Journey to the Center of Earth
... constantly changes is called theory of plate tectonic. • The theory states that the earth’s outer shell, the lithosphere is divided into eight large plates. • Because each plate moves as a single unit, the interiors of the plates are generally stable. All major activity such as ...
... constantly changes is called theory of plate tectonic. • The theory states that the earth’s outer shell, the lithosphere is divided into eight large plates. • Because each plate moves as a single unit, the interiors of the plates are generally stable. All major activity such as ...
Geosphere PP
... • Scien4sts use seismic waves to learn about Earth’s interior (waves altered by the material it travels through) • Measure changes in the speed and direc4on of seismic waves that penetrate the interior ...
... • Scien4sts use seismic waves to learn about Earth’s interior (waves altered by the material it travels through) • Measure changes in the speed and direc4on of seismic waves that penetrate the interior ...
Earth as a System
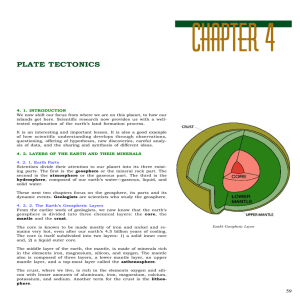
... 1. Crust-- _________, solid uppermost zone of Earth. The crust varies from thin on the ____________ ___________ to thick at the ______________ _______________ The crust is ____________ thick under the oceans Made of _______________ Continental crust is between _____________ thick Made of ___ ...
... 1. Crust-- _________, solid uppermost zone of Earth. The crust varies from thin on the ____________ ___________ to thick at the ______________ _______________ The crust is ____________ thick under the oceans Made of _______________ Continental crust is between _____________ thick Made of ___ ...
Volcanoes - BSHGCSEgeography
... ages broken by short warm periods called interglacials. • The cycle is driven by Milankovitch cycles. Long term changes in the Earth's orbit trigger an initial warming which warms the oceans and melts ice sheets - this releases CO2. • The extra CO2 in the atmosphere causes further warming leading to ...
... ages broken by short warm periods called interglacials. • The cycle is driven by Milankovitch cycles. Long term changes in the Earth's orbit trigger an initial warming which warms the oceans and melts ice sheets - this releases CO2. • The extra CO2 in the atmosphere causes further warming leading to ...
Ch 6 Vocab Earth`s Surface
... 5. Plate Tectonics – the idea that giant plates of rock are moving slowly across the Earth’s surface 6. Earthquake – a violent shaking of the Earth’s crust as built-up energy is released 7. Epicenter – the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus of an earthquake 8. Fault – a crack in t ...
... 5. Plate Tectonics – the idea that giant plates of rock are moving slowly across the Earth’s surface 6. Earthquake – a violent shaking of the Earth’s crust as built-up energy is released 7. Epicenter – the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus of an earthquake 8. Fault – a crack in t ...
Geological Past - Government of New Brunswick
... New Brunswick geology forms a rich tapestry of rock types and landscapes. In several areas of the province, the rocks are quarried for commercial purposes or contain valuable mineral deposits. Some of the deposits are being mined today, whereas others remain to be discovered. But how and when did th ...
... New Brunswick geology forms a rich tapestry of rock types and landscapes. In several areas of the province, the rocks are quarried for commercial purposes or contain valuable mineral deposits. Some of the deposits are being mined today, whereas others remain to be discovered. But how and when did th ...
Earth - edl.io
... Alternating patterns of magnetic properties were discovered in rocks found on the seafloor. Dating of the rocks indicated that as one moved away from the ridge, the rocks became older. New crust was being created at volcanic rift zones. ...
... Alternating patterns of magnetic properties were discovered in rocks found on the seafloor. Dating of the rocks indicated that as one moved away from the ridge, the rocks became older. New crust was being created at volcanic rift zones. ...
Chapter 04 Plate Tectonics
... 270 million years ago all of Earth’s continents formed one large continent called Pangaea. ...
... 270 million years ago all of Earth’s continents formed one large continent called Pangaea. ...
SS_Planet_Characteristics
... the Great Red Spot is a high pressure area with significantly taller clouds than the surrounding areas, two Earths could fit in the Great Red Spot Like Jupiter, Saturn has winds that blow its clouds around, but the belts and zones are much fainter and wider near the equator, storms can last for year ...
... the Great Red Spot is a high pressure area with significantly taller clouds than the surrounding areas, two Earths could fit in the Great Red Spot Like Jupiter, Saturn has winds that blow its clouds around, but the belts and zones are much fainter and wider near the equator, storms can last for year ...
Vocabulary for Earth`s Structure and Note Cards Crust – the
... Crust – the outermost layer of the Earth Mantle – The layer of the Earth between the crust and the outer core Core – the Earth’s layer that extends from below the mantle to the center of the Earth. Outer core – liquid part of the core, made of molten iron and nickel Inner core – solid part of the co ...
