Study questions for Quiz 8 Plate Tectonics – more questions on
... What is the probable cause of the Earth’s internal convection? What is the source of the Earth’s internal heat generation? What name did Wegner give to the ‘original’ large land mass? What was the paleontological evidence for continental drift? What is the evidence from structure and rock type for c ...
... What is the probable cause of the Earth’s internal convection? What is the source of the Earth’s internal heat generation? What name did Wegner give to the ‘original’ large land mass? What was the paleontological evidence for continental drift? What is the evidence from structure and rock type for c ...
Topic Earth`s crust Key Question How do natural forces shape the
... Erosion can be divided into two components, transport and deposition. Transport is the movement of the weathered materials. The movement of these eroded materials is most often through water. Materials are often moved from one place and deposited in another location. The scientific term for this por ...
... Erosion can be divided into two components, transport and deposition. Transport is the movement of the weathered materials. The movement of these eroded materials is most often through water. Materials are often moved from one place and deposited in another location. The scientific term for this por ...
Plate Tectonic Quiz Review
... • Heat transfers by movement of currents in liquids and gasses. This is caused by differences in temperature and density. An example of this type of heat transfer occurs when mantle rock moves from near the core, towards the crust, and back again. A. Radiation B. Conduction C. Convection D. Compact ...
... • Heat transfers by movement of currents in liquids and gasses. This is caused by differences in temperature and density. An example of this type of heat transfer occurs when mantle rock moves from near the core, towards the crust, and back again. A. Radiation B. Conduction C. Convection D. Compact ...
classifying rocks
... Sedimentary rocks have characteristics unique to how they form. Forces on Earth’s surface can break down rocks. This process is called weathering. Rocks can be broken down through physical weathering or chemical weathering. Physical weathering breaks down rocks into smaller pieces through physical p ...
... Sedimentary rocks have characteristics unique to how they form. Forces on Earth’s surface can break down rocks. This process is called weathering. Rocks can be broken down through physical weathering or chemical weathering. Physical weathering breaks down rocks into smaller pieces through physical p ...
File
... 9.What process is taking place in the mantle causing the tectonic plates to move? _____Convection Currents____________________. ...
... 9.What process is taking place in the mantle causing the tectonic plates to move? _____Convection Currents____________________. ...
Inside the Earth
... • Friction, when denser core material sinks • Decay of radioactive elements, mostly uranium and thorium according to physicists. ...
... • Friction, when denser core material sinks • Decay of radioactive elements, mostly uranium and thorium according to physicists. ...
4 Deforming the Earth`s Crust
... 6. In slab pull, the driving force comes from subducting slabs. In ridge push, the driving force comes from the formation of new sea floor. ...
... 6. In slab pull, the driving force comes from subducting slabs. In ridge push, the driving force comes from the formation of new sea floor. ...
Meet Planet Earth Study Questions Summary
... started accreting into ever larger masses. All formed by about 4.56 billion years ago. ...
... started accreting into ever larger masses. All formed by about 4.56 billion years ago. ...
Physical Geology
... • Why do we see, at the earths surface, – Intrusive igneous rocks and – Metamorphic rocks – Formed many km deep? ...
... • Why do we see, at the earths surface, – Intrusive igneous rocks and – Metamorphic rocks – Formed many km deep? ...
02-Plate-Tectonics
... http://www.physics.mcgill.ca/~crawford/PSG/PSG12/204_97_L12.2_earthxn.html January 24, 2008 ...
... http://www.physics.mcgill.ca/~crawford/PSG/PSG12/204_97_L12.2_earthxn.html January 24, 2008 ...
Forces in Earth`s Crust
... Oceanic crust created along a mid-ocean ridge is destroyed at a deep-ocean trench. During the process of subduction, oceanic crust sinks down beneath the trench into the ...
... Oceanic crust created along a mid-ocean ridge is destroyed at a deep-ocean trench. During the process of subduction, oceanic crust sinks down beneath the trench into the ...
Plate Tectonics, Earthquakes, and Volcanoes Study Guide
... 17.Suppose the arrows in the diagram represent patterns of convection in Earth’s mantle. Which type of plate boundary is most likely to form along the region labeled “A” 18.What is happening at the region marked “B” on the diagram? ...
... 17.Suppose the arrows in the diagram represent patterns of convection in Earth’s mantle. Which type of plate boundary is most likely to form along the region labeled “A” 18.What is happening at the region marked “B” on the diagram? ...
Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor opens with a brief history of
... these features to current tectonic theory. 8. Recount oceanographic changes in Earth’s oceans from 540 million years ago to the present. ...
... these features to current tectonic theory. 8. Recount oceanographic changes in Earth’s oceans from 540 million years ago to the present. ...
Mechanisms of Plate Motion
... Mantle Plumes – hot plumes of rock that are attributed to the upward flowing arms of mantle convection Mantle plumes sometimes show themselves on the surface as hot spots and volcanoes Whole-mantle convection is when slabs of cold oceanic lithosphere descend into the lower mantle, at the same time, ...
