File - Hoblitzell`s Science Spot
... 1995:5). There are now over 100,000 homes and over 200,000 Puget Sound residents that work in buildings located on these deposits (Krakauer, 1996:34). The largest of these lahars is the Osceola Mudflow that occurred approximately 5,600 years ago and extends to the Port of Tacoma including the areas ...
... 1995:5). There are now over 100,000 homes and over 200,000 Puget Sound residents that work in buildings located on these deposits (Krakauer, 1996:34). The largest of these lahars is the Osceola Mudflow that occurred approximately 5,600 years ago and extends to the Port of Tacoma including the areas ...
Earth`s Layers
... •Thickness varies. Under mountains it can be as thick as 60 km and less than 5 km under the ocean. •It is the least dense of all the layers. (lightest layer) •It is made up of silicon and oxygen. ...
... •Thickness varies. Under mountains it can be as thick as 60 km and less than 5 km under the ocean. •It is the least dense of all the layers. (lightest layer) •It is made up of silicon and oxygen. ...
Earth`s Layers ppt
... •Thickness varies. Under mountains it can be as thick as 60 km and less than 5 km under the ocean. •It is the least dense of all the layers. (lightest layer) •It is made up of silicon and oxygen. ...
... •Thickness varies. Under mountains it can be as thick as 60 km and less than 5 km under the ocean. •It is the least dense of all the layers. (lightest layer) •It is made up of silicon and oxygen. ...
Chapter 2 Practice Assessment October 2014 File
... B. less than 25 miles thick. C. about 250 miles in thickness. D. 80 to 400 miles thick. _____20. Which of the following is composed of magma? A. the crust B. the plates C. the core D. the continents _____21. The Earth’s plates are A. stationary. B. found where the continents meet. C. slowly moving. ...
... B. less than 25 miles thick. C. about 250 miles in thickness. D. 80 to 400 miles thick. _____20. Which of the following is composed of magma? A. the crust B. the plates C. the core D. the continents _____21. The Earth’s plates are A. stationary. B. found where the continents meet. C. slowly moving. ...
Chapt12RHS2014
... •Continents have split apart and joined as tectonic plates drifted Fig. 12-2, p. 277 atop the earth’s asthenosphere. ...
... •Continents have split apart and joined as tectonic plates drifted Fig. 12-2, p. 277 atop the earth’s asthenosphere. ...
Introduction to Plate Tectonics
... The Theory of Plate Tectonics The theory that the Earth's lithospheric plates move slowly relative to each other, and it is driven by the convection currents in the Earth's mantle. ...
... The Theory of Plate Tectonics The theory that the Earth's lithospheric plates move slowly relative to each other, and it is driven by the convection currents in the Earth's mantle. ...
Inside Earth WebQuest
... When completing this WebQuest you will visit many Websites that will enhance your knowledge in the areas of the earth's interior (layers), heat transfer, continental drift and plate tectonics. Task This WebQuest is divided into sections similar to your "Inside Earth" textbook. When you come to a lin ...
... When completing this WebQuest you will visit many Websites that will enhance your knowledge in the areas of the earth's interior (layers), heat transfer, continental drift and plate tectonics. Task This WebQuest is divided into sections similar to your "Inside Earth" textbook. When you come to a lin ...
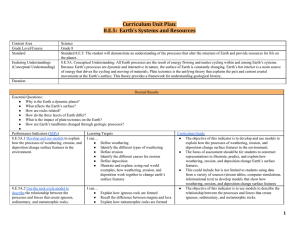
Earth`s Systems and Resources - Lexington County School District
... deposition change surface features in the environment. ● The focus of assessment should be for students to construct representations to illustrate, predict, and explain how weathering, erosion, and deposition change Earth’s surface features. ● This could include but is not limited to students using ...
... deposition change surface features in the environment. ● The focus of assessment should be for students to construct representations to illustrate, predict, and explain how weathering, erosion, and deposition change Earth’s surface features. ● This could include but is not limited to students using ...
ASTR1010_HW07
... Earth, the thin, brittle crust breaks up into tectonic plates (see Figure 8.17) which are dragged around by convective motion in the mantle (see Figure 8.15). This both creates new crust (as plates move apart), and destroys old crust (as they come together) – see Figure 8.16. The Earth basically res ...
... Earth, the thin, brittle crust breaks up into tectonic plates (see Figure 8.17) which are dragged around by convective motion in the mantle (see Figure 8.15). This both creates new crust (as plates move apart), and destroys old crust (as they come together) – see Figure 8.16. The Earth basically res ...
