1. 1. Draw a subduction zone in which an oceanic plate collides with
... Label the following on your sketch: the oceanic plate, the continental plate, location of seismicity (if any), location of volcanism (if any). Draw the boundary between the crust and the mantle and the boundary between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. Draw arrows to show the direction of motio ...
... Label the following on your sketch: the oceanic plate, the continental plate, location of seismicity (if any), location of volcanism (if any). Draw the boundary between the crust and the mantle and the boundary between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. Draw arrows to show the direction of motio ...
Earth internal energy (solucionario)
... Although scientists do not understand all of the details, they know that motions of molten metals in the Earth’s core generate our planet’s magnetic field. Movement of molten iron and nickel generate electrical and magnetic fields that produce Earth’s magnetism. The flows of these molten metals in E ...
... Although scientists do not understand all of the details, they know that motions of molten metals in the Earth’s core generate our planet’s magnetic field. Movement of molten iron and nickel generate electrical and magnetic fields that produce Earth’s magnetism. The flows of these molten metals in E ...
Are the oceans spreading at the mid
... After World War II the Russians and Americans were locked into the 'Cold-war'. Submarine warfare and control of the oceans was strategically important to both sides. The US Navy badly needed accurate maps of the world’s ocean floor and the only way to do this was for a ship to sail backwards and for ...
... After World War II the Russians and Americans were locked into the 'Cold-war'. Submarine warfare and control of the oceans was strategically important to both sides. The US Navy badly needed accurate maps of the world’s ocean floor and the only way to do this was for a ship to sail backwards and for ...
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift
... dikes (extensively sampled) – Third layer is thought to be composed of sill-like gabbro intrusions (not directly sampled) ...
... dikes (extensively sampled) – Third layer is thought to be composed of sill-like gabbro intrusions (not directly sampled) ...
Layers of the Earth
... liquid, when the inner core is solid? The intense pressure at the center of the Earth squeezes it into a solid! ...
... liquid, when the inner core is solid? The intense pressure at the center of the Earth squeezes it into a solid! ...
QUAKE NOTES
... rock materials take on the property of liquid, often as a result of severe ground-shaking tsunami- a large ocean wave that results from an underwater earthquake fire storm- a large out-of-control fire caused by gas and water lines breaking during an earthquake ...
... rock materials take on the property of liquid, often as a result of severe ground-shaking tsunami- a large ocean wave that results from an underwater earthquake fire storm- a large out-of-control fire caused by gas and water lines breaking during an earthquake ...
Plate Tectonics Reading Passage
... locations they are in now. Our continents have changed and drifted closer together or farther apart over the course of billions of years. The most recent time when all the continents were part of the same landmass happened about 300 million years ago. Scientists have named this huge landmass Pang ...
... locations they are in now. Our continents have changed and drifted closer together or farther apart over the course of billions of years. The most recent time when all the continents were part of the same landmass happened about 300 million years ago. Scientists have named this huge landmass Pang ...
Lesson 3
... the students describe what happened to the paths of the road and the river. What might happen to the trees and the road if the ground shook violently? 2. Ask the students to look for the focus on the side of one of the moved blocks. The focus is the place where the earthquake began. The point on the ...
... the students describe what happened to the paths of the road and the river. What might happen to the trees and the road if the ground shook violently? 2. Ask the students to look for the focus on the side of one of the moved blocks. The focus is the place where the earthquake began. The point on the ...
dynamic earth - cannonexperiment
... Throughout Earth’s history, its surface has been pushed up into mountains, pushed down into trenches, broken along faults, and divided into ridges. Geologists divide the forces that change the surface of the Earth into two groups: constructive and destructive forces. Constructive forces shape the su ...
... Throughout Earth’s history, its surface has been pushed up into mountains, pushed down into trenches, broken along faults, and divided into ridges. Geologists divide the forces that change the surface of the Earth into two groups: constructive and destructive forces. Constructive forces shape the su ...
PowerPoint
... 1. The theory of continental drift suggests that they were the continents were once joined together and have since split and moved apart. 2. Continents (e.g. Africa and South America) have shapes that fit closely together and have similar patterns of rocks and fossils ...
... 1. The theory of continental drift suggests that they were the continents were once joined together and have since split and moved apart. 2. Continents (e.g. Africa and South America) have shapes that fit closely together and have similar patterns of rocks and fossils ...
Chapter 7 Section 1
... by looking at the composition of magma. Magma from volcanoes gives scientists clues about the composition of the mantle. ...
... by looking at the composition of magma. Magma from volcanoes gives scientists clues about the composition of the mantle. ...
