B3 C3 P3 REVISION QUIZ!
... 9. The following questions are about the National Grid. a) What is the purpose of the National Grid? To distribute electricity to all the places we need it. b) What is the voltage of the UK domestic power supply? 230 V c) Why is it more efficient to distribute electricity at much higher voltages (e. ...
... 9. The following questions are about the National Grid. a) What is the purpose of the National Grid? To distribute electricity to all the places we need it. b) What is the voltage of the UK domestic power supply? 230 V c) Why is it more efficient to distribute electricity at much higher voltages (e. ...
Lesson 3 - cisdsocialstudies
... G1.3.1 Use the fundamental themes of geography (location, place, human environment interaction, movement, region) to describe regions or places on earth. G2.2.2 Explain that communities are affected positively or negatively by changes in technology (e.g., Canada with regard to mining, forestry, hydr ...
... G1.3.1 Use the fundamental themes of geography (location, place, human environment interaction, movement, region) to describe regions or places on earth. G2.2.2 Explain that communities are affected positively or negatively by changes in technology (e.g., Canada with regard to mining, forestry, hydr ...
Convection Currents
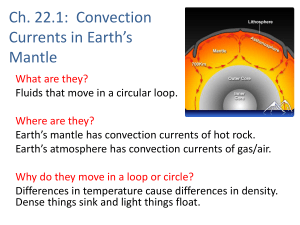
... Currents in Earth’s Mantle What are they? Fluids that move in a circular loop. Where are they? Earth’s mantle has convection currents of hot rock. Earth’s atmosphere has convection currents of gas/air. Why do they move in a loop or circle? Differences in temperature cause differences in density. Den ...
... Currents in Earth’s Mantle What are they? Fluids that move in a circular loop. Where are they? Earth’s mantle has convection currents of hot rock. Earth’s atmosphere has convection currents of gas/air. Why do they move in a loop or circle? Differences in temperature cause differences in density. Den ...
Lecture Exam 1
... 2____ Which of the following is one of the most important fundamental discoveries about the Earth? a. The Earth is unchanging, and what we see today has always looked that way throughout history. b. The Earth is constantly changing over time. c. The Earth is a dead planet d. The Earth’s continents a ...
... 2____ Which of the following is one of the most important fundamental discoveries about the Earth? a. The Earth is unchanging, and what we see today has always looked that way throughout history. b. The Earth is constantly changing over time. c. The Earth is a dead planet d. The Earth’s continents a ...
Plate Tectonics Guided Notes
... The Earth is made up of 3 main layers (_________ , _____________ , ___________) On the surface of the Earth are __________________ ________________ that move very slowly around the world ______________________ ________________ are made up of crust and upper mantle There are 2 types of plates ...
... The Earth is made up of 3 main layers (_________ , _____________ , ___________) On the surface of the Earth are __________________ ________________ that move very slowly around the world ______________________ ________________ are made up of crust and upper mantle There are 2 types of plates ...
Layers of the Earth
... called the inner core. • The outer core temperature ranges from 2,200 to 5000 degrees C. which is the temperature of the inner core. • Both cores are made up of iron and nickel. • However, while the iron and nickel in the outer core are liquids, the same metals in the inner core are solids. • The me ...
... called the inner core. • The outer core temperature ranges from 2,200 to 5000 degrees C. which is the temperature of the inner core. • Both cores are made up of iron and nickel. • However, while the iron and nickel in the outer core are liquids, the same metals in the inner core are solids. • The me ...
Document
... A scale that rates earthquakes according to their intensity and how much damage they cause at a particular place ...
... A scale that rates earthquakes according to their intensity and how much damage they cause at a particular place ...
Earth`s Structure - SD43 Teacher Sites
... will find rock. Earth’s outer layer of rock is called crust. The crust extends under the ocean and is between less then 5Km thick to 50Km thick. This is not very thick when you compare it to the center of the Earth (approx 6441Km). The crust is approx. 10ºC. ...
... will find rock. Earth’s outer layer of rock is called crust. The crust extends under the ocean and is between less then 5Km thick to 50Km thick. This is not very thick when you compare it to the center of the Earth (approx 6441Km). The crust is approx. 10ºC. ...
Earth Space Science Week 10
... Students will be able to describe the relationship between tectonic plates and the rock cycle. ...
... Students will be able to describe the relationship between tectonic plates and the rock cycle. ...
Using Google Earth to Explore Strain Rate Models - SERC
... the future at intervals of 50 thousand years. Using a North American reference frame, graphical output for the topography and faults and numerical output for locations of faults and points on the crust marked by the locations on cities were used to create data in KML format that can be used in Googl ...
... the future at intervals of 50 thousand years. Using a North American reference frame, graphical output for the topography and faults and numerical output for locations of faults and points on the crust marked by the locations on cities were used to create data in KML format that can be used in Googl ...
Unit 3: Formation of Earth and Geology
... Define the following: • Precession • Nutation • Barycenter • 45 seconds starts now….. ...
... Define the following: • Precession • Nutation • Barycenter • 45 seconds starts now….. ...
Crust - UNLV Geoscience
... system and thus most likely formed at the same time… So, what do we know about the solar system and it’s structure? These are the observations which are needed to come up with an idea (hypothesis) for how the solar system (and Earth) formed. ...
