Earth`s internal structure
... lava and magma). It is the only region of the planet that we can investigate directly by boring into it and taking samples. In continental areas, the crust's average thickness is 36 km but may be anything from 10 km to 80 km depending on the last movement of the tectonic plates in that area. The cru ...
... lava and magma). It is the only region of the planet that we can investigate directly by boring into it and taking samples. In continental areas, the crust's average thickness is 36 km but may be anything from 10 km to 80 km depending on the last movement of the tectonic plates in that area. The cru ...
Unwrapped Standard 3
... Essential Questions from Big Ideas to Guide Instruction and Assessment: 1. What are the internal and external methods of energy transfer as it relates to plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes and the physical structures that they create? 2. Why is the rock cycle an example of earth’s ever-chan ...
... Essential Questions from Big Ideas to Guide Instruction and Assessment: 1. What are the internal and external methods of energy transfer as it relates to plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes and the physical structures that they create? 2. Why is the rock cycle an example of earth’s ever-chan ...
Section 1 - Pelham City Schools
... transported from one place to another by natural agents such as wind, water, ice or gravity • ______________ erosion – Rivers carve deep canyons or gorges into bedrock – Depositing of dust, pebbles, rocks forms new land areas – Oceans erode coastlines ...
... transported from one place to another by natural agents such as wind, water, ice or gravity • ______________ erosion – Rivers carve deep canyons or gorges into bedrock – Depositing of dust, pebbles, rocks forms new land areas – Oceans erode coastlines ...
Yr9 Revision Geography 2016 June
... The Chinese government decided in the 1970s to control population growth. This has proved a very complex task. The main strategy the government introduced in 1982 was a radical family planning program to encourage couples to restrict their family size to just one child. This has become known as the ...
... The Chinese government decided in the 1970s to control population growth. This has proved a very complex task. The main strategy the government introduced in 1982 was a radical family planning program to encourage couples to restrict their family size to just one child. This has become known as the ...
Carrying Capacity
... Is it hospitable? It most resembles Earth in size, density and distance from the Sun, but atmosphere is rich in carbon dioxide and caustic sulfuric clouds fill the sky. Lead would melt at the surface…why so different then Earth? ...
... Is it hospitable? It most resembles Earth in size, density and distance from the Sun, but atmosphere is rich in carbon dioxide and caustic sulfuric clouds fill the sky. Lead would melt at the surface…why so different then Earth? ...
The Milky Way
... • Crust not broken into tectonic plates • Volcanic activity (including highest volcano in the solar system) ...
... • Crust not broken into tectonic plates • Volcanic activity (including highest volcano in the solar system) ...
Macroevolution - CPBiologyClass
... Geographical Isolation • Isolating the pop. by a geographical barrier can lead to speciation – We can apply microevolution (genetic drift and Natural Selection) to the evolution of the new species – Ex. Darwin’s finches ...
... Geographical Isolation • Isolating the pop. by a geographical barrier can lead to speciation – We can apply microevolution (genetic drift and Natural Selection) to the evolution of the new species – Ex. Darwin’s finches ...
Directed Reading B
... Read the description. Then, draw a line from the dot next to each description to the matching word. ...
... Read the description. Then, draw a line from the dot next to each description to the matching word. ...
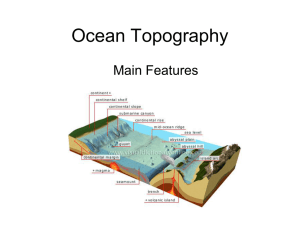
Ocean Topography
... • A mid-ocean ridge is an underwater mountain range, typically having a valley known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. It is usually an oceanic spreading center, which is responsible for seafloor spreading. ...
... • A mid-ocean ridge is an underwater mountain range, typically having a valley known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. It is usually an oceanic spreading center, which is responsible for seafloor spreading. ...
Chapter 1 Study Guide – Plate Tectonics
... What are the three main layers of the Earth and what are they made up of? a. crust – a layer of solid rock that includes both dry land and ocean floor b. mantle – very hot rock that is solid c. core – made mostly of iron and nickel. It has a liquid outer core and a solid inner core ...
