Objective Recovery Packet Unit 2
... 1. Soil is made of weathered rocks and minerals. The three major components of soil, in order according to how much water they retain are (lowest to highest): a) silt, sand, clay b) sand, silt, clay c) sand, minerals, clay d) clay, silt, sand 2. Rocks weather at different rates. Which of the followi ...
... 1. Soil is made of weathered rocks and minerals. The three major components of soil, in order according to how much water they retain are (lowest to highest): a) silt, sand, clay b) sand, silt, clay c) sand, minerals, clay d) clay, silt, sand 2. Rocks weather at different rates. Which of the followi ...
ScherstenNERCArticle..
... of these osmium isotopes in the lava inferred at least some of it must come from the core. But there’s a problem. Since platinum and rhenium still exist in the silicate portion of the Earth (i.e. all but the metallic core), and continue to decay into isotopes of osmium, the ratios of isotopes will c ...
... of these osmium isotopes in the lava inferred at least some of it must come from the core. But there’s a problem. Since platinum and rhenium still exist in the silicate portion of the Earth (i.e. all but the metallic core), and continue to decay into isotopes of osmium, the ratios of isotopes will c ...
The Moving Crust
... they travel through the Earth The area where they do not come through the other side of the earth is called a shadow zone ...
... they travel through the Earth The area where they do not come through the other side of the earth is called a shadow zone ...
8th Grade Earth Science Study Guide Where`s is most of Earth`s
... 17. Why would a volcanic island arc be a landform most likely created when two oceanic plates converge? When plates are converging they are moving toward each other. When this happens, on plate can be pushed under the other. The plate pushed underground will melt back into magma and a volcano can be ...
... 17. Why would a volcanic island arc be a landform most likely created when two oceanic plates converge? When plates are converging they are moving toward each other. When this happens, on plate can be pushed under the other. The plate pushed underground will melt back into magma and a volcano can be ...
Unit 6 Vocabulary Review
... • Intrusion – an igneous rock formation forming in/through other layers. • Inclusion – part of another layer found in an intrustion • Extrustion – an igneous rock formation formed ON TOP of all layers (it reached the surface of the earth). It is younger than all layers below it. It is older than any ...
... • Intrusion – an igneous rock formation forming in/through other layers. • Inclusion – part of another layer found in an intrustion • Extrustion – an igneous rock formation formed ON TOP of all layers (it reached the surface of the earth). It is younger than all layers below it. It is older than any ...
(1) the distribution of fossils on different continents
... •Pangaea existed during the Permian and Triassic geological time periods, which were times of great change. ...
... •Pangaea existed during the Permian and Triassic geological time periods, which were times of great change. ...
Layers of the Earth
... The Earth’s Core – Almost as hot as the surface of the sun (due to radioactive decay) Escape of this inner heat drives geological activity on the planet. It also has heat left over from Earth’s formation. •Inner Core •Under immense pressure •Solid metal mostly iron and nickel •Very high density 13. ...
... The Earth’s Core – Almost as hot as the surface of the sun (due to radioactive decay) Escape of this inner heat drives geological activity on the planet. It also has heat left over from Earth’s formation. •Inner Core •Under immense pressure •Solid metal mostly iron and nickel •Very high density 13. ...
File
... kilometer network of volcanoes, generates new oceanic crust at the rate of 17 km3 per year, covering the ocean floor with an igneous rock called basalt. Hawaii and Iceland are two examples of the accumulation of basalt islands. ...
... kilometer network of volcanoes, generates new oceanic crust at the rate of 17 km3 per year, covering the ocean floor with an igneous rock called basalt. Hawaii and Iceland are two examples of the accumulation of basalt islands. ...
Unit 1 Review - Hicksville Public Schools
... Parts of the hydrosphere, lithosphere, and atmosphere where life exists ...
... Parts of the hydrosphere, lithosphere, and atmosphere where life exists ...
Convection in the Mantle and The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... support his theory. -He could not explain how the plates moved. -Because he could not explain how the plates moved, scientist did not accept his theory. ...
... support his theory. -He could not explain how the plates moved. -Because he could not explain how the plates moved, scientist did not accept his theory. ...
The four layers of the Earth
... • The mantle is made up of rock materials and is sandwiched between the core and the crust. • It consists of mainly solid rocks, but the upper mantle (closer to the crust) is actually a layer of semi-liquid molten rock called magma. This magma flows slowly underneath the crust like plastic (think of ...
... • The mantle is made up of rock materials and is sandwiched between the core and the crust. • It consists of mainly solid rocks, but the upper mantle (closer to the crust) is actually a layer of semi-liquid molten rock called magma. This magma flows slowly underneath the crust like plastic (think of ...
