Continents Adrift: An Introduction to Continental Drift
... 1. Prior to viewing the program, ask students the following about the region where they live: Do you know if there have been any earthquakes in this area? Do you think an earthquake is likely to occur in the future? Why or why not? Are there signs of past volcanic activity in the area? If so, where? ...
... 1. Prior to viewing the program, ask students the following about the region where they live: Do you know if there have been any earthquakes in this area? Do you think an earthquake is likely to occur in the future? Why or why not? Are there signs of past volcanic activity in the area? If so, where? ...
Earth`s Internal Heat
... Divergent plate boundaries exist where two tectonic plates move away from each other. Where two oceanic plates pull apart, magma rises and erupts as lava at the surface. The lava quickly cools and hardens to form new crust. However, the newly formed crust is still much hotter than older crust farthe ...
... Divergent plate boundaries exist where two tectonic plates move away from each other. Where two oceanic plates pull apart, magma rises and erupts as lava at the surface. The lava quickly cools and hardens to form new crust. However, the newly formed crust is still much hotter than older crust farthe ...
Plate Tectonics NASA Rocky Mountain Model
... The solid Earth consists of several layers. The outermost layer is the solid crust on which we walk. The crust is about 35 kilometers thick under the continents. The crust is the thinnest layer of the Earth. The lithosphere below the crust is solid and consists mainly of materials more dense than cr ...
... The solid Earth consists of several layers. The outermost layer is the solid crust on which we walk. The crust is about 35 kilometers thick under the continents. The crust is the thinnest layer of the Earth. The lithosphere below the crust is solid and consists mainly of materials more dense than cr ...
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves An earthquake is
... energy is stored in the rock until it changes shape or breaks. The change in the shape or volume of the crust is called deformation. Three kinds of stress cause deformation: shearing, tension, and compression. Shearing pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions. Tension pulls on the crust, str ...
... energy is stored in the rock until it changes shape or breaks. The change in the shape or volume of the crust is called deformation. Three kinds of stress cause deformation: shearing, tension, and compression. Shearing pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions. Tension pulls on the crust, str ...
Earth Layers and PT study guide ANSWERS
... The oceanic crust sits lower than continental crust because the density of oceanic crust is greater due to the type of rock (basalt) ...
... The oceanic crust sits lower than continental crust because the density of oceanic crust is greater due to the type of rock (basalt) ...
STAAR Science Tutorial 38 TEK 8.9A: Plate Tectonic Theory Evidence
... currently accept this theory as the best available explanation of the geologic processes that shape Earth’s crust. ...
... currently accept this theory as the best available explanation of the geologic processes that shape Earth’s crust. ...
Convergent Plate Boundaries
... • Earth’s interior is layered, and the layers are arranged by density. Each deeper layer is denser than the layer above. • Continents are not supported above sea level by resting mechanically on a rigid base. Instead, continents rise to great height because they “float” on a dense, deformable layer ...
... • Earth’s interior is layered, and the layers are arranged by density. Each deeper layer is denser than the layer above. • Continents are not supported above sea level by resting mechanically on a rigid base. Instead, continents rise to great height because they “float” on a dense, deformable layer ...
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries
... • Some earthquakes occur more than 100km below Earth’s surface • The deepest earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries – Here the denser oceanic plate subducts into the mantle – These earthquakes release tremendous amounts of energy ...
... • Some earthquakes occur more than 100km below Earth’s surface • The deepest earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries – Here the denser oceanic plate subducts into the mantle – These earthquakes release tremendous amounts of energy ...
Section 19.3 - CPO Science
... 19.3 Divergent boundaries Divergent boundaries can also be found on continents as rift valleys. When a rift valley forms on ...
... 19.3 Divergent boundaries Divergent boundaries can also be found on continents as rift valleys. When a rift valley forms on ...
Today`s Agenda Today`s Agenda Syllabus Syllabus Syllabus
... 1963-1968 J. Tuzo Wilson was the first to describe global tectonics in terms of rigid surface "plates“, and recognized ocean ...
... 1963-1968 J. Tuzo Wilson was the first to describe global tectonics in terms of rigid surface "plates“, and recognized ocean ...
