Practice 1 - WordPress.com
... 14contacts where plates slide past each other. New oceanic crust is formed along one or 15more margins of each plate by material issuing from deeper layers of the Earth's crust, 16for example, by volcanic eruptions of lava at midocean ridges. If at such a spreading 17contact the two plates support c ...
... 14contacts where plates slide past each other. New oceanic crust is formed along one or 15more margins of each plate by material issuing from deeper layers of the Earth's crust, 16for example, by volcanic eruptions of lava at midocean ridges. If at such a spreading 17contact the two plates support c ...
Objective: Describe the composition and structure of Earth.
... Terms of Use: Tectonic Plates, Divergent Boundaries, Convergent Boundaries, Seafloor Spreading, Subduction, Convection ...
... Terms of Use: Tectonic Plates, Divergent Boundaries, Convergent Boundaries, Seafloor Spreading, Subduction, Convection ...
Plate Tectonics Vocabulary
... a break in a body of rock along which one block slides relative to another; a form of brittle strain ...
... a break in a body of rock along which one block slides relative to another; a form of brittle strain ...
Layers of the Earth - study notes
... Most of the earthquakes and volcanoes in the world occur where two plates meet. The most active area of volcanoes and earthquakes is called the Ring of Fire. It circles around the Pacific Ocean. The Atlantic Ocean is growing because the Mid Atlantic Ridge continues to separate. Magma seeps up ...
... Most of the earthquakes and volcanoes in the world occur where two plates meet. The most active area of volcanoes and earthquakes is called the Ring of Fire. It circles around the Pacific Ocean. The Atlantic Ocean is growing because the Mid Atlantic Ridge continues to separate. Magma seeps up ...
9th grade ch 3 notes simplified..
... 1. Convergent: 2 plates come towards each other. If one plate is an ocean plate, it will dive under the less dense continental plate, producing a subduction zone and a trench. If both are continents, the rock will fold, fault, and lead to mountain-building – like the Himalayas! 2. Transform: 2 p ...
... 1. Convergent: 2 plates come towards each other. If one plate is an ocean plate, it will dive under the less dense continental plate, producing a subduction zone and a trench. If both are continents, the rock will fold, fault, and lead to mountain-building – like the Himalayas! 2. Transform: 2 p ...
Tectonic And Surface Processes Interaction
... intimately coupled with degradation. The agents that intervene are water (such as running water, groundwater, waves, currents, tides) glaciers, mass wasting, and wind. The erosion causes the leveling of the relief and the deposition of the weathered and eroded material. It has been active throughout ...
... intimately coupled with degradation. The agents that intervene are water (such as running water, groundwater, waves, currents, tides) glaciers, mass wasting, and wind. The erosion causes the leveling of the relief and the deposition of the weathered and eroded material. It has been active throughout ...
video guide bb4
... 10. The theory explains that earth’s solid outer shell called the ______________________________________________ is broken into ____________________________________________. 11. Because _______________________% of the earth is covered in water, the majority of plate boundaries are found on the _____ ...
... 10. The theory explains that earth’s solid outer shell called the ______________________________________________ is broken into ____________________________________________. 11. Because _______________________% of the earth is covered in water, the majority of plate boundaries are found on the _____ ...
Ch 9 4 Testing Plate Tectonics
... earthquakes along the oceanic ridge system was shown to be consistent with the new theory Scientists have found that intermediate and deep focus earthquakes occur within the subducting plate as it goes into the mantle Shallow-focus earthquakes are produced as the descending slab reacts with the ...
... earthquakes along the oceanic ridge system was shown to be consistent with the new theory Scientists have found that intermediate and deep focus earthquakes occur within the subducting plate as it goes into the mantle Shallow-focus earthquakes are produced as the descending slab reacts with the ...
Continental Drift and Sea-Floor Spreading 7.2
... switched directions every time the Earth’s polarity switched. ...
... switched directions every time the Earth’s polarity switched. ...
Hello this is Venus Ice, and this is a podcast for 6th grade science
... Then in 1947 the army was mapping the ocean floor and discovered the midAtlantic ridge. With this new discovery came a new theory. The theory of plate tectonics. The tectonic theory says that the earth’s surface is fragmented into huge slabs called tectonic plates. These chunks of the earth’s crust ...
... Then in 1947 the army was mapping the ocean floor and discovered the midAtlantic ridge. With this new discovery came a new theory. The theory of plate tectonics. The tectonic theory says that the earth’s surface is fragmented into huge slabs called tectonic plates. These chunks of the earth’s crust ...