... Mantle Plumes – hot plumes of rock that are attributed to the upward flowing arms of mantle convection Mantle plumes sometimes show themselves on the surface as hot spots and volcanoes Whole-mantle convection is when slabs of cold oceanic lithosphere descend into the lower mantle, at the same time, ...
Convergent plate boundary - Department of Geology UPRM
... Source: After R.S. Dietz and J.C. Holden, “Reconstruction of Pangaea,” Journal of Geophysical Research, 75:4939-4956, 1970, copyright by the American Geophysical Union. ...
... Source: After R.S. Dietz and J.C. Holden, “Reconstruction of Pangaea,” Journal of Geophysical Research, 75:4939-4956, 1970, copyright by the American Geophysical Union. ...
Chapter 7 Section 2 Pages 198-201
... •Where plates collide, great mountain ranges may be pushed up, such as the Himalayas; or if one plate sinks below another, deep oceanic trenches and chains of volcanoes are formed. Earthquakes are by far most common along plate boundaries and rift zones: plotting the location of earthquakes allows ...
... •Where plates collide, great mountain ranges may be pushed up, such as the Himalayas; or if one plate sinks below another, deep oceanic trenches and chains of volcanoes are formed. Earthquakes are by far most common along plate boundaries and rift zones: plotting the location of earthquakes allows ...
Presentation
... •Where plates collide, great mountain ranges may be pushed up, such as the Himalayas; or if one plate sinks below another, deep oceanic trenches and chains of volcanoes are formed. Earthquakes are by far most common along plate boundaries and rift zones: plotting the location of earthquakes allows ...
... •Where plates collide, great mountain ranges may be pushed up, such as the Himalayas; or if one plate sinks below another, deep oceanic trenches and chains of volcanoes are formed. Earthquakes are by far most common along plate boundaries and rift zones: plotting the location of earthquakes allows ...
Continental Drift and Seafloor Spreading
... 3. Glossopteris- plant fossils found on different continents- Plant fossils 4. Tropical plant fossils that were found on an island in Artic Ocean! (Scratches in rocks made by glaciers in South Africa) The continental drift theory was NOT accepted because Wegener could not explain HOW the continents ...
... 3. Glossopteris- plant fossils found on different continents- Plant fossils 4. Tropical plant fossils that were found on an island in Artic Ocean! (Scratches in rocks made by glaciers in South Africa) The continental drift theory was NOT accepted because Wegener could not explain HOW the continents ...
Our Changing Planet
... (NH3), water (H2O) and hydrogen (H2), which were all present in the earth’s early atmosphere, may have reacted to form the amino acids which we are all made of. The energy required to make this happen could have been provided by lightning. In the laboratory they mixed these gases and produced sparks ...
... (NH3), water (H2O) and hydrogen (H2), which were all present in the earth’s early atmosphere, may have reacted to form the amino acids which we are all made of. The energy required to make this happen could have been provided by lightning. In the laboratory they mixed these gases and produced sparks ...
File
... How many marks would you give the answer above and why? What words can you use to contrast the two types of crust? However, on the other hand, alternatively, whereas Denser, Darker, more slowly, larger cristals Extension Exam question (8 marks) Describe two different types of the earths crust and ex ...
... How many marks would you give the answer above and why? What words can you use to contrast the two types of crust? However, on the other hand, alternatively, whereas Denser, Darker, more slowly, larger cristals Extension Exam question (8 marks) Describe two different types of the earths crust and ex ...
Name: - Cobb Learning
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time B ...
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time B ...
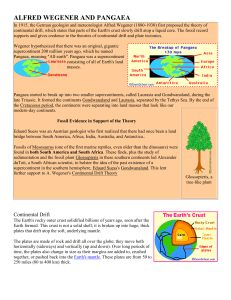
ALFRED WEGENER AND PANGAEA In 1915, the German geologist
... continental drift, which states that parts of the Earth's crust slowly drift atop a liquid core. The fossil record supports and gives credence to the theories of continental drift and plate tectonics. Wegener hypothesized that there was an original, gigantic supercontinent 200 million years ago, whi ...
... continental drift, which states that parts of the Earth's crust slowly drift atop a liquid core. The fossil record supports and gives credence to the theories of continental drift and plate tectonics. Wegener hypothesized that there was an original, gigantic supercontinent 200 million years ago, whi ...
9-5 The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... Earth’s Lithosphere are in constant, slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. The Theory of Plate tectonics explains the formation, movement, and subduction of Earth’s plates. ...
... Earth’s Lithosphere are in constant, slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. The Theory of Plate tectonics explains the formation, movement, and subduction of Earth’s plates. ...
8.3: Plates move apart
... plumes (thin columns) from the mantle Volcanoes often develop above the plume Often far from plate boundaries, but offer a way to measure plate movement Heat from the plume partly melts some of the rock in the tectonic plate above it: eventually the rock above will melt A volcano will form at ...
... plumes (thin columns) from the mantle Volcanoes often develop above the plume Often far from plate boundaries, but offer a way to measure plate movement Heat from the plume partly melts some of the rock in the tectonic plate above it: eventually the rock above will melt A volcano will form at ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.