Earth Scavenger Hunt
... 6. Scientists study meteorites called chondrites to help estimate the chemical composition of the earth and use seismographs to study vibrations during earthquakes. The changes in vibrations help scientists understand the chemical composition of the materials they are traveling through. 7. The press ...
... 6. Scientists study meteorites called chondrites to help estimate the chemical composition of the earth and use seismographs to study vibrations during earthquakes. The changes in vibrations help scientists understand the chemical composition of the materials they are traveling through. 7. The press ...
InsidetheEarth
... from that point, the temperature rises 1 Celsius degree. This rapid rise in temperature continues for several kilometers. After that, the temperature increases more slowly, but steadily. ...
... from that point, the temperature rises 1 Celsius degree. This rapid rise in temperature continues for several kilometers. After that, the temperature increases more slowly, but steadily. ...
Notes: Plate Tectonics - Riverdale Middle School
... 2. Reversals of Earth’s magnetic field are recorded by rocks in strips parallel to ridges ...
... 2. Reversals of Earth’s magnetic field are recorded by rocks in strips parallel to ridges ...
Earth*s Interior - Mr. Cramer
... Magnetic field affects the whole Earth A compass needle aligns with the line of force in Earth’s magnetic field ...
... Magnetic field affects the whole Earth A compass needle aligns with the line of force in Earth’s magnetic field ...
File
... Objective 16: I can identify folding and the types of folding. Folding: bends in rock that form when compression shortens and thickens part of Earth’s crust. Anticline: a fold in rock that bends upward into an arch. (horizontal stress) Syncline: a fold in rock that bends downward in the middle to f ...
... Objective 16: I can identify folding and the types of folding. Folding: bends in rock that form when compression shortens and thickens part of Earth’s crust. Anticline: a fold in rock that bends upward into an arch. (horizontal stress) Syncline: a fold in rock that bends downward in the middle to f ...
NOTES Plate Tectonics
... 12. The Pacific Ocean is shrinking and the Atlantic Ocean is expanding. 13. The three kinds of plate boundaries are: a. Transform - where two plates slip past each other in opposite directions. b. Divergent - where two plates move apart (mid-ocean ridge). c. Convergent - where two plates come toget ...
... 12. The Pacific Ocean is shrinking and the Atlantic Ocean is expanding. 13. The three kinds of plate boundaries are: a. Transform - where two plates slip past each other in opposite directions. b. Divergent - where two plates move apart (mid-ocean ridge). c. Convergent - where two plates come toget ...
Why do Volcanoes erupt? A volcano is a mountain that opens
... A volcano is a mountain that opens downward to a pool of molten rock below the surface of the earth. The large masses build up over time through eruptions in the earth’s upper mantle. They look like large mountains but are far more dangerous. .How are volcanoes formed? Volcanoes are formed when magm ...
... A volcano is a mountain that opens downward to a pool of molten rock below the surface of the earth. The large masses build up over time through eruptions in the earth’s upper mantle. They look like large mountains but are far more dangerous. .How are volcanoes formed? Volcanoes are formed when magm ...
Jeopardy Template
... Earth's surface or cools after erupting from a volcano as lava, igneous rock is formed. Rocks formed from other types of rocks by intense heat and pressure deep within the Earth are called metamorphic rocks. ...
... Earth's surface or cools after erupting from a volcano as lava, igneous rock is formed. Rocks formed from other types of rocks by intense heat and pressure deep within the Earth are called metamorphic rocks. ...
Vocabulary Quiz
... B. Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis that the continents were once joined together and have broken and drifted apart ...
... B. Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis that the continents were once joined together and have broken and drifted apart ...
Chapter 5 Section 1
... 1. Why is it difficult to determine Earth’s inner structure? 2. What is the difference between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere? 3. How do temperature and pressure change as you go deeper into the Earth? 4. How are oceanic and continental crusts alike and different? 5. Place these terms in corr ...
... 1. Why is it difficult to determine Earth’s inner structure? 2. What is the difference between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere? 3. How do temperature and pressure change as you go deeper into the Earth? 4. How are oceanic and continental crusts alike and different? 5. Place these terms in corr ...
Study Guide Chapt 7: Solid Earth
... interaction of the solar wind (Stream of charged particles) with Earth’s magnetic field. The Magnetic field focuses the charged particles of the solar wind to high latitudes on the night time side of Earth. As these energetic particles collide with Earth’s atmosphere light is given off. Earth’s magn ...
... interaction of the solar wind (Stream of charged particles) with Earth’s magnetic field. The Magnetic field focuses the charged particles of the solar wind to high latitudes on the night time side of Earth. As these energetic particles collide with Earth’s atmosphere light is given off. Earth’s magn ...
Study Guide Chapt 7
... interaction of the solar wind (Stream of charged particles) with Earth’s magnetic field. The Magnetic field focuses the charged particles of the solar wind to high latitudes on the night time side of Earth. As these energetic particles collide with Earth’s atmosphere light is given off. Earth’s magn ...
... interaction of the solar wind (Stream of charged particles) with Earth’s magnetic field. The Magnetic field focuses the charged particles of the solar wind to high latitudes on the night time side of Earth. As these energetic particles collide with Earth’s atmosphere light is given off. Earth’s magn ...
Plate Tectonics
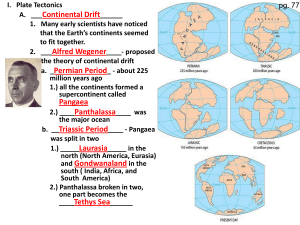
... He suggested that all of the ____________________________________ were once ___________________________ together to form a _____________________________________________ Pangaea Wegener called this super landmass _____________________________ and believed that it broke apart _____________________ ...
