Chapter 17 Study Guide 16
... ____________________________________________________________________________________ 13) What takes place in the asthenosphere to cause the plates to move? ____________________________________________________________________________________ convection currents → heated material rises, cools, and sin ...
... ____________________________________________________________________________________ 13) What takes place in the asthenosphere to cause the plates to move? ____________________________________________________________________________________ convection currents → heated material rises, cools, and sin ...
Periodic Table, Metals, Non-metals, Metalloids, Elements
... Archaea: don’t have a nucleus (prokaryotic), live in extreme habitats, reproduce asexually, unicellular Bacteria: don’t have a nucleus (prokaryotic), can be found anywhere, reproduce asexually, unicellular 2. What is the difference between an autotroph and a heterotroph? Autotroph: organisms that ma ...
... Archaea: don’t have a nucleus (prokaryotic), live in extreme habitats, reproduce asexually, unicellular Bacteria: don’t have a nucleus (prokaryotic), can be found anywhere, reproduce asexually, unicellular 2. What is the difference between an autotroph and a heterotroph? Autotroph: organisms that ma ...
Lecture 2: Dynamic Earth: Plate Tectonics
... Earth is a dynamic planet The surface of the Earth is constantly changing. Going back a billion years, there were no Grand Canyon, Appalachian Mountains, or Himalayan Mountains. (Thick sedimentary rock accumulated as horizontal layers on an ocean floor are now folded and faulted to from the highest ...
... Earth is a dynamic planet The surface of the Earth is constantly changing. Going back a billion years, there were no Grand Canyon, Appalachian Mountains, or Himalayan Mountains. (Thick sedimentary rock accumulated as horizontal layers on an ocean floor are now folded and faulted to from the highest ...
Name__________________ EARTH SCIENCE FIRST QUARTER
... 20 matching terms from Process of Science, Earth’s Systems, Plate tectonics, and Minerals units. (40 pts) 10 Multiple choice from the same units mentioned above (20 pts) 5 numbers to put in scientific notation (10 pts) 5 metric conversions (15 pts) 3 Short Answer Questions from the same units mentio ...
... 20 matching terms from Process of Science, Earth’s Systems, Plate tectonics, and Minerals units. (40 pts) 10 Multiple choice from the same units mentioned above (20 pts) 5 numbers to put in scientific notation (10 pts) 5 metric conversions (15 pts) 3 Short Answer Questions from the same units mentio ...
Chapter 2: The Earth
... continents of the Earth formed what was known as Pangaea. Over millions of years, this “super-continent” has broken apart into small continents. The theory that the continents were once joined then slowly drifted apart is known as Continental Drift. ...
... continents of the Earth formed what was known as Pangaea. Over millions of years, this “super-continent” has broken apart into small continents. The theory that the continents were once joined then slowly drifted apart is known as Continental Drift. ...
earth science fact packet
... equator, high pressure to low pressure. 34. An air mass is a large section of air with the same temperature and pressure. 35. The boundary between two air masses is called a front. Changes in the weather occur at fronts. 36. Different air masses have different temperatures and pressures. Air masses ...
... equator, high pressure to low pressure. 34. An air mass is a large section of air with the same temperature and pressure. 35. The boundary between two air masses is called a front. Changes in the weather occur at fronts. 36. Different air masses have different temperatures and pressures. Air masses ...
Earth Science Chapter 5
... • Blasts from the Earth have brought rocks from 100 ft to the surface ...
... • Blasts from the Earth have brought rocks from 100 ft to the surface ...
Our Dynamic Earth
... and volcanic eruptions occur in the basin of the Pacific ocean. • Roughly 90% of earthquakes occur along the Ring of Fire and dotted with 75% of volcanoes on Earth. • There are 452 active volcanoes along the Ring of Fire. • The Ring is shaped like a horse-shoe. ...
