Rocks the House - Natural History Museum
... Learning outcomes Students will gain an understanding: • that Earth’s crust is made up of tectonic plates, which move • of geological interactions at plate boundaries, specifically where plates collide, slide past each other and separate, and the effect of these interactions on the landscape • of h ...
... Learning outcomes Students will gain an understanding: • that Earth’s crust is made up of tectonic plates, which move • of geological interactions at plate boundaries, specifically where plates collide, slide past each other and separate, and the effect of these interactions on the landscape • of h ...
The Earth February 7 − Why does Earth support life?
... • e.g. “Rim of Fire” around Pacific Ocean. • Plates can slide at the boundaries • San Andreas Fault in California ...
... • e.g. “Rim of Fire” around Pacific Ocean. • Plates can slide at the boundaries • San Andreas Fault in California ...
Chapter 4 Plate tectonics Review Game
... molten material? Pillow lava and other forms of hardened lava are scattered across the ocean floor, this is evidence that molten material constantly erupts from the mid-ocean ridge ...
... molten material? Pillow lava and other forms of hardened lava are scattered across the ocean floor, this is evidence that molten material constantly erupts from the mid-ocean ridge ...
Earth`s Interior
... Objectives: By the end of this section you should be able to: Explain Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis about the continents; list the evidence used by Wegener to support his hypothesis; Explain why other scientists at the time rejected Wegener’s theory. ...
... Objectives: By the end of this section you should be able to: Explain Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis about the continents; list the evidence used by Wegener to support his hypothesis; Explain why other scientists at the time rejected Wegener’s theory. ...
Plan for Living on a Restless Planet Sets NASA`s Solid Earth Agenda
... with mantle convection, although their interpretation requires information on the structure of the tectonic plates and the variation of viscosity within the mantle. Improved information on plate characteristics and mantle viscosity can come,in turn,from measurements of the time-dependent response of ...
... with mantle convection, although their interpretation requires information on the structure of the tectonic plates and the variation of viscosity within the mantle. Improved information on plate characteristics and mantle viscosity can come,in turn,from measurements of the time-dependent response of ...
APES Review Part 1
... (b) Marine zonation. Like lakes, the marine environment is generally classified on the basis of light penetration (photic and aphotic zones), distance from shore and water depth (intertidal, neritic, and oceanic zones), and whether it is open water (pelagic zone) or bottom (benthic and abyssal zones ...
... (b) Marine zonation. Like lakes, the marine environment is generally classified on the basis of light penetration (photic and aphotic zones), distance from shore and water depth (intertidal, neritic, and oceanic zones), and whether it is open water (pelagic zone) or bottom (benthic and abyssal zones ...
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide
... 31. List the Earth’s layers from the center to the surface. 32. What is the difference between the inner core and the outer core? 33. What can an earthquake on the sea floor produce? 34. What was the name of Alfred Wegener’s theory of horizontal movement of the Earth’s crust? 35. What were the key p ...
... 31. List the Earth’s layers from the center to the surface. 32. What is the difference between the inner core and the outer core? 33. What can an earthquake on the sea floor produce? 34. What was the name of Alfred Wegener’s theory of horizontal movement of the Earth’s crust? 35. What were the key p ...
Introduction and Overview
... F5: the tendency of the overriding plate to be drawn toward a subduction zone as the subducting slab bends (otherwise it would move away from the overriding plate) F6: friction between the subducting slab and the overlying lithosphere F7: tendency of the oceanic plate to sink as it cools and becomes ...
... F5: the tendency of the overriding plate to be drawn toward a subduction zone as the subducting slab bends (otherwise it would move away from the overriding plate) F6: friction between the subducting slab and the overlying lithosphere F7: tendency of the oceanic plate to sink as it cools and becomes ...
Earth internal energy (solucionario)
... molten metals in the Earth’s core generate our planet’s magnetic field. Movement of molten iron and nickel generate electrical and magnetic fields that produce Earth’s magnetism. The flows of these molten metals in Earth’s outer core are not perfectly steady over time, so the Earth’s magnetic field ...
... molten metals in the Earth’s core generate our planet’s magnetic field. Movement of molten iron and nickel generate electrical and magnetic fields that produce Earth’s magnetism. The flows of these molten metals in Earth’s outer core are not perfectly steady over time, so the Earth’s magnetic field ...