View the Sample
... Earths surface follows the release for energy Seismic waves travel outwards from the source of earthquakes Some are high frequency and some are very low This vibration cause the earth to move A fault is the fracture in the earth crust and slipped rock. These faults are divided into three – Normal Fa ...
... Earths surface follows the release for energy Seismic waves travel outwards from the source of earthquakes Some are high frequency and some are very low This vibration cause the earth to move A fault is the fracture in the earth crust and slipped rock. These faults are divided into three – Normal Fa ...
6th Grade Earth Science
... • _________ - solid particles that are moved from sediments one place to another deposition __________ - sediments that form during weathering and erosion are deposited in another location During the process of deposition, the _______ and shape direction of a river’s flow changes ________ As rivers ...
... • _________ - solid particles that are moved from sediments one place to another deposition __________ - sediments that form during weathering and erosion are deposited in another location During the process of deposition, the _______ and shape direction of a river’s flow changes ________ As rivers ...
SCHOOL---SCIENCE---Grade-3---Earth-Changes
... 13. Earth’s ________________________ makes up the continents and the ocean floor. 14. Earth’s crust is a(n) ________________________________, cool layer. 15. Under the crust is a layer called the ___________________________. 16. The deepest and hottest layer of the Earth is the _______________. 17. ...
... 13. Earth’s ________________________ makes up the continents and the ocean floor. 14. Earth’s crust is a(n) ________________________________, cool layer. 15. Under the crust is a layer called the ___________________________. 16. The deepest and hottest layer of the Earth is the _______________. 17. ...
Plate Tectonics
... Alfred Wegner • (1910s) German scientist who believed all continents were once joined together in one giant landmass called... ...
... Alfred Wegner • (1910s) German scientist who believed all continents were once joined together in one giant landmass called... ...
Earth science quarter 3 review sheet
... 34. review tension (normal fault), compression (reverse fault) and shear (strike slip fault) 35. surface waves are the most destructive 36. Kilauea is the most active volcano, and is non explosive 37. it may take 1,000 years for new topsoil to form 38. what is no till farming – leave last year’s pl ...
... 34. review tension (normal fault), compression (reverse fault) and shear (strike slip fault) 35. surface waves are the most destructive 36. Kilauea is the most active volcano, and is non explosive 37. it may take 1,000 years for new topsoil to form 38. what is no till farming – leave last year’s pl ...
Warm- Up
... Which later of Earth contains the greatest volume and what percentage of Earth’s volume does it make up? What are the 2 metals that make up the core? ...
... Which later of Earth contains the greatest volume and what percentage of Earth’s volume does it make up? What are the 2 metals that make up the core? ...
EARTH LAYERS PROJECT DUE: Monday September 29, 2014 To
... Pretend that you are about to embark on a journey to the center of the earth. Discuss in detail the type of clothing you will need to wear, the equipment to help you dig your way to the center of the earth. The 8 layers you will go through in their correct order, a brief description and important in ...
... Pretend that you are about to embark on a journey to the center of the earth. Discuss in detail the type of clothing you will need to wear, the equipment to help you dig your way to the center of the earth. The 8 layers you will go through in their correct order, a brief description and important in ...
The Layer`s Of The Earth!
... Made up of large amounts of silicon and aluminum (Common rocks: Basalt and Granite) Two types of crust: oceanic crust and continental crust Composed of plates on which the continents and oceans rest ...
... Made up of large amounts of silicon and aluminum (Common rocks: Basalt and Granite) Two types of crust: oceanic crust and continental crust Composed of plates on which the continents and oceans rest ...
Author - Princeton ISD
... meter sticks, magnets, collecting nets, and notebooks; timing devices, including clocks and stopwatches materials to support observations of habitats or organisms such as terrariums and aquariums. ...
... meter sticks, magnets, collecting nets, and notebooks; timing devices, including clocks and stopwatches materials to support observations of habitats or organisms such as terrariums and aquariums. ...
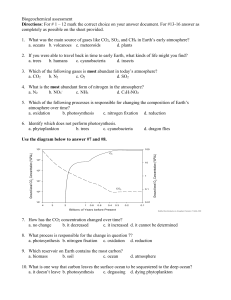
Biogeochemical assessments
... c. Draw a simple diagram of two forms of life that make a complete cycle of consumption/production of O2 and the gas in question b. 15. Nitrogen cycle a. How biologically available is N2? Can every life form use it? b. How do animals acquire nitrogen from the environment? c. Explain how nitrogen get ...
... c. Draw a simple diagram of two forms of life that make a complete cycle of consumption/production of O2 and the gas in question b. 15. Nitrogen cycle a. How biologically available is N2? Can every life form use it? b. How do animals acquire nitrogen from the environment? c. Explain how nitrogen get ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.