... and volcanic eruptions occur in the basin of the Pacific ocean. • Roughly 90% of earthquakes occur along the Ring of Fire and dotted with 75% of volcanoes on Earth. • There are 452 active volcanoes along the Ring of Fire. • The Ring is shaped like a horse-shoe. ...
8th grade MSP review test
... Renewable energy sources have disadvantages to them. Which one of the following is a disadvantage for the energy production above. a. Water is hard to find. b. Dams destroy the habitats and environment where the reservoir is ...
... Renewable energy sources have disadvantages to them. Which one of the following is a disadvantage for the energy production above. a. Water is hard to find. b. Dams destroy the habitats and environment where the reservoir is ...
Density and Earth`s Layers Review Answer Key
... 9. In March the American Fork River is going to be full of muddy, silty water. The river may even pick up small rocks and gravel in the upper sections of the canyon where the river is steep and the water is moving fast. Explain to me how that sediment is going to settle out of the water as the river ...
... 9. In March the American Fork River is going to be full of muddy, silty water. The river may even pick up small rocks and gravel in the upper sections of the canyon where the river is steep and the water is moving fast. Explain to me how that sediment is going to settle out of the water as the river ...
Hawaii Hotspot - cloudfront.net
... 4.2 Earth, like other planets, is still cooling, though radioactive decay continuously generates internal heat. This heat flows through and out of Earth’s interior largely through convection, but also through conduction and radiation. The flow of Earth’s heat is like its lifeblood, driving its inte ...
... 4.2 Earth, like other planets, is still cooling, though radioactive decay continuously generates internal heat. This heat flows through and out of Earth’s interior largely through convection, but also through conduction and radiation. The flow of Earth’s heat is like its lifeblood, driving its inte ...
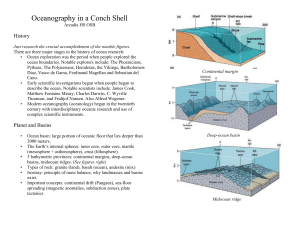
InAConchShell - some tryout study material
... salinity (average 35 ppt, saltier termed brine). Seawater most dense at 4 degrees C, freezes at -2. Also pH (acidic, basic, buffers). Concentration of solute in seawater measured in ppt (parts per thousand, also ppm, ppb). There are major constituents, nutrients, gases, and trace elements. Residence ...
... salinity (average 35 ppt, saltier termed brine). Seawater most dense at 4 degrees C, freezes at -2. Also pH (acidic, basic, buffers). Concentration of solute in seawater measured in ppt (parts per thousand, also ppm, ppb). There are major constituents, nutrients, gases, and trace elements. Residence ...
Grade 8 Science
... 120 000 years ago ending 11 000 years ago. Glaciers covered ~ 20% of land on Earth. ...
... 120 000 years ago ending 11 000 years ago. Glaciers covered ~ 20% of land on Earth. ...
117 Ways to Pass the Earth Science Regents
... Cold fronts force warm air up and are associated with short narrow bands of heavy precipitation and thunder/lightning in advance of the front! ...
... Cold fronts force warm air up and are associated with short narrow bands of heavy precipitation and thunder/lightning in advance of the front! ...
Plate Tectonic Outline Notes
... C. ______________________– steep walled depression around a volcano’s vent D. _______________________________ – areas where magma from deep in Earth’s mantle has melted through the crust to form several volcanoes 1. Ex. ___________________________________________ the Pacific Plate is moving over a s ...
... C. ______________________– steep walled depression around a volcano’s vent D. _______________________________ – areas where magma from deep in Earth’s mantle has melted through the crust to form several volcanoes 1. Ex. ___________________________________________ the Pacific Plate is moving over a s ...
Sc 7 Unit 5 Review Booklet
... 82. Most mountains are large areas that have been uplifted due to the ______________ or ______________ of plates. 83. Sedimentary rocks that are placed under slow, gradual pressure can either ________ or ___________. (p. 413) 84. Rocks can fold if there is enough ________ and ___________. 85. The up ...
