Lesson 37 Causes of Extinction
... Lesson 37 Causes of Extinction Extinction and its effects Extinctions occurs ______________________ over time. Extinctions occur after a sudden, drastic change in the ______________________. Populations may not be able to ______________________ to survive the change. Natural Causes of Extinction 99 ...
... Lesson 37 Causes of Extinction Extinction and its effects Extinctions occurs ______________________ over time. Extinctions occur after a sudden, drastic change in the ______________________. Populations may not be able to ______________________ to survive the change. Natural Causes of Extinction 99 ...
Plate Tectonics – Study Guide
... 1. A_____ W______ found evidence of continental drift. When he proposed this theory at first he could not identify the force that would move tectonic plates; other _____ did not accept his theory because he could not explain what could move such large plates. Later scientists linked the idea of c___ ...
... 1. A_____ W______ found evidence of continental drift. When he proposed this theory at first he could not identify the force that would move tectonic plates; other _____ did not accept his theory because he could not explain what could move such large plates. Later scientists linked the idea of c___ ...
Pangea
... Jurassic time period, about 175 million years ago. Have you ever noticed that the east coast of South America and the west coast of Africa look like they could fit together like a giant jig saw puzzle? That's because they used to be stuck together. At one point North America, Greenland and Europe ...
... Jurassic time period, about 175 million years ago. Have you ever noticed that the east coast of South America and the west coast of Africa look like they could fit together like a giant jig saw puzzle? That's because they used to be stuck together. At one point North America, Greenland and Europe ...
Activity 1 quiz File
... 10) _____ Which type of seismic wave arrives first at the seismic station on the surface because it travels the fastest? a) S-waves b) P-waves c) Surface waves 11) _____ Which type of seismic wave causes the most damage to buildings? a) S-waves b) P-waves c) Surface waves 12) _____ Which type of se ...
... 10) _____ Which type of seismic wave arrives first at the seismic station on the surface because it travels the fastest? a) S-waves b) P-waves c) Surface waves 11) _____ Which type of seismic wave causes the most damage to buildings? a) S-waves b) P-waves c) Surface waves 12) _____ Which type of se ...
EES Chapter 8 and Plate Tectonics Review - Bennatti
... ______________________3. Area of a fault where an earthquake has not occurred for many years ______________________4. Fast moving compressional seismic waves that travel through the Earth _____________________5. Thin layer of rock on the surface of the Earth _____________________6. Region where a de ...
... ______________________3. Area of a fault where an earthquake has not occurred for many years ______________________4. Fast moving compressional seismic waves that travel through the Earth _____________________5. Thin layer of rock on the surface of the Earth _____________________6. Region where a de ...
SOL_5.7_Earth
... Ocean trenches are created when a plate carrying ocean floor collides (convergent) with another plate. Volcanic activity can occur at divergent and convergent plate boundaries. ...
... Ocean trenches are created when a plate carrying ocean floor collides (convergent) with another plate. Volcanic activity can occur at divergent and convergent plate boundaries. ...
Chapter 10 * Plate Tectonics
... a single landmass called a supercontinent. According to Wegener, this supercontinent began breaking up into smaller continents during the Mesozoic Era (250 million years ago). It has taken millions of years for these continents to drift to their present locations. Some mountains may be the result of ...
... a single landmass called a supercontinent. According to Wegener, this supercontinent began breaking up into smaller continents during the Mesozoic Era (250 million years ago). It has taken millions of years for these continents to drift to their present locations. Some mountains may be the result of ...
ES Chapter 11 Notes - Ridgefield School District
... 12.2 Eruptions - Eruptions depend on 3 factors ...
... 12.2 Eruptions - Eruptions depend on 3 factors ...
Earth Systems 3209 - Heritage Collegiate
... different from] the current causes. 12. The rates of natural processes [do/do not] vary at different times and different places. 13. Uniformitarianism requires that Earth be [older/younger] than the age required by catastrophism. 14. Placing events in proper sequence is known as [relative/absolute] ...
