CHICXULUB CRATER - University of Colorado Boulder
... at that time went extinct in a short period of time (less than 2 million years or so). ...
... at that time went extinct in a short period of time (less than 2 million years or so). ...
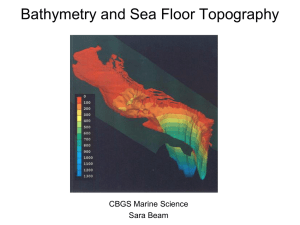
Bathymetry
... • A theoretical model of the formation of magnetic striping. New oceanic crust forming continuously at the crest of the mid-ocean ridge cools and becomes increasingly older as it moves away from the ridge crest with seafloor spreading : a. the spreading ridge about 5 million years ago; b. about 2 to ...
... • A theoretical model of the formation of magnetic striping. New oceanic crust forming continuously at the crest of the mid-ocean ridge cools and becomes increasingly older as it moves away from the ridge crest with seafloor spreading : a. the spreading ridge about 5 million years ago; b. about 2 to ...
GG 101, Spring 2006 Name_________________________ Exam 2
... is a desert, while much of the Himalayas are cloaked with thick vegetation. Plant leaves and the type of vegetation changes with temperature and rainfall and thus in the Himalayas vegetation changes with altitude. The variety of leaf shapes have been used to create a “leaf thermometer”. This thermom ...
... is a desert, while much of the Himalayas are cloaked with thick vegetation. Plant leaves and the type of vegetation changes with temperature and rainfall and thus in the Himalayas vegetation changes with altitude. The variety of leaf shapes have been used to create a “leaf thermometer”. This thermom ...
WG3200 Unit 1 Term Sheet File
... ____________ - formed when two normal faults occur parallel to each, with the plate in-between dropping down as plates move away from each other. ____________ - land between two parallel faults rise to form this. ____________ - fault where movement is up, rather than down, the face over which moveme ...
... ____________ - formed when two normal faults occur parallel to each, with the plate in-between dropping down as plates move away from each other. ____________ - land between two parallel faults rise to form this. ____________ - fault where movement is up, rather than down, the face over which moveme ...
Quiz #2 - University of Hawaii at Hilo
... 4. Where are most of the earth’s earthquakes located A. B. C. D. ...
... 4. Where are most of the earth’s earthquakes located A. B. C. D. ...
Evolution of Organisms and Landforms EOG review
... 6. Which best explains how geologic time scales can help scientists study the evolution of life on Earth? A. They describe the existence of rocks before there was life on Earth. B. They show that geological features have evolved at the same rate as organisms. C. They compare the life histories of s ...
... 6. Which best explains how geologic time scales can help scientists study the evolution of life on Earth? A. They describe the existence of rocks before there was life on Earth. B. They show that geological features have evolved at the same rate as organisms. C. They compare the life histories of s ...
Provincial Exam Review: Earth Science Natural Causes of Climate
... 4. How much cooler would Earth be on average without the natural greenhouse effect? 5. List three types of motion that influence Earth’s climate. 6. Which type of Earth motion is responsible for seasons? 7. Which greenhouse gas is most abundant in Earth’s atmosphere? 8. What two factors affect the d ...
... 4. How much cooler would Earth be on average without the natural greenhouse effect? 5. List three types of motion that influence Earth’s climate. 6. Which type of Earth motion is responsible for seasons? 7. Which greenhouse gas is most abundant in Earth’s atmosphere? 8. What two factors affect the d ...
Slide 1 - MisterSyracuse.com
... of boundary in the Atlantic Ocean between Africa and South America? What feature is being formed? ...
... of boundary in the Atlantic Ocean between Africa and South America? What feature is being formed? ...
Vocabulary Word Definition Your Sketch/ memory aid 1. Inner core
... Continental crust includes all continents (less dense; mostly composed of granite) Oceanic includes all the ocean floors (more dense; mostly composed of basalt) ...
... Continental crust includes all continents (less dense; mostly composed of granite) Oceanic includes all the ocean floors (more dense; mostly composed of basalt) ...
E.S. Ch. 3 Study Guide
... Divergent boundary- is when plates move apart. Hot molten rock from the mantle rises, cools, and causes the floor to spread, causing new rock to form. Examples: Mid-Atlantic Ridge and Iceland Convergent Boundary- is when the plates come together. Continental plates collide/crash into each other and ...
... Divergent boundary- is when plates move apart. Hot molten rock from the mantle rises, cools, and causes the floor to spread, causing new rock to form. Examples: Mid-Atlantic Ridge and Iceland Convergent Boundary- is when the plates come together. Continental plates collide/crash into each other and ...
9_Origin_earth
... Think of an ice skater in a spin. With her arms apart she spins slowly (her hands have a small momentum times a large distance from her rotation axis). As she brings her hands in she spins much faster. Angular momentum is conserved. Because her hands are nearer the rotation axis they must have a hig ...
... Think of an ice skater in a spin. With her arms apart she spins slowly (her hands have a small momentum times a large distance from her rotation axis). As she brings her hands in she spins much faster. Angular momentum is conserved. Because her hands are nearer the rotation axis they must have a hig ...
