Paleontological Perspectives on Climate Change
... • Take all claims of “catastrophic climate change” with a grain of salt • How much the Earth and its climate have changed in the last 500 million years • Give context to discussions about change on the geologic scale • Convince you that humans will not cause the end of the world (any time soon) ...
... • Take all claims of “catastrophic climate change” with a grain of salt • How much the Earth and its climate have changed in the last 500 million years • Give context to discussions about change on the geologic scale • Convince you that humans will not cause the end of the world (any time soon) ...
18.1-homework- - Human Resources Department
... At 27________________________________________________ plate boundaries, magma is forced upward into fractures and faults that form as plates separate or spread apart. Most of the volcanoes that form along divergent boundaries are located underwater along 28___________________________________________ ...
... At 27________________________________________________ plate boundaries, magma is forced upward into fractures and faults that form as plates separate or spread apart. Most of the volcanoes that form along divergent boundaries are located underwater along 28___________________________________________ ...
mid-ocean ridges - River Mill Academy
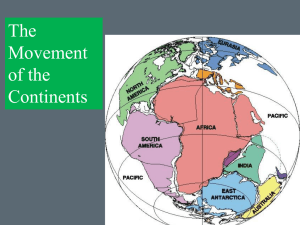
... •noticed that the shorelines of the continents seemed • to ‘fit together’like the pieces of a giant jig saw puzzle. Wegener’s theory stated: 1) The continents were once all together in one place forming a supercontinent, Pangea. 2) The continents broke apart and drifted to their present locations. W ...
... •noticed that the shorelines of the continents seemed • to ‘fit together’like the pieces of a giant jig saw puzzle. Wegener’s theory stated: 1) The continents were once all together in one place forming a supercontinent, Pangea. 2) The continents broke apart and drifted to their present locations. W ...
Classzone webquest plate tectonics and Wegener
... 7. As Earth rotates, the liquid outer core _________, creating ____________________________. 8. The _________part of the mantle is ___________ and ________ ________ than the deep mantle and along with the crust forms the rigid layer of rock called the _______________________. (a sphere) 9. ‘Lithos’ ...
... 7. As Earth rotates, the liquid outer core _________, creating ____________________________. 8. The _________part of the mantle is ___________ and ________ ________ than the deep mantle and along with the crust forms the rigid layer of rock called the _______________________. (a sphere) 9. ‘Lithos’ ...
SECTION II The Physical World: The Earth, Climate and Water
... precipitation. They provide a quick visual summary of the climate of an area. Months are placed on the x-axis of the graph, temperature (°C) is plotted on the left y-axis with a line connecting the monthly values, and precipitation (cm) is plotted as vertical bars on the right y axis. 1. Use two of ...
... precipitation. They provide a quick visual summary of the climate of an area. Months are placed on the x-axis of the graph, temperature (°C) is plotted on the left y-axis with a line connecting the monthly values, and precipitation (cm) is plotted as vertical bars on the right y axis. 1. Use two of ...
Earth`s structure - Deakin University Blogs
... Earth’s crust formed at different times. Within some rocks there are small particles of magnetite that are magnetic and, when the rocks were formed, these magnetite particles aligned themselves with Earth’s magnetic field. As the rocks cooled, the direction of the particles’ magnetic polarity was fi ...
... Earth’s crust formed at different times. Within some rocks there are small particles of magnetite that are magnetic and, when the rocks were formed, these magnetite particles aligned themselves with Earth’s magnetic field. As the rocks cooled, the direction of the particles’ magnetic polarity was fi ...
Y10 Earthquakes - Learning on the Loop
... fossilised in the rocks then uplifted and exposed. Coastal areas such as Marlborough have only been pushed up to become land in the last 50,000 years so we don’ have many old fossils. Rich deposits of beautifully preserved Pleistocene sea shell fossils can be found at Motunau Beach (Marlborough). Th ...
... fossilised in the rocks then uplifted and exposed. Coastal areas such as Marlborough have only been pushed up to become land in the last 50,000 years so we don’ have many old fossils. Rich deposits of beautifully preserved Pleistocene sea shell fossils can be found at Motunau Beach (Marlborough). Th ...
This Dynamic Planet
... (for example, the western margins of the Americas), along island chains (for example, Japan and the Aleutians), or along oceanic ridge crests (for example, the Mid-Atlantic Ridge). Although geologists have long known this, it is only in the past 30 years that a concept has emerged to satisfactorily ...
... (for example, the western margins of the Americas), along island chains (for example, Japan and the Aleutians), or along oceanic ridge crests (for example, the Mid-Atlantic Ridge). Although geologists have long known this, it is only in the past 30 years that a concept has emerged to satisfactorily ...
Warm-Up - mssarnelli
... although the continents were once joined, they slowly drifted apart! Wegener’s Evidence: 1. Matching rock layers on different continents ...
... although the continents were once joined, they slowly drifted apart! Wegener’s Evidence: 1. Matching rock layers on different continents ...
Earth`s Internal Processes
... Figure 7 Large lakes and volpart oceanic and part continental crust. J. T. Wilson is credited canic mountains are characteristics with describing the cycle of repeated openof a continental rift valley. ing and closing of ocean basins through Earth’s history. Arabian There are three main kinds of pla ...
... Figure 7 Large lakes and volpart oceanic and part continental crust. J. T. Wilson is credited canic mountains are characteristics with describing the cycle of repeated openof a continental rift valley. ing and closing of ocean basins through Earth’s history. Arabian There are three main kinds of pla ...
