. ...
... The rocks of Gros Morne National Park and adjacent parts of western Newfoundland are world-renowned for the light they shed on the geological evolution of ancient mountain belts. The geology of the park illustrates the concept of plate tectonics, one of the most important ideas in modern science. ...
document
... oldest rocks of the region and range in age from late Ordovician up through the Mississippian. The rest of the Appalachian Plateau is of Pennsylvanian and Permian age and is where coal seams are located. The folded and thrusted rock of the plateau is made up mainly of marine sedimentary rock and vol ...
... oldest rocks of the region and range in age from late Ordovician up through the Mississippian. The rest of the Appalachian Plateau is of Pennsylvanian and Permian age and is where coal seams are located. The folded and thrusted rock of the plateau is made up mainly of marine sedimentary rock and vol ...
Plate Tectonics - Helena High School
... Antarctica, therefore Antarctica must have been closer to the equator at one time. ...
... Antarctica, therefore Antarctica must have been closer to the equator at one time. ...
Review Questions For Earth crust (answers)
... 15. List the three types of weathering, and give and example for each one. Mechanical Weathering – the physical action of breaking rock into smaller pieces Examples- Ice forming in cracks of rocks, Animals walking on the rocks, sun on rocks Chemical Weathering- Breaking rocks apart using chemical re ...
... 15. List the three types of weathering, and give and example for each one. Mechanical Weathering – the physical action of breaking rock into smaller pieces Examples- Ice forming in cracks of rocks, Animals walking on the rocks, sun on rocks Chemical Weathering- Breaking rocks apart using chemical re ...
A1,A2 and A3 : Introduction to Geophysics
... ● The outer core has a radius of 3480 km. Composition is believed to be liquid Fe-O or Fe-S alloy. Rapid convection generates the Earth's magnetic field. Outer surface of the core is termed the core-mantle boundary (CMB). ● The inner core has a radius of 1221 km and is composed of solid iron (roughl ...
... ● The outer core has a radius of 3480 km. Composition is believed to be liquid Fe-O or Fe-S alloy. Rapid convection generates the Earth's magnetic field. Outer surface of the core is termed the core-mantle boundary (CMB). ● The inner core has a radius of 1221 km and is composed of solid iron (roughl ...
Glossary
... The wearing away of any part of the Earth’s surface by natural agencies — water, ice, wind etc. The actual physical process of magma being brought to and dispersed on the surface of the Earth. The separation, by weathering, of successive thin onion-like shells from the bare surfaces of rocks like ba ...
... The wearing away of any part of the Earth’s surface by natural agencies — water, ice, wind etc. The actual physical process of magma being brought to and dispersed on the surface of the Earth. The separation, by weathering, of successive thin onion-like shells from the bare surfaces of rocks like ba ...
Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rock Formation and Characteristics
... 1) ______________________________ - associated with __________ temperatures and pressures 2) ______________________________ - associated with __________ temperatures and pressures Types of Metamorphic Rock 1) _________________________________ ...
... 1) ______________________________ - associated with __________ temperatures and pressures 2) ______________________________ - associated with __________ temperatures and pressures Types of Metamorphic Rock 1) _________________________________ ...
Earth`s Matter
... ● The changes of the rock cycle are closely related to plate tectonics. ○ help drive the rock cycle by helping to form magma, the source of igneous rocks. ○ The collision of continental plates can be strong enough to push up a mountain range resulting in sedimentary rock ...
... ● The changes of the rock cycle are closely related to plate tectonics. ○ help drive the rock cycle by helping to form magma, the source of igneous rocks. ○ The collision of continental plates can be strong enough to push up a mountain range resulting in sedimentary rock ...
Earth`s crust, the surface layer of the planet, is
... and unbroken. The forces that rage inside the planet have fractured this brittle layer. Some of these fractures, called faults, lie beneath the surface of the crust. Other faults, however, have ruptured the surface, cracking the crust into various-sized blocks of rock. These blocks dip and rise alon ...
... and unbroken. The forces that rage inside the planet have fractured this brittle layer. Some of these fractures, called faults, lie beneath the surface of the crust. Other faults, however, have ruptured the surface, cracking the crust into various-sized blocks of rock. These blocks dip and rise alon ...
Important Vocabulary Terms: Match them with definitions below
... 19. Where do you find magma and where do you find lava? Magma in the Earth, Lava outside the crust ...
... 19. Where do you find magma and where do you find lava? Magma in the Earth, Lava outside the crust ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.