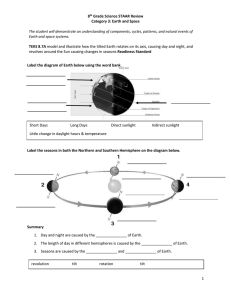
8th Grade Science STAAR Review Category 3: Earth and Space
... 3. What is the current temperature of New York (NY) like? _________________________________ 4. What is the future temperature of Georgia (GA) going to be like? _________________________ ...
... 3. What is the current temperature of New York (NY) like? _________________________________ 4. What is the future temperature of Georgia (GA) going to be like? _________________________ ...
Earth`s Spheres
... 1. Atmosphere - The atmosphere is not very deep when compared to the radius of the Earth. About 99.9% of the atmosphere is within 30 miles of the Earth’s surface. Nevertheless, there are some atmospheric gases out to distances of several hundred miles. The atmosphere has been divide into a number of ...
... 1. Atmosphere - The atmosphere is not very deep when compared to the radius of the Earth. About 99.9% of the atmosphere is within 30 miles of the Earth’s surface. Nevertheless, there are some atmospheric gases out to distances of several hundred miles. The atmosphere has been divide into a number of ...
It`s easy! Each plate is named after the major land mass
... Your job is to know the names and locations of the 6 major plates. (It's easy! You will see how the names of the plates match up to the names of Earth's continents and oceans). INSTRUCTIONS: Use the next slides and your paper maps to complete this activity. ...
... Your job is to know the names and locations of the 6 major plates. (It's easy! You will see how the names of the plates match up to the names of Earth's continents and oceans). INSTRUCTIONS: Use the next slides and your paper maps to complete this activity. ...
TEST REVIEW KEY – Cat Events, W-E
... On hillsides, plant’s ROOTS can help hold the sediment in place and help to slow down erosion. ...
... On hillsides, plant’s ROOTS can help hold the sediment in place and help to slow down erosion. ...
“HOW DO WE KNOW WHAT IS INSIDE THE EARTH” The deepest
... The deepest hole ever drilled in the Earth was only about 12 km deep, yet scientists are confident that they understand the internal structure of the Earth thousands of kilometers below the surface. How is this possible? This is another example of the importance of observations and inference for det ...
... The deepest hole ever drilled in the Earth was only about 12 km deep, yet scientists are confident that they understand the internal structure of the Earth thousands of kilometers below the surface. How is this possible? This is another example of the importance of observations and inference for det ...
Earth Science - Issaquah Connect
... • Plate tectonics is the concept that the outer surface of the Earth is made of large plates of crust and outer mantle that are slowly moving over the surface of the liquid outer mantle. – Heat from the Earth causes the slow movement. – Plates are pulling apart in some areas, and colliding in others ...
... • Plate tectonics is the concept that the outer surface of the Earth is made of large plates of crust and outer mantle that are slowly moving over the surface of the liquid outer mantle. – Heat from the Earth causes the slow movement. – Plates are pulling apart in some areas, and colliding in others ...
Earth and Space Science (Volcanoes)
... Strand ESS Earth and Space Science Topic ESS.1 This topic focuses on the physical features of Earth and how they formed. This includes the interior of Earth, the rock record, plate tectonics and landforms. Content Statement ESS.1.2 Earth’s crust consists of major and minor tectonic plates that move ...
... Strand ESS Earth and Space Science Topic ESS.1 This topic focuses on the physical features of Earth and how they formed. This includes the interior of Earth, the rock record, plate tectonics and landforms. Content Statement ESS.1.2 Earth’s crust consists of major and minor tectonic plates that move ...
Unit 1 Major land forms and water forms DEFINITIONS
... See also lateral erosion. volcano. An opening of the crust out of which magma, ash, and gases erupt. The shape of the volcano depends very much on the type of lava. Most volcanoes are located at plate margins. wave refraction. The change in the approach angle of a wave as it moves towards the shore. ...
... See also lateral erosion. volcano. An opening of the crust out of which magma, ash, and gases erupt. The shape of the volcano depends very much on the type of lava. Most volcanoes are located at plate margins. wave refraction. The change in the approach angle of a wave as it moves towards the shore. ...
The Layer`s Of The Earth!
... 2) The Earth’s crust is very ______? 3) The mantle is the largest layer of the Earth? True or False 4) Is the Outer Core a liquid or a solid? ...
... 2) The Earth’s crust is very ______? 3) The mantle is the largest layer of the Earth? True or False 4) Is the Outer Core a liquid or a solid? ...
Earth Science EOG Review
... A.Earth’s climate is constantly changing B.The continents of Earth are continually moving ...
... A.Earth’s climate is constantly changing B.The continents of Earth are continually moving ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.