... He suggested that all of the ____________________________________ were once ___________________________ together to form a _____________________________________________ Pangaea Wegener called this super landmass _____________________________ and believed that it broke apart _____________________ ...
Earth Systems and Cycles Study Guide
... b. Mantle is hot middle section where convection occurs. c. Core is dense and solid inner most section that creates magnetic field. 2. Know that Earth can be divided into 4 spheres (or 4 separate systems). a. Geosphere – consists of the crust, mantle, and core. i. Where tectonic plates converge, div ...
... b. Mantle is hot middle section where convection occurs. c. Core is dense and solid inner most section that creates magnetic field. 2. Know that Earth can be divided into 4 spheres (or 4 separate systems). a. Geosphere – consists of the crust, mantle, and core. i. Where tectonic plates converge, div ...
pptx
... TW scales relative to U Cosmochemical: uses meteorites – 10 TW 10, 20, 30 TW ≈ 10, 20, 30 ppb Geochemical: uses terrestrial rocks –20 TW Geodynamical: parameterized convection – 30 TW ...
... TW scales relative to U Cosmochemical: uses meteorites – 10 TW 10, 20, 30 TW ≈ 10, 20, 30 ppb Geochemical: uses terrestrial rocks –20 TW Geodynamical: parameterized convection – 30 TW ...
Unit 3: Forces Within - Lemon Bay High School
... The type of deformation in which the object permanently changes size and shape without fracturing is called ____________________ . Plate Tectonics What hypothesis states that the continents were once joined to form a single supercontinent? ...
... The type of deformation in which the object permanently changes size and shape without fracturing is called ____________________ . Plate Tectonics What hypothesis states that the continents were once joined to form a single supercontinent? ...
Name - Cedar Hill ISD
... 15. The oceanic plate is SUBDUCTED below the continental plate in a convergent boundary because the oceanic plate is MORE dense then the continental plate. When this happens, the oceanic plate returns to the MANTLE. 16. Why does subduction not occur when two continental plates converge? THEY ARE THE ...
... 15. The oceanic plate is SUBDUCTED below the continental plate in a convergent boundary because the oceanic plate is MORE dense then the continental plate. When this happens, the oceanic plate returns to the MANTLE. 16. Why does subduction not occur when two continental plates converge? THEY ARE THE ...
CHAPTER 3 TECTONICS Vatnajokull Glacier- Iceland
... Da Vinci, Bacon- fit of the continents Evidence: 1. Glassopteris 3. Glaciers 2. Rocks 4. Climate Pangea, Panthalassa Wadati-1935- earthquakes/ volcanoes may be associated with the continental drift Benioff-1940-revealed Pacific Ring of Fire Hess-1960s- Seafloor Spreading >Ocean Crust is young (less ...
... Da Vinci, Bacon- fit of the continents Evidence: 1. Glassopteris 3. Glaciers 2. Rocks 4. Climate Pangea, Panthalassa Wadati-1935- earthquakes/ volcanoes may be associated with the continental drift Benioff-1940-revealed Pacific Ring of Fire Hess-1960s- Seafloor Spreading >Ocean Crust is young (less ...
Earth`s Landforms Study Guide
... a. the dune will move toward the land. b. the dune will move toward the ocean. c. the dune will erode more slowly and may even grow. d. the dune will erode more quickly. 27. How do volcanoes change Earth’s landforms? a. They release pressure that has built up under Earth’s crust. b. They blow ash an ...
... a. the dune will move toward the land. b. the dune will move toward the ocean. c. the dune will erode more slowly and may even grow. d. the dune will erode more quickly. 27. How do volcanoes change Earth’s landforms? a. They release pressure that has built up under Earth’s crust. b. They blow ash an ...
Overhead: Continental Drift / Plate Tectonics
... themselves with the earth’s magnetic field. ⑥ Mid-oceanic Ridge – Rocks are younger closer to the ridge and older as you move further away from it. ⑦ Satellite Measurements – Satellites have detected that the plates are moving 1-2 cm per year. ...
... themselves with the earth’s magnetic field. ⑥ Mid-oceanic Ridge – Rocks are younger closer to the ridge and older as you move further away from it. ⑦ Satellite Measurements – Satellites have detected that the plates are moving 1-2 cm per year. ...
6th grade Science Unit 1.3 Structures of the Earth and Energy
... My learning targets: 6.7 Matter and energy. The student knows that some of Earth's energy resources are available on a nearly perpetual basis, while others can be renewed over a relatively short period of time. Some energy resources, once depleted, are essentially nonrenewable. 6.10 Earth and space. ...
... My learning targets: 6.7 Matter and energy. The student knows that some of Earth's energy resources are available on a nearly perpetual basis, while others can be renewed over a relatively short period of time. Some energy resources, once depleted, are essentially nonrenewable. 6.10 Earth and space. ...
58 Earth Review Power Point 2011
... under a tremendous amount of heat and pressure as it changed, so it must be a… metamorphic rock. 24. Alternating layers of cinders, lava and ash make up the composition of… composite volcanoes. ...
... under a tremendous amount of heat and pressure as it changed, so it must be a… metamorphic rock. 24. Alternating layers of cinders, lava and ash make up the composition of… composite volcanoes. ...
Chapter 15
... formation of lithostratigraphic units that cut across time lines is almost inevitable (see Figure 15.2C for example). As described in the section entitled “Gaps in the Record” we need to forget the concept that the stratigraphic record is like a tape recording that provides us with a sequential reco ...
... formation of lithostratigraphic units that cut across time lines is almost inevitable (see Figure 15.2C for example). As described in the section entitled “Gaps in the Record” we need to forget the concept that the stratigraphic record is like a tape recording that provides us with a sequential reco ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.