Exam Block #5
... accumulation of nebular debris (Nebular Hypothesis) but quickly begin to form layers. The planet’s gravity causes the densest material (iron) to settle to the center and form the core. Less dense rock rises to form the mantle and even less dense rock forms the crust. The best way to learn about ...
... accumulation of nebular debris (Nebular Hypothesis) but quickly begin to form layers. The planet’s gravity causes the densest material (iron) to settle to the center and form the core. Less dense rock rises to form the mantle and even less dense rock forms the crust. The best way to learn about ...
Earth and Environmental Science
... During the Archaean eon, Earth’s surface received higher levels of ultraviolet radiation than it does now. What is the main reason for the reduction in the level of ultraviolet radiation reaching Earth’s surface today? (A) The increased greenhouse effect blocks incoming ultraviolet radiation. (B) ...
... During the Archaean eon, Earth’s surface received higher levels of ultraviolet radiation than it does now. What is the main reason for the reduction in the level of ultraviolet radiation reaching Earth’s surface today? (A) The increased greenhouse effect blocks incoming ultraviolet radiation. (B) ...
The Earth`s Layers Foldable
... Oceanic Crust - dark brown Continental Crust - light brown Ocean - blue ...
... Oceanic Crust - dark brown Continental Crust - light brown Ocean - blue ...
Name
... Argentina. There were also similar coal fields in Europe and North America. The reason Wegener’s theory was tossed out, was because he was unable to explain how the continents moved. ...
... Argentina. There were also similar coal fields in Europe and North America. The reason Wegener’s theory was tossed out, was because he was unable to explain how the continents moved. ...
Plate Tectonics
... are continuously beamed from satellites to GPS ground stations, which record the exact distance between the satellites and the ground station. Over time, these distances change slightly. By recording the time it takes for the GPS ground stations to move a given distance, scientists can measure the s ...
... are continuously beamed from satellites to GPS ground stations, which record the exact distance between the satellites and the ground station. Over time, these distances change slightly. By recording the time it takes for the GPS ground stations to move a given distance, scientists can measure the s ...
Name Plate Tectonics Introduction Go to the following site: http
... c. What was the name he gave to his supercontinent? d. What theory did these ideas lead to? ...
... c. What was the name he gave to his supercontinent? d. What theory did these ideas lead to? ...
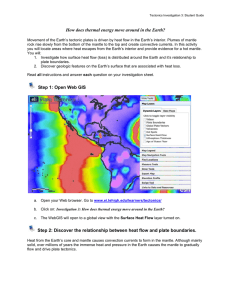
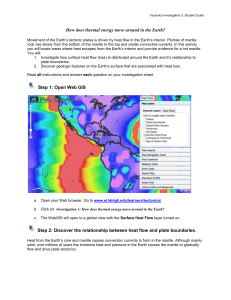
Project-Based Inquiry Science: Ever
... analyze their findings to build a relationship between volcanoes and earthquakes and plate boundaries. Students share their findings with the class adding new evidence to support their understanding of the location of plate boundaries as well as the forces causing changes on the Earth’s surface. Sec ...
... analyze their findings to build a relationship between volcanoes and earthquakes and plate boundaries. Students share their findings with the class adding new evidence to support their understanding of the location of plate boundaries as well as the forces causing changes on the Earth’s surface. Sec ...
Chapter 8
... These are usually laid down by water and were probably laid down during the worldwide flood… In many places, heat and pressure have compacted these sediments into solid rock… ...
... These are usually laid down by water and were probably laid down during the worldwide flood… In many places, heat and pressure have compacted these sediments into solid rock… ...
Swigert sample curriculum template.7th Grade.Science
... ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS AND COMMON ASSESSMENTS WILL NEED TO BE ADDED AS THE MAPPING CYCLE CONTINUES The World is changing. Meet the future. ...
... ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS AND COMMON ASSESSMENTS WILL NEED TO BE ADDED AS THE MAPPING CYCLE CONTINUES The World is changing. Meet the future. ...
plate tectonics
... “all land”). He further suggested that this supercontinent later broke into smaller pieces and drifted to their present positions. ...
... “all land”). He further suggested that this supercontinent later broke into smaller pieces and drifted to their present positions. ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.