This Dynamic Planet
... relieved by large earthquakes (for example: San Francisco, 1906). Transform boundaries typically produce shallow earthquakes and accompanying ground faulting, rather than volcanic activity. Many transform faults horizontally offset the divergent plate boundaries. The oceanic fracture zones formed in ...
... relieved by large earthquakes (for example: San Francisco, 1906). Transform boundaries typically produce shallow earthquakes and accompanying ground faulting, rather than volcanic activity. Many transform faults horizontally offset the divergent plate boundaries. The oceanic fracture zones formed in ...
Background information - Science Web Australia
... This is where the material is moved away by water. • Sheet erosion occurs when the top plain of the soil is moved. This occurs with the saturation of the soil and results in water and soil run-off. • Splash erosion occurs when the force of rain droplet impact displaces soil particles. • Rill eros ...
... This is where the material is moved away by water. • Sheet erosion occurs when the top plain of the soil is moved. This occurs with the saturation of the soil and results in water and soil run-off. • Splash erosion occurs when the force of rain droplet impact displaces soil particles. • Rill eros ...
Earth Science - Adventist Education
... Recognize God as the Designer and Creator of our earth within the universe. Introduce and relate terminology appropriate to Earth Science. Demonstrate understanding of the structure and composition of earth (geologic time table, plate tectonics, rocks and minerals). Become acquainted with the geolog ...
... Recognize God as the Designer and Creator of our earth within the universe. Introduce and relate terminology appropriate to Earth Science. Demonstrate understanding of the structure and composition of earth (geologic time table, plate tectonics, rocks and minerals). Become acquainted with the geolog ...
Plate tectonics - Brogranoni-GEO1
... The earth is made up of 4 distinct layers: 1. The inner core is in the centre of the earth and is the hottest part of the earth. The inner core is solid. It is made up of iron and nickel with temperatures of up to 5500°C. With its immense heat energy, the inner core is like the engine room of the Ea ...
... The earth is made up of 4 distinct layers: 1. The inner core is in the centre of the earth and is the hottest part of the earth. The inner core is solid. It is made up of iron and nickel with temperatures of up to 5500°C. With its immense heat energy, the inner core is like the engine room of the Ea ...
Plate Tectonics – Lab
... model is used to describe various geologic features, geological rock environments, and the pattern of volcanism as well as earthquake activity. According to the plate tectonic model, the surface of the Earth consists of a series of relatively thin but rigid plates which are in constant motion. The s ...
... model is used to describe various geologic features, geological rock environments, and the pattern of volcanism as well as earthquake activity. According to the plate tectonic model, the surface of the Earth consists of a series of relatively thin but rigid plates which are in constant motion. The s ...
oceanic ridges
... Most earthquakes and volcanic eruptions happen at plate boundaries. Three types of relative motions between plates: ...
... Most earthquakes and volcanic eruptions happen at plate boundaries. Three types of relative motions between plates: ...
FOSS Weather on Earth Module Glossary 3 Edition © 2012 absorb
... reradiation when the warmed Earth radiates energy back into the air (IG) river a large natural stream of water emptying into an ocean, lake, or other body of water (IG) salt water ocean water (IG) season a time of year that brings predictable weather conditions to a region on Earth (SRB) severe wea ...
... reradiation when the warmed Earth radiates energy back into the air (IG) river a large natural stream of water emptying into an ocean, lake, or other body of water (IG) salt water ocean water (IG) season a time of year that brings predictable weather conditions to a region on Earth (SRB) severe wea ...
Oceanic Crust
... The first 50 miles (80km) of the mantle are believed to consist of very hard, rigid rock. The next 150 miles (241km) or so are believed to be super-heated solid rock that due to the heat energy is very weak. Below that for the next several hundred miles, the Earth's mantle is believed to once again ...
... The first 50 miles (80km) of the mantle are believed to consist of very hard, rigid rock. The next 150 miles (241km) or so are believed to be super-heated solid rock that due to the heat energy is very weak. Below that for the next several hundred miles, the Earth's mantle is believed to once again ...
Work Package 3 Drifting Apart Story
... changing weather, but it’s perhaps not so obvious in relation to the ground we walk on and the rocks found beneath. Processes above and below the Earth’s surface, atmosphere, oceans, continents, lithosphere, crust, mantle and core, not to mention the moon and the sun are interacting across the globe ...
... changing weather, but it’s perhaps not so obvious in relation to the ground we walk on and the rocks found beneath. Processes above and below the Earth’s surface, atmosphere, oceans, continents, lithosphere, crust, mantle and core, not to mention the moon and the sun are interacting across the globe ...
Journey to the centre Examining the crust
... t he mantle and, above this, the crust. There are two types of crust: • Continental crust forms the land. This is made mostly of granite, which is a low density igneous rock. Continental crust is on average 30-50 km thick. • Under the oceans is oceanic crust. This is much thinner, usually 6-8 km thi ...
... t he mantle and, above this, the crust. There are two types of crust: • Continental crust forms the land. This is made mostly of granite, which is a low density igneous rock. Continental crust is on average 30-50 km thick. • Under the oceans is oceanic crust. This is much thinner, usually 6-8 km thi ...
Plate Tectonics Theory
... separate continents. • Large striations found in solid bedrock. • This could also be explained by erosion and deposition caused by submarine landslides. ...
... separate continents. • Large striations found in solid bedrock. • This could also be explained by erosion and deposition caused by submarine landslides. ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.