8-3 Unit HW Sheet Name: Date: Standard 8
... 12. Which seismic wave is the fastest wave and which wave stops at the outer core-Explain why? P wave/ S wave stops at the outer core because it only travels through solids. 13. What is a fault? Crack in the Earth’s crust or rock 14. What is the process scientist use to locate the epicenter? Triangu ...
... 12. Which seismic wave is the fastest wave and which wave stops at the outer core-Explain why? P wave/ S wave stops at the outer core because it only travels through solids. 13. What is a fault? Crack in the Earth’s crust or rock 14. What is the process scientist use to locate the epicenter? Triangu ...
SCIENCE
... c. transform boundary d. none of these __a___21. Two plates move apart at a a. divergent boundary b. a convergent boundary c. transform boundary d. none of these __c___22. Two plates slide past each other at a a. divergent boundary b. a convergent boundary c. transform boundary d. none of these __d_ ...
... c. transform boundary d. none of these __a___21. Two plates move apart at a a. divergent boundary b. a convergent boundary c. transform boundary d. none of these __c___22. Two plates slide past each other at a a. divergent boundary b. a convergent boundary c. transform boundary d. none of these __d_ ...
MineralsRocksCycle
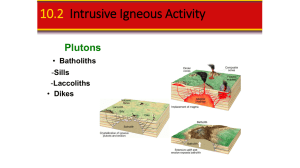
... crystal size • Glassy Texture- form from lava that cools rapidly, ions don’t have time to arrange = ...
... crystal size • Glassy Texture- form from lava that cools rapidly, ions don’t have time to arrange = ...
Notes: Plate Tectonics - Riverdale Middle School
... What Are the Features of Earth’s Layers? B. The three main layers of Earth are the crust, mantle and core. 1.) The layers vary greatly in size, composition, temperature, and pressure. 2.) The deeper down inside Earth, the greater the pressure. 3.) The temperature inside earth increases as depth inc ...
... What Are the Features of Earth’s Layers? B. The three main layers of Earth are the crust, mantle and core. 1.) The layers vary greatly in size, composition, temperature, and pressure. 2.) The deeper down inside Earth, the greater the pressure. 3.) The temperature inside earth increases as depth inc ...
Physical Geology
... (3) As ocean crust ages and cools, its great density relative to the continents results in subduction as plates converge. [As a result, old ocean crust cannot persist, whereas old parts of the buoyant continents can survive for eons.] (4) The other kind of plate margins, transforms, are parallel ...
... (3) As ocean crust ages and cools, its great density relative to the continents results in subduction as plates converge. [As a result, old ocean crust cannot persist, whereas old parts of the buoyant continents can survive for eons.] (4) The other kind of plate margins, transforms, are parallel ...
Unit 4 - Dynamic Crust Earthquakes & Volcanoes
... --A theory that says the Earth’s lithosphere (Remember what that is?...hint: think crust) is divided into solid sections of rock called “plates.” These plates move in relation to one Another. Tectonics are the forces that cause the Earth’s crust to continually move and create new landforms such as ...
... --A theory that says the Earth’s lithosphere (Remember what that is?...hint: think crust) is divided into solid sections of rock called “plates.” These plates move in relation to one Another. Tectonics are the forces that cause the Earth’s crust to continually move and create new landforms such as ...
Earth`s Surface
... Approximately 4.5 billion years ago, the Earth and the solar system began to form from clouds of dust that resulted from the Big Bang. Scientists estimate that the Big Bang, which is thought to have been a great cosmic explosion of matter and energy from a single point, occurred about 13.7 billion y ...
... Approximately 4.5 billion years ago, the Earth and the solar system began to form from clouds of dust that resulted from the Big Bang. Scientists estimate that the Big Bang, which is thought to have been a great cosmic explosion of matter and energy from a single point, occurred about 13.7 billion y ...
What is a Rock?
... streams, glaciers, wind, and gravity When this debris is deposited as permanent sediment, the processes of burial, compression, and chemical alteration over long periods of time produce sedimentary rocks ...
... streams, glaciers, wind, and gravity When this debris is deposited as permanent sediment, the processes of burial, compression, and chemical alteration over long periods of time produce sedimentary rocks ...
a. asthenosphere b. lithosphere c. mesosphere d. outer core e. inner
... ____ 2. A substance composed of two or more elements is a(n) a. mix. c. compound. b. amalgam. d. complex. 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ ...
... ____ 2. A substance composed of two or more elements is a(n) a. mix. c. compound. b. amalgam. d. complex. 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ ...
Lesson 3.3 - Earth`s Spheres
... well as the softer asthenosphere. As this layer moves, it drags large sections of lithosphere, called tectonic plates, across Earth’s surface. Earth’s center is called the core and is made up of molten and solid metals. ...
... well as the softer asthenosphere. As this layer moves, it drags large sections of lithosphere, called tectonic plates, across Earth’s surface. Earth’s center is called the core and is made up of molten and solid metals. ...