... 82. Most mountains are large areas that have been uplifted due to the ______________ or ______________ of plates. 83. Sedimentary rocks that are placed under slow, gradual pressure can either ________ or ___________. (p. 413) 84. Rocks can fold if there is enough ________ and ___________. 85. The up ...
Earthquakes, Volcanoes & The Ring of Fire
... 16. When plates collide, rather than being subducted, the plates pile into each other, causing one or both plates to fold up like an accordion. This process elevates the crust, folds and deforms it heavily, and produces a mountain range. ...
... 16. When plates collide, rather than being subducted, the plates pile into each other, causing one or both plates to fold up like an accordion. This process elevates the crust, folds and deforms it heavily, and produces a mountain range. ...
Earth`s Crust
... Continental drift – idea that continents have moved slowly to their current positions due to convection currents in the mantel. Pangea – the idea that the all land masses on earth were once a single large land mass. ...
... Continental drift – idea that continents have moved slowly to their current positions due to convection currents in the mantel. Pangea – the idea that the all land masses on earth were once a single large land mass. ...
Earth_sCrust2
... Continental drift – idea that continents have moved slowly to their current positions due to convection currents in the mantel. Pangea – the idea that the all land masses on earth were once a single large land mass. ...
... Continental drift – idea that continents have moved slowly to their current positions due to convection currents in the mantel. Pangea – the idea that the all land masses on earth were once a single large land mass. ...
The Structure of the Earth
... • Two types: –Continental Crust (thicker) –Oceanic Crust (thin and more dense) ...
... • Two types: –Continental Crust (thicker) –Oceanic Crust (thin and more dense) ...
1 Billion Years Ago 450 Million Years Ago 400 Million Years Ago
... standing near a soaring mountain range on a giant continent called Pangea. The rocks you see today were formed on the floor of an ancient ocean that divided that continent as plates in the Earth’s crust moved apart. Today’s Green Mountains formed as these plates eventually collided again, closing th ...
... standing near a soaring mountain range on a giant continent called Pangea. The rocks you see today were formed on the floor of an ancient ocean that divided that continent as plates in the Earth’s crust moved apart. Today’s Green Mountains formed as these plates eventually collided again, closing th ...
geology
... standing near a soaring mountain range on a giant continent called Pangea. The rocks you see today were formed on the floor of an ancient ocean that divided that continent as plates in the Earth’s crust moved apart. Today’s Green Mountains formed as these plates eventually collided again, closing th ...
... standing near a soaring mountain range on a giant continent called Pangea. The rocks you see today were formed on the floor of an ancient ocean that divided that continent as plates in the Earth’s crust moved apart. Today’s Green Mountains formed as these plates eventually collided again, closing th ...
Module E: Unit 4, Lesson 1 – Earth`s Layers
... • Both types of crust are made mostly of oxygen, silicon, and aluminum. • Oceanic crust is denser than continental crust because it contains almost twice as much iron, calcium, and magnesium. • The mantle is located between the crust and the core. • The mantle is a region of hot, slow-flowing solid ...
... • Both types of crust are made mostly of oxygen, silicon, and aluminum. • Oceanic crust is denser than continental crust because it contains almost twice as much iron, calcium, and magnesium. • The mantle is located between the crust and the core. • The mantle is a region of hot, slow-flowing solid ...
Earth`s Systems and Resources Unit Test
... B. Where plates of earth are coming apart. C. Where large plates of earth are transforming. D. Where large plates of earth are colliding. 29. Use the map to the right to answer this question. California has been plagued with earthquakes over the centuries; earthquakes that are a severe danger to lif ...
... B. Where plates of earth are coming apart. C. Where large plates of earth are transforming. D. Where large plates of earth are colliding. 29. Use the map to the right to answer this question. California has been plagued with earthquakes over the centuries; earthquakes that are a severe danger to lif ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.