... system and thus most likely formed at the same time… So, what do we know about the solar system and it’s structure? These are the observations which are needed to come up with an idea (hypothesis) for how the solar system (and Earth) formed. ...
Section 1: Earth: A Unique Planet
... • All natural cycles can be altered by human activities. • The carbon cycle is affected when humans use fossil fuels. ...
... • All natural cycles can be altered by human activities. • The carbon cycle is affected when humans use fossil fuels. ...
Earths_interior_2013 Page 1
... Scientific theory that the earth is a dynamic planet and the continents are moving A scientific theory of the origin of species of plants and animal The theory that the universe originated 20 billion years ago ...
... Scientific theory that the earth is a dynamic planet and the continents are moving A scientific theory of the origin of species of plants and animal The theory that the universe originated 20 billion years ago ...
Unit Name: Earth`s History - Red Clay Secondary Science Wiki
... Standard 1.1.F: Understand that: Scientific habits of mind and other sources of knowledge and skills are essential to scientific inquiry. Habits of mind include tolerance of ambiguity, skepticism, openness to new ideas, and objectivity. Other knowledge and skills include mathematics, reading, writin ...
... Standard 1.1.F: Understand that: Scientific habits of mind and other sources of knowledge and skills are essential to scientific inquiry. Habits of mind include tolerance of ambiguity, skepticism, openness to new ideas, and objectivity. Other knowledge and skills include mathematics, reading, writin ...
Features of Earth`s Crust, Mantle, and Core
... Earth’s Mantle The solid material of the mantle is a layer of hot rock. Earth’s mantle is made of rock that is very hot, but solid. Scientists divide the mantle into layers based on the physical characteristics of those layers. Overall, the mantle is nearly 3,000 kilometers thick. Geologists often g ...
... Earth’s Mantle The solid material of the mantle is a layer of hot rock. Earth’s mantle is made of rock that is very hot, but solid. Scientists divide the mantle into layers based on the physical characteristics of those layers. Overall, the mantle is nearly 3,000 kilometers thick. Geologists often g ...
Earthquake Study Guide Key
... Earthquakes and volcanoes both tend to occur along plate boundaries. The most common area for earthquakes and volcanoes worldwide is the Ring of Fire (The Circum-Pacific Belt). The Ring of Fire is a nearly continuous chain of volcanoes around the edges of the Pacific Ocean. 7. What can the locations ...
... Earthquakes and volcanoes both tend to occur along plate boundaries. The most common area for earthquakes and volcanoes worldwide is the Ring of Fire (The Circum-Pacific Belt). The Ring of Fire is a nearly continuous chain of volcanoes around the edges of the Pacific Ocean. 7. What can the locations ...
Section 19.2
... know today had once been part of an earlier supercontinent. He called this great landmass Pangaea. ...
... know today had once been part of an earlier supercontinent. He called this great landmass Pangaea. ...
200 200 200 200 200 200 400 400 400 400 400 400 600 600 600
... In our model of sea-floor spreading, describe which type of plate boundary was found at each of the two areas of activity and tell which plate boundary was not represented in the model. ...
... In our model of sea-floor spreading, describe which type of plate boundary was found at each of the two areas of activity and tell which plate boundary was not represented in the model. ...
This is - Welcome to St Paul Lutheran Church & School
... In our model of sea-floor spreading, describe which type of plate boundary was found at each of the two areas of activity and tell which plate boundary was not represented in the model. ...
... In our model of sea-floor spreading, describe which type of plate boundary was found at each of the two areas of activity and tell which plate boundary was not represented in the model. ...
File
... In our model of sea-floor spreading, describe which type of plate boundary was found at each of the two areas of activity and tell which plate boundary was not represented in the model. ...
... In our model of sea-floor spreading, describe which type of plate boundary was found at each of the two areas of activity and tell which plate boundary was not represented in the model. ...
Notes: Ocean Floor
... •What is the deepest place in our oceans? _____________________________________ •What type of plate boundary make deep oceanic trenches? ________________________ •Where is sediment carried by rivers deposited in our oceans? ______________________ •What type of plate boundary is located at mid-ocean ...
... •What is the deepest place in our oceans? _____________________________________ •What type of plate boundary make deep oceanic trenches? ________________________ •Where is sediment carried by rivers deposited in our oceans? ______________________ •What type of plate boundary is located at mid-ocean ...
Dynamic Crust
... OPPOSITE THE FOCUS OF THE EARTHQUAKE. SEISMIC STATIONS RECEIVE NEITHER P NOR S WAVES. THE CAUSE OF THE SHADOW ZONE IS THE EARTH’S OUTER CORE. S-WAVES CAN NOT TRAVEL THROUGH THE LIQUID OUTER CORE. WHILE P WAVES ARE REFRACTED (BENT) IN A SMOOTH ARC BACK TO THE SURFACE. ...
... OPPOSITE THE FOCUS OF THE EARTHQUAKE. SEISMIC STATIONS RECEIVE NEITHER P NOR S WAVES. THE CAUSE OF THE SHADOW ZONE IS THE EARTH’S OUTER CORE. S-WAVES CAN NOT TRAVEL THROUGH THE LIQUID OUTER CORE. WHILE P WAVES ARE REFRACTED (BENT) IN A SMOOTH ARC BACK TO THE SURFACE. ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.