Earth`s Interior
... 1. Describe the changes of temperature, pressure and density at increasing depths below the earth’s surface . 2. Explain how the earth’s structure has been determined from seismic evidence. 3. Compare and contrast the properties of P waves and S waves. 4. Describe the location and composition of the ...
... 1. Describe the changes of temperature, pressure and density at increasing depths below the earth’s surface . 2. Explain how the earth’s structure has been determined from seismic evidence. 3. Compare and contrast the properties of P waves and S waves. 4. Describe the location and composition of the ...
Pangaea Wegener video guide 2016 17
... 1) Alfred Wegener noticed that the shapes of our present day continents could fit together like puzzle pieces. He called this massive land mass “Pangaea” meaning all/whole earth. He theorized further that around 250 million years ago these continents drifted apart. His theories needed evidence to su ...
... 1) Alfred Wegener noticed that the shapes of our present day continents could fit together like puzzle pieces. He called this massive land mass “Pangaea” meaning all/whole earth. He theorized further that around 250 million years ago these continents drifted apart. His theories needed evidence to su ...
Earth Cores Script: Inner core The inner core is the
... below the Earth’s crust. The temperature of the inner core reaches over 9,000 F (4,982 C), making it the hottest spot on the planet. Despite this temperature, the nickel and iron that make up the inner core do not melt, due to the extreme pressure exerted on it. The inner core, and along with the ou ...
... below the Earth’s crust. The temperature of the inner core reaches over 9,000 F (4,982 C), making it the hottest spot on the planet. Despite this temperature, the nickel and iron that make up the inner core do not melt, due to the extreme pressure exerted on it. The inner core, and along with the ou ...
Earth as a planet
... ice is present at both the north and south lunar poles, in agreement with Clementine results for the south pole reported in November 1996. The ice could represent relatively pristine cometary or asteroid material which has existed on the Moon for millions or billions of years. Deposits of ice on the ...
... ice is present at both the north and south lunar poles, in agreement with Clementine results for the south pole reported in November 1996. The ice could represent relatively pristine cometary or asteroid material which has existed on the Moon for millions or billions of years. Deposits of ice on the ...
Science Contracts for Week 1
... 2. Examine properties of each layer that cause layers to form: temperature, thickness, composition and density. 3. Label layers where convection currents are found and describes the cause of convection inside the Earth Eighth Grade Science Contract Week One Choice One Rubric ...
... 2. Examine properties of each layer that cause layers to form: temperature, thickness, composition and density. 3. Label layers where convection currents are found and describes the cause of convection inside the Earth Eighth Grade Science Contract Week One Choice One Rubric ...
Section 2 - Burnet Middle School
... • Many parts of the world, even though they are very distant from one another, have similar climates. • This is known as having the same climate zone, or similar patterns of temperature, precipitation, and vegetation. • Climate zones include biomes, or areas such as rain forest, desert, grassland, a ...
... • Many parts of the world, even though they are very distant from one another, have similar climates. • This is known as having the same climate zone, or similar patterns of temperature, precipitation, and vegetation. • Climate zones include biomes, or areas such as rain forest, desert, grassland, a ...
Earth as a planet
... ice is present at both the north and south lunar poles, in agreement with Clementine results for the south pole reported in November 1996. The ice could represent relatively pristine cometary or asteroid material which has existed on the Moon for millions or billions of years. Deposits of ice on the ...
... ice is present at both the north and south lunar poles, in agreement with Clementine results for the south pole reported in November 1996. The ice could represent relatively pristine cometary or asteroid material which has existed on the Moon for millions or billions of years. Deposits of ice on the ...
A Core Sample of Planet Earth I
... 6. Use pages 391-392 in your book to put a very brief description of the composition/structure of each layer. Write words or phrases (not sentences). Include whether it is mostly rock or metal, the state of matter, and other important qualities (such as “rigid” for lithosphere and “weak, soft, flow ...
... 6. Use pages 391-392 in your book to put a very brief description of the composition/structure of each layer. Write words or phrases (not sentences). Include whether it is mostly rock or metal, the state of matter, and other important qualities (such as “rigid” for lithosphere and “weak, soft, flow ...
The Layer`s Of The Earth!
... • It is composed of mostly iron, magnesium and silicon. • The mantle accounts for about 70% of the Earth’s mass • It is divided into two regions: the upper and ...
... • It is composed of mostly iron, magnesium and silicon. • The mantle accounts for about 70% of the Earth’s mass • It is divided into two regions: the upper and ...
(1) the distribution of fossils on different continents
... •The continents fit together almost like puzzle pieces forming Pangaea (one super-continent). •During the time of Pangaea most of the dry land on Earth was joined into one huge landmass that covered nearly a third of the planet's surface. The giant ocean that surrounded the continent is known as Pa ...
... •The continents fit together almost like puzzle pieces forming Pangaea (one super-continent). •During the time of Pangaea most of the dry land on Earth was joined into one huge landmass that covered nearly a third of the planet's surface. The giant ocean that surrounded the continent is known as Pa ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.