... different from] the current causes. 12. The rates of natural processes [do/do not] vary at different times and different places. 13. Uniformitarianism requires that Earth be [older/younger] than the age required by catastrophism. 14. Placing events in proper sequence is known as [relative/absolute] ...
Dynamic Earth Webquest
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time ...
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time ...
GEO Team Practice Test Question Stems
... ____ 13. In Figure 3-1, what process or processes would be occurring in the part of the rock cycle labeled E? ____ 14. A rock that forms from cooling lava is classified as an ____. ____ 15. When large masses of magma solidify far below Earth’s surface, they form igneous rocks that have a ____. ____ ...
... ____ 13. In Figure 3-1, what process or processes would be occurring in the part of the rock cycle labeled E? ____ 14. A rock that forms from cooling lava is classified as an ____. ____ 15. When large masses of magma solidify far below Earth’s surface, they form igneous rocks that have a ____. ____ ...
1 - contentextra
... and the United Nations to adopt better governance of the largely unprotected high seas, and to enact measures that would better conserve ocean ecosystems. [3 marks] 3. (i) global volcanic eruption leading to rapid climate change; catastrophic events such as meteorite impact leading to rapid climate ...
... and the United Nations to adopt better governance of the largely unprotected high seas, and to enact measures that would better conserve ocean ecosystems. [3 marks] 3. (i) global volcanic eruption leading to rapid climate change; catastrophic events such as meteorite impact leading to rapid climate ...
Plate Boundaries and Earthquake Science
... we will go over some example questions at the start of the lecture today o material covered: first 8 lectures (including the video) o up to next Tuesday's class Prof. Ramsey will return for that class and answer any exam-related ...
... we will go over some example questions at the start of the lecture today o material covered: first 8 lectures (including the video) o up to next Tuesday's class Prof. Ramsey will return for that class and answer any exam-related ...
4 Resources from the Ocean Critical Thinking
... What Are the Living Resources of the Ocean? People have been harvesting plants and animals from the ocean for thousands of years. Today, harvesting food from the ocean is a multi-billion-dollar industry. As the population of humans on Earth has grown, the demand for these resources has increased. Ho ...
... What Are the Living Resources of the Ocean? People have been harvesting plants and animals from the ocean for thousands of years. Today, harvesting food from the ocean is a multi-billion-dollar industry. As the population of humans on Earth has grown, the demand for these resources has increased. Ho ...
Geology Study Guide
... recrystallization, melting, and metamorphism. (Page 90 – 111) Weathering is the process of breaking down rock into smaller pieces called sediment by water, wind, ice or heat. Erosion is the process by which wind, water, ice or gravity will transport soil and sediment from one place to another. Depos ...
... recrystallization, melting, and metamorphism. (Page 90 – 111) Weathering is the process of breaking down rock into smaller pieces called sediment by water, wind, ice or heat. Erosion is the process by which wind, water, ice or gravity will transport soil and sediment from one place to another. Depos ...
The Solid Earth
... classified by particles size (eg. conglomerate, sandstone, shale) particle size related to distance from source and transport mechanism chemical sedimentary rocks material carried in solution to lakes and seas physical precipitation biochemical (water ingested by water-dwelling creatures and solid m ...
... classified by particles size (eg. conglomerate, sandstone, shale) particle size related to distance from source and transport mechanism chemical sedimentary rocks material carried in solution to lakes and seas physical precipitation biochemical (water ingested by water-dwelling creatures and solid m ...
Take A Journey to… - Mr. Jensen`s Science
... the metals are squeezed together and are not able to move about like a liquid, but are forced to vibrate in place as a solid. • The inner core is made of nickel and iron. • The inner core begins about 4000 miles beneath the crust and is about 800 miles thick. ...
... the metals are squeezed together and are not able to move about like a liquid, but are forced to vibrate in place as a solid. • The inner core is made of nickel and iron. • The inner core begins about 4000 miles beneath the crust and is about 800 miles thick. ...