... What are the three main layers of the Earth and what are they made up of? a. crust – a layer of solid rock that includes both dry land and ocean floor b. mantle – very hot rock that is solid c. core – made mostly of iron and nickel. It has a liquid outer core and a solid inner core ...
la teoria della deriva dei continenti e della tettonica a zolle
... Earth’s crust changes such as the seismic activity, the orogeny, the presence of the volcanos on the territory and the formation of the oceanics trenches. ...
... Earth’s crust changes such as the seismic activity, the orogeny, the presence of the volcanos on the territory and the formation of the oceanics trenches. ...
Chapter 7 Earth and the Terrestrial Worlds
... surface features are somewhat similar also – they both have few impact craters, and they all have volcanoes and evidence of tectonic activities. Although there is a very large difference in the amount of gases on Venus and Mars, their chemical compositions are very similar – high percentage of CO2 A ...
... surface features are somewhat similar also – they both have few impact craters, and they all have volcanoes and evidence of tectonic activities. Although there is a very large difference in the amount of gases on Venus and Mars, their chemical compositions are very similar – high percentage of CO2 A ...
Final Review - Academic Computer Center
... The following statement is a fact: “The Sun will continue as a yellow star for another 10 billion years.” _____ 3. ...
... The following statement is a fact: “The Sun will continue as a yellow star for another 10 billion years.” _____ 3. ...
Study Guide Answers
... Luster, Color, Streak, Hardness Supercontinent, when all continents were one ...
... Luster, Color, Streak, Hardness Supercontinent, when all continents were one ...
Earth as a system
... remaining from the formation and heat that is continuously generated by radioactive decay powers the internal processes that produce volcanoes, earthquakes, and mountains ...
... remaining from the formation and heat that is continuously generated by radioactive decay powers the internal processes that produce volcanoes, earthquakes, and mountains ...
Benchmark 1 Study Guide 6th Grade Earth Science Mr. Ventiquattro
... 17. Divergent plates, move away from each other 18. Convergent subduction, ocean plate hits continental plate and ocean plate sinks back into mantle ...
... 17. Divergent plates, move away from each other 18. Convergent subduction, ocean plate hits continental plate and ocean plate sinks back into mantle ...
Introduction to Earth Science
... that extends from the ocean floor upward several kilometers in the atmosphere. • The geosphere consists of the solid parts of the planet and is not uniform. • Based on differences in composition it is divided into three main regions, the core, the mantle, and the crust. ...
... that extends from the ocean floor upward several kilometers in the atmosphere. • The geosphere consists of the solid parts of the planet and is not uniform. • Based on differences in composition it is divided into three main regions, the core, the mantle, and the crust. ...
Script - FOG - City College of San Francisco
... very different one – Earth’s. Venus and Mars both have carbon dioxide as the major atmospheric gas, much like Earth’s early atmosphere, followed by nitrogen and argon. Notice the lack of any oxygen. Why is Earth’s atmosphere today so different than it was originally and so different than the other t ...
... very different one – Earth’s. Venus and Mars both have carbon dioxide as the major atmospheric gas, much like Earth’s early atmosphere, followed by nitrogen and argon. Notice the lack of any oxygen. Why is Earth’s atmosphere today so different than it was originally and so different than the other t ...
Ocean Depth through Deep Time
... The Earth’s oceans have played an important role in the evolution of life and tectonics on Earth, and yet our understanding of basic connections between these remains limited. One of the central, and still unanswered questions, is whether Earth’s oceans have been present over all of Earth’s history, ...
... The Earth’s oceans have played an important role in the evolution of life and tectonics on Earth, and yet our understanding of basic connections between these remains limited. One of the central, and still unanswered questions, is whether Earth’s oceans have been present over all of Earth’s history, ...
Inner Structure of the Earth 3. Mantle
... continental plate. Results: volcanic mountain building and earthquakes. ...
... continental plate. Results: volcanic mountain building and earthquakes. ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.