Note on Plate tectonics
... -layer below the lithosphere; -part of the mantle that has partially melted rock enabling plates to slide over each other ...
... -layer below the lithosphere; -part of the mantle that has partially melted rock enabling plates to slide over each other ...
Introduction to Geomagnetism
... No geomagnetic field has been detected on Venus – probably no convecting core. The surface temperature is 740K; most minerals are well above their Curie temperature at 740K – no field imprinted in crustal rocks. What we can say about the surface is that it is very “young” -- completely resurfa ...
... No geomagnetic field has been detected on Venus – probably no convecting core. The surface temperature is 740K; most minerals are well above their Curie temperature at 740K – no field imprinted in crustal rocks. What we can say about the surface is that it is very “young” -- completely resurfa ...
Document
... Plates consist of crust and lithospheric mantle Any individual plate contains oceanic and/or continental crust Each plate relatively rigid, little internal deformation Plate boundaries defined by active seismic and volcanic activity Dynamic: new ones form, boundaries change character, etc. ...
... Plates consist of crust and lithospheric mantle Any individual plate contains oceanic and/or continental crust Each plate relatively rigid, little internal deformation Plate boundaries defined by active seismic and volcanic activity Dynamic: new ones form, boundaries change character, etc. ...
Review Plate Tectonics
... b. Convection currents worked in the past the same way they work now c. The world’s climate has changed a lot over time d. Carbon dating is an accurate way to measure age 29. Consider the following three pieces of data: which of the following best describes the relationship between the statements? 1 ...
... b. Convection currents worked in the past the same way they work now c. The world’s climate has changed a lot over time d. Carbon dating is an accurate way to measure age 29. Consider the following three pieces of data: which of the following best describes the relationship between the statements? 1 ...
Landforms depend on types of crust that meet
... • What is the theory of • An explanation of how many of Earth’s features form plate tectonics? • What are convection • The heating, rising, cooling & sinking of magma within the currents? asthenosphere, caused by uneven heating • They make the lithospheric • How do “ccs” play a plates move, changing ...
... • What is the theory of • An explanation of how many of Earth’s features form plate tectonics? • What are convection • The heating, rising, cooling & sinking of magma within the currents? asthenosphere, caused by uneven heating • They make the lithospheric • How do “ccs” play a plates move, changing ...
First life fish reptiles mammals
... divided into units based on geologic events found in the fossil record. • First developed in the 19th century as a relative time scale using relative dating principles • Later modified, in the 20th century, to include absolute ages ...
... divided into units based on geologic events found in the fossil record. • First developed in the 19th century as a relative time scale using relative dating principles • Later modified, in the 20th century, to include absolute ages ...
Plate Tectonics
... 1. Summarize the theory of plate tectonics. 2. Compare the characteristic geologic activities that occur along the three types of plate boundaries. 3. Explain the possible role of convection currents in plate movement. 4. Summarize the theory of microplate terranes. ...
... 1. Summarize the theory of plate tectonics. 2. Compare the characteristic geologic activities that occur along the three types of plate boundaries. 3. Explain the possible role of convection currents in plate movement. 4. Summarize the theory of microplate terranes. ...
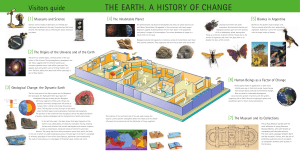
Folleto-Guia ok ingles
... The positions of the continents have changed, as well as the global distribution of oceans, climates, landscapes and the characteristics of plants and animals. In the last forty years it has been shown that large fragments of the Earth’s crust, called plates, are slowly but constantly moving, creati ...
... The positions of the continents have changed, as well as the global distribution of oceans, climates, landscapes and the characteristics of plants and animals. In the last forty years it has been shown that large fragments of the Earth’s crust, called plates, are slowly but constantly moving, creati ...
Dynamic Earth Webquest
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time ...
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time ...
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics
... 37. _____ appears to cause movement of Earth's tectonic plates. convection currents below the lithosphere 38. The speed of seismic waves depends on the ____ of the layer through which they travel. ...
... 37. _____ appears to cause movement of Earth's tectonic plates. convection currents below the lithosphere 38. The speed of seismic waves depends on the ____ of the layer through which they travel. ...
High School Science Proficiency Review #3 Earth Science
... Critical Information to focus on while reviewing Earth Science Earth’s Composition and Structure E.12.C.1 Students know how successive rock strata and fossils can be used to confirm the age, history, and changing life forms of the Earth, ...
... Critical Information to focus on while reviewing Earth Science Earth’s Composition and Structure E.12.C.1 Students know how successive rock strata and fossils can be used to confirm the age, history, and changing life forms of the Earth, ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.