EarthHW_Eqk_Vol
... It will move faster and faster because there is no force to stop it. It will stop gradually because there is no force to keep it moving. It will stop immediately when the force that started its motion has stopped. Its motion will not change, and it will continue in the same direction at the same ...
... It will move faster and faster because there is no force to stop it. It will stop gradually because there is no force to keep it moving. It will stop immediately when the force that started its motion has stopped. Its motion will not change, and it will continue in the same direction at the same ...
Chapter 2 c Primary Structures e
... notes about each of the layers/intrusions found in an outcrop. The process really forces you to LOOK. We work up or down section as appropriate. Note rock/sediment type, primary and secondary structures, fossils, note color, orient surfaces and lineations with the brunton, etc. ...
... notes about each of the layers/intrusions found in an outcrop. The process really forces you to LOOK. We work up or down section as appropriate. Note rock/sediment type, primary and secondary structures, fossils, note color, orient surfaces and lineations with the brunton, etc. ...
Lesson 15 - Seismology Earths Interior
... increase with increasing depth (from more pressure) P waves: compressional waves: are fastest vibrate material back/forth in direction wave travels S waves: shear waves: slower than P-waves vibrate material side-to-side in direction wave travels ...
... increase with increasing depth (from more pressure) P waves: compressional waves: are fastest vibrate material back/forth in direction wave travels S waves: shear waves: slower than P-waves vibrate material side-to-side in direction wave travels ...
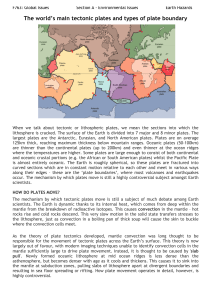
The world`s main tectonic plates and types of
... As the theory of plate tectonics developed, mantle convection was long thought to be responsible for the movement of tectonic plates across the Earth’s surface. This theory is now largely out of favour, with modern imaging techniques unable to identify convection cells in the mantle sufficiently lar ...
... As the theory of plate tectonics developed, mantle convection was long thought to be responsible for the movement of tectonic plates across the Earth’s surface. This theory is now largely out of favour, with modern imaging techniques unable to identify convection cells in the mantle sufficiently lar ...
Objective 8 - Reading Guide pages 150
... When two plates converge, the result is called a _________________________. When two plates collide, the _____________________ of the plates determine which one comes out on top. ________________________ crust becomes __________________ and denser as it spreads away from the mid-ocean ridge. Where t ...
... When two plates converge, the result is called a _________________________. When two plates collide, the _____________________ of the plates determine which one comes out on top. ________________________ crust becomes __________________ and denser as it spreads away from the mid-ocean ridge. Where t ...
Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era 46
... 5. because sea-floor spreading is due to pulling apart, or movement of plates, at mid-ocean ridges ...
... 5. because sea-floor spreading is due to pulling apart, or movement of plates, at mid-ocean ridges ...
Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: What are terrestrial planets like on the
... – Giant shield volcanoes – Evidence of tectonic activity ...
... – Giant shield volcanoes – Evidence of tectonic activity ...
1 - Tahoma
... 5. From obtaining radiometric ages on rocks of known polarity, geologists have established the paleomagnetic time scale. There is now a reliable one extending back to the early Mesozoic, around 200 million years ago. This timescale can be used as a third option for placing rocks into the geologic ti ...
... 5. From obtaining radiometric ages on rocks of known polarity, geologists have established the paleomagnetic time scale. There is now a reliable one extending back to the early Mesozoic, around 200 million years ago. This timescale can be used as a third option for placing rocks into the geologic ti ...
earth`s components & characteristics
... more dense materials sank to center of earth, less dense ...
... more dense materials sank to center of earth, less dense ...
Happy Valentine`s Day!
... Ash falls – choke people, animals, kill animals that eat it, collapse roofs – worsened by rain Pyroclastic flows – suffocation and burning, knock over anything in their way Mudflows (lahars) – ice and snow melt, rain on ash flow Volcanic landslide Lava flow Poisonous gas emission – Lake Nyos in Came ...
... Ash falls – choke people, animals, kill animals that eat it, collapse roofs – worsened by rain Pyroclastic flows – suffocation and burning, knock over anything in their way Mudflows (lahars) – ice and snow melt, rain on ash flow Volcanic landslide Lava flow Poisonous gas emission – Lake Nyos in Came ...
Earth`s Systems and Resources
... information about the relative position, density, and composition of Earth’s layers (crust, mantle and core). Therefore, the primary focus of assessment should be for students to obtain and communicate information from a variety of sources (informational texts, primary and secondary sources, models ...
... information about the relative position, density, and composition of Earth’s layers (crust, mantle and core). Therefore, the primary focus of assessment should be for students to obtain and communicate information from a variety of sources (informational texts, primary and secondary sources, models ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.