... Crust – the outermost layer of the Earth Mantle – The layer of the Earth between the crust and the outer core Core – the Earth’s layer that extends from below the mantle to the center of the Earth. Outer core – liquid part of the core, made of molten iron and nickel Inner core – solid part of the co ...
plate tectonics review - Hicksville Public Schools
... 2. What are the 4 layers of the Earth? (starting from the surface) CRUST, MANTLE, OUTER CORE, INNER CORE. 3. Describe each layer in terms of being made of rock or metal and if they are solid or able to flow. CRUST- SOLID ROCK MANTLE- HOT ROCK THAT CAN FLOW OUTER CORE- HOT METAL THAT CAN FLOW INNER C ...
... 2. What are the 4 layers of the Earth? (starting from the surface) CRUST, MANTLE, OUTER CORE, INNER CORE. 3. Describe each layer in terms of being made of rock or metal and if they are solid or able to flow. CRUST- SOLID ROCK MANTLE- HOT ROCK THAT CAN FLOW OUTER CORE- HOT METAL THAT CAN FLOW INNER C ...
Benchmark 2 Study Guide Answer Key
... 26. Label the five major oceans on the map above. 27. For a solar eclipse to occur, the moon must be in what phase? _New moon phase_____ 28. For a lunar eclipse to occur, the moon must be in what phase? __Full moon phase___ 29. Waning means shrinking, so when the moon is waning the sunlight part is ...
... 26. Label the five major oceans on the map above. 27. For a solar eclipse to occur, the moon must be in what phase? _New moon phase_____ 28. For a lunar eclipse to occur, the moon must be in what phase? __Full moon phase___ 29. Waning means shrinking, so when the moon is waning the sunlight part is ...
Earth Science Grade
... through the crust, oceans, and atmosphere in what is known as the “water cycle” Water is a solvent and, as it passes through the water cycle it dissolves minerals and gases and carries them to the oceans Water evaporates from the earth’s surface, rises and cools as it moves to higher elevations, ...
... through the crust, oceans, and atmosphere in what is known as the “water cycle” Water is a solvent and, as it passes through the water cycle it dissolves minerals and gases and carries them to the oceans Water evaporates from the earth’s surface, rises and cools as it moves to higher elevations, ...
Study Questions for the first week of ESS 210
... the approximate thickness of these layers) ((Need to know approximate radius of Earth and the radii of various boundaries) 3. What is the thickness of oceanic crust? Of continental crust? 4. How did the compositional layers develop from an originally homogeneous Earth? 5. What are the layers having ...
... the approximate thickness of these layers) ((Need to know approximate radius of Earth and the radii of various boundaries) 3. What is the thickness of oceanic crust? Of continental crust? 4. How did the compositional layers develop from an originally homogeneous Earth? 5. What are the layers having ...
Earth
... estimated Earth’s circumference by geometry. He used the length of a building shadow in Alexandria at noon on the summer solstice. He knew that, simultaneously, sunlight was hitting the bottom of a water well in Aswan. ...
... estimated Earth’s circumference by geometry. He used the length of a building shadow in Alexandria at noon on the summer solstice. He knew that, simultaneously, sunlight was hitting the bottom of a water well in Aswan. ...
The earth`s layers: http://mediatheek
... Now click on Metamorphic Rock. What did these rocks use to be? ____________________________________________________________________ How are these rocks transformed into a new kind of rock? ____________________________________________________________________ Finally, click on Igneous Rock. Which of t ...
... Now click on Metamorphic Rock. What did these rocks use to be? ____________________________________________________________________ How are these rocks transformed into a new kind of rock? ____________________________________________________________________ Finally, click on Igneous Rock. Which of t ...
CGF 3MO - TeacherWeb
... Multiple Choice – a variety of questions from throughout the course with greater emphasis on material learned since midterm. True or False – primarily questions from the current unit on atmosphere & storms with a few questions from oceans and glaciers Short Answer – questions primarily from material ...
... Multiple Choice – a variety of questions from throughout the course with greater emphasis on material learned since midterm. True or False – primarily questions from the current unit on atmosphere & storms with a few questions from oceans and glaciers Short Answer – questions primarily from material ...
Marine Geology Final Exam Information and Review
... • Describe the major layers of the Earth based on chemical composition. What type of material represents the general composition of each of the layers? • Distinguish between continental crust and oceanic crust. • Explain the concept of “isostacy”. • Describe the major layers of the Earth based on ph ...
... • Describe the major layers of the Earth based on chemical composition. What type of material represents the general composition of each of the layers? • Distinguish between continental crust and oceanic crust. • Explain the concept of “isostacy”. • Describe the major layers of the Earth based on ph ...
Chapter 2
... As earth cooled: Densest material flowed toward center of earth. Lighter materials floated toward the surface. ...
... As earth cooled: Densest material flowed toward center of earth. Lighter materials floated toward the surface. ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.