19.1 Earthquakes Power point
... movement in crust Are the result of movement of crust produced by Plate tectonics Stress = total force acting on crustal rocks ...
... movement in crust Are the result of movement of crust produced by Plate tectonics Stress = total force acting on crustal rocks ...
Lesson 7.1: Volcanoes and Plate Boundaries
... • Magma comes up to the surface is called lava. • Volcanoes can erupt liquid, gas, or solid materials. ...
... • Magma comes up to the surface is called lava. • Volcanoes can erupt liquid, gas, or solid materials. ...
Abstract - Geological Society of America
... Manhattan Formation (Manhattan Schists, Inwood dolomite and calcareous schists and Fordham gneiss) and Hartland Formation (gneiss, granite gneiss, granodiorite-gneiss, granodiorites, diorites. amphibolites and schists). These two units are separated by Cameron thrust fault, a major NE/SW trending st ...
... Manhattan Formation (Manhattan Schists, Inwood dolomite and calcareous schists and Fordham gneiss) and Hartland Formation (gneiss, granite gneiss, granodiorite-gneiss, granodiorites, diorites. amphibolites and schists). These two units are separated by Cameron thrust fault, a major NE/SW trending st ...
Earth, continental drift, plate tectonics, sea floor spreading
... Mid-ocean ridges occur along the kind of plate boundary where new ocean floor is created as the plates spread apart. "divergent plate boundary." The plates spread apart at rates of 1 cm to 20 cm per year. As oceanic plates move apart, rock melts and wells up from tens of kilometers deep. Some of the ...
... Mid-ocean ridges occur along the kind of plate boundary where new ocean floor is created as the plates spread apart. "divergent plate boundary." The plates spread apart at rates of 1 cm to 20 cm per year. As oceanic plates move apart, rock melts and wells up from tens of kilometers deep. Some of the ...
Soil and Geology Test
... estimated that at its highest, 30% of the earth’s surface was covered with ice. The cretaceous period is the last portion of the age of dinosaurs, this period ended with the extinction of dinosaurs and was the second largest extinction in the history of the earth. The Triassic period began after th ...
... estimated that at its highest, 30% of the earth’s surface was covered with ice. The cretaceous period is the last portion of the age of dinosaurs, this period ended with the extinction of dinosaurs and was the second largest extinction in the history of the earth. The Triassic period began after th ...
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift
... floor is constantly spreading along the MidAtlantic Ridge. ...
... floor is constantly spreading along the MidAtlantic Ridge. ...
History of geology
... strata can be defined as horizontal layers of rock having approximately the same composition throughout.[5] The popular mining industry during the 18th century both increased social interest and drove scientists to form more systematic and detailed studies of the composition of the Earth’s strata. F ...
... strata can be defined as horizontal layers of rock having approximately the same composition throughout.[5] The popular mining industry during the 18th century both increased social interest and drove scientists to form more systematic and detailed studies of the composition of the Earth’s strata. F ...
The Dynamic Earth www.mnh.si.edu/earth/ Plate Tectonics and
... What is happening at each plate boundary. Key: Spreading ridges: plates move ______. ...
... What is happening at each plate boundary. Key: Spreading ridges: plates move ______. ...
Geology: Inside the Earth Chapter 1 Notes and Vocabulary
... along the lithosphere’s ________________ and weak areas in Earth’s crust called ________ _____. __________________ rises through the __________ in these stressed places to form a _______________. Most volcanoes form due to the forces built up from ________________ (at ____________ boundaries) and __ ...
... along the lithosphere’s ________________ and weak areas in Earth’s crust called ________ _____. __________________ rises through the __________ in these stressed places to form a _______________. Most volcanoes form due to the forces built up from ________________ (at ____________ boundaries) and __ ...
10.2 Dir. Reading Plate Tectonics
... 29. Where are most divergent boundaries located? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 31. When oceanic lithosphere collides with continental lithosphere, the oceanic lithosphere is less dense than the cont ...
... 29. Where are most divergent boundaries located? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 31. When oceanic lithosphere collides with continental lithosphere, the oceanic lithosphere is less dense than the cont ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
... a. _________________ _____________________- occur along spreading centers where plates are ________________ _____________and new crust is created by ___________pushing up from the mantle. The best known of the divergent boundaries is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. This submerged mountain range, which exten ...
... a. _________________ _____________________- occur along spreading centers where plates are ________________ _____________and new crust is created by ___________pushing up from the mantle. The best known of the divergent boundaries is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. This submerged mountain range, which exten ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.