Deforming the Earth`s Crust
... • Forms when opposing forces ‘Shearing’ cause rock to break and moves horizontally • If you were standing on one side of the fault when it moved, the ground on the other side would appear to move to your left or right ...
... • Forms when opposing forces ‘Shearing’ cause rock to break and moves horizontally • If you were standing on one side of the fault when it moved, the ground on the other side would appear to move to your left or right ...
igneous rocks
... Igneous differentiation is a general term for processes that change the compositions of magmas and the igneous rocks that they produce. The three most important processes that cause igneous differentiation are crystal fractionation, crustal contamination and magma mixing. In some magmas liquid immis ...
... Igneous differentiation is a general term for processes that change the compositions of magmas and the igneous rocks that they produce. The three most important processes that cause igneous differentiation are crystal fractionation, crustal contamination and magma mixing. In some magmas liquid immis ...
CHAPTER 14
... A. The earth is made up of a core, mantle, and crust and is constantly changing as a result of processes taking place on and below its surface. Geology is the study of dynamic processes occurring on the earth’s surface and in its interior. B. Huge volumes of heated and molten rock moving around the ...
... A. The earth is made up of a core, mantle, and crust and is constantly changing as a result of processes taking place on and below its surface. Geology is the study of dynamic processes occurring on the earth’s surface and in its interior. B. Huge volumes of heated and molten rock moving around the ...
Alper Midterm 1 Solution (1)
... Which is not one of Wegener's lines of evidence? (4pt) The same rock types formed under different climatic conditions support the fact that they were one together. Earth's crust is thicker under continents. The structural trends, mountain belts and rock types in different pieces of this puzzle are c ...
... Which is not one of Wegener's lines of evidence? (4pt) The same rock types formed under different climatic conditions support the fact that they were one together. Earth's crust is thicker under continents. The structural trends, mountain belts and rock types in different pieces of this puzzle are c ...
Earth Layers and Continental Drift
... deep inside Earth) 2. Indirect evidence from seismic waves (produced by earthquakes; speed gives clues to the material) ...
... deep inside Earth) 2. Indirect evidence from seismic waves (produced by earthquakes; speed gives clues to the material) ...
1 Plate Tectonics Post-Test
... 10. Crust is _______________ at spreading ridges and ___________________ at subduction zones. a. Destroyed, Created b. Created, Destroyed c. Fluid, Solid d. Solid, Fluid ...
... 10. Crust is _______________ at spreading ridges and ___________________ at subduction zones. a. Destroyed, Created b. Created, Destroyed c. Fluid, Solid d. Solid, Fluid ...
plate tectonics notes
... Wegener could not explain how or why this occurred. He thought the continents floated around the Earth’s surface. His theory was rejected based on lack of evidence. This led to the commonly accepted theory today, _______________. Evidence for Plate Tectonics Pangaea 225 million years ago, all of the ...
... Wegener could not explain how or why this occurred. He thought the continents floated around the Earth’s surface. His theory was rejected based on lack of evidence. This led to the commonly accepted theory today, _______________. Evidence for Plate Tectonics Pangaea 225 million years ago, all of the ...
Lecture 2 - Early Earth and Plate Tectonics
... Ridge elevation, high heat flow, and abundant basaltic volcanism are evidence of this ...
... Ridge elevation, high heat flow, and abundant basaltic volcanism are evidence of this ...
topic 12 Notes revised
... Principle of Original Horizontality: • The assumption that sedimentary rocks form in horizontal layers. Drawing: ...
... Principle of Original Horizontality: • The assumption that sedimentary rocks form in horizontal layers. Drawing: ...
1163 Geo T Guide - TMW Media Group
... is to place diluted hydochloric acid on the specimen. The acid will cause the calcium carbonate to fizz as it releases carbon dioxide. Even vinegar (acidic acid) will have a chemical reaction but may be slower. 6. METAMORPHIC ROCKS are often found in the mountains because in the mountain building pr ...
... is to place diluted hydochloric acid on the specimen. The acid will cause the calcium carbonate to fizz as it releases carbon dioxide. Even vinegar (acidic acid) will have a chemical reaction but may be slower. 6. METAMORPHIC ROCKS are often found in the mountains because in the mountain building pr ...
Great Ideas in Science: Lecture 9 – Earth as a Planet
... Features of solar system – All planets orbit in the same direction – All planets orbit in the same plane – Most planets rotate in the direction of orbit ...
... Features of solar system – All planets orbit in the same direction – All planets orbit in the same plane – Most planets rotate in the direction of orbit ...
Internal Forces That Shape the Earth
... Web Article: Go to the following website http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/dynamic.html You will explore the article “This Dynamic Earth: The Story of Plate Tectonics.” Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on “Historic Perspective.” Scientific theories develop over time based on available evide ...
... Web Article: Go to the following website http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/dynamic.html You will explore the article “This Dynamic Earth: The Story of Plate Tectonics.” Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on “Historic Perspective.” Scientific theories develop over time based on available evide ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.