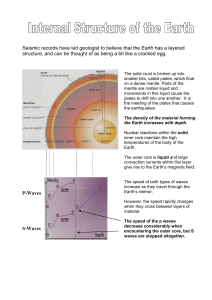
Internal Structure of the Earth File
... on a dense mantle. Parts of the mantle are molten liquid and movements in this liquid cause the plates to drift into one another. It is the meeting of the plates that causes the earthquakes. The density of the material forming the Earth increases with depth. Nuclear reactions within the solid inner ...
... on a dense mantle. Parts of the mantle are molten liquid and movements in this liquid cause the plates to drift into one another. It is the meeting of the plates that causes the earthquakes. The density of the material forming the Earth increases with depth. Nuclear reactions within the solid inner ...
Plate Tectonics Vocabulary Continental Drift The
... A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other A break or crack in Earth’s lithosphere along which the rocks move The preserved remains or traces of living things The undersea mountain chain where new ocean floor is produced The name of the single landmass that broke apart 225 million y ...
... A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other A break or crack in Earth’s lithosphere along which the rocks move The preserved remains or traces of living things The undersea mountain chain where new ocean floor is produced The name of the single landmass that broke apart 225 million y ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Part 1 Multiple Choice
... 24. Which of the following was the biggest problem with Wegener's Theory of Continental Drift? a. He could not explain the mechanism for movement of the continents b. Too many scientists already came up with the same theory c. All of his evidence turned out to be fake 25. Which two mountain ranges a ...
... 24. Which of the following was the biggest problem with Wegener's Theory of Continental Drift? a. He could not explain the mechanism for movement of the continents b. Too many scientists already came up with the same theory c. All of his evidence turned out to be fake 25. Which two mountain ranges a ...
The Quran on Mountains DOC
... to describe mountains on the basis of this information is the word ‘peg,’ since most of a properly set peg is hidden under the surface of the ground. The history of science tells us that the theory of mountains having deep roots was introduced only in the latter half of the nineteenth century.3 Moun ...
... to describe mountains on the basis of this information is the word ‘peg,’ since most of a properly set peg is hidden under the surface of the ground. The history of science tells us that the theory of mountains having deep roots was introduced only in the latter half of the nineteenth century.3 Moun ...
Topic/Objective: ______ _____ Full Name: __________ Class: __
... The locus of _______________ movement is called a ___________. Faults come in all _______________, millimeter to meters of separation of _____________________ plates. The initial point of a rupture or source is known as the ______________ of the earthquake. The point on the earth’s ___________ ...
... The locus of _______________ movement is called a ___________. Faults come in all _______________, millimeter to meters of separation of _____________________ plates. The initial point of a rupture or source is known as the ______________ of the earthquake. The point on the earth’s ___________ ...
Name
... the exact distance between the satellites and the ground station. Over time, these distances change slightly. By recording the time it takes for the GPS ground stations to move a given distance, scientists can measure the speed at which each tectonic plate moves. What happens when plates separate on ...
... the exact distance between the satellites and the ground station. Over time, these distances change slightly. By recording the time it takes for the GPS ground stations to move a given distance, scientists can measure the speed at which each tectonic plate moves. What happens when plates separate on ...
Reading: Inside Earth
... outer skin. On the crust you find rocks and mountains. But the crust also includes the soil and water that cover large parts of Earth's surface. This outer rind of rock is much thinner than what lies beneath it. In fact, you can think of Earth's crust as being similar to the paper-thin skin of an on ...
... outer skin. On the crust you find rocks and mountains. But the crust also includes the soil and water that cover large parts of Earth's surface. This outer rind of rock is much thinner than what lies beneath it. In fact, you can think of Earth's crust as being similar to the paper-thin skin of an on ...
Michela Griffin
... Mineral: naturally occurring, inorganic, solid element or composed with a definite chemical composition and a regular internal crystal structure Most fundamental characteristics: 1) Chemical Composition and 2) Crystal Structure No 2 Minerals are the same ...
... Mineral: naturally occurring, inorganic, solid element or composed with a definite chemical composition and a regular internal crystal structure Most fundamental characteristics: 1) Chemical Composition and 2) Crystal Structure No 2 Minerals are the same ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.