Part A The Rock Cycle
... 15. In the process of FRACTIONAL CRYSTALLIZATION, early-formed crystals may settle out of the magma, thus changing the composition of the remaining melt. 16. The process by which a magma incorporates the rock around it is called ASSIMILATION. 17. In magma mixing, two or more magmas combine to produc ...
... 15. In the process of FRACTIONAL CRYSTALLIZATION, early-formed crystals may settle out of the magma, thus changing the composition of the remaining melt. 16. The process by which a magma incorporates the rock around it is called ASSIMILATION. 17. In magma mixing, two or more magmas combine to produc ...
Rock Cycle Questions and Short Story
... 1. Magma rose from the mantle and slowly cooled in a crack deep below the earth’s surface. 2. An earthquake shook a mountain causing an avalanche. The rocks fell down the side of a mountain and landed in a shallow ocean where they were buried for millions of years. 3. A river carried little sand gra ...
... 1. Magma rose from the mantle and slowly cooled in a crack deep below the earth’s surface. 2. An earthquake shook a mountain causing an avalanche. The rocks fell down the side of a mountain and landed in a shallow ocean where they were buried for millions of years. 3. A river carried little sand gra ...
Chapter 4 Exercises 1. Observations and experiments show that rate
... 7. Plutons are more likely than dikes to show the effects of fractional crystallization because they contain a larger volume of melted material and have less surface area for their size and thus are likely to cool more slowing than dikes. 8. The origin of a rock composed almost entirely of olivine w ...
... 7. Plutons are more likely than dikes to show the effects of fractional crystallization because they contain a larger volume of melted material and have less surface area for their size and thus are likely to cool more slowing than dikes. 8. The origin of a rock composed almost entirely of olivine w ...
Earth Science – Quiz 2
... D) as ash particles that join together in the eruptive plume and fall as cobble-sized objects 68. ________ magma is the most abundant type of magma erupted at oceanic spreading centers. A) Basaltic B) Granitic C) Andesitic D) Pegmatitic 69. Why would a plume of solid silicate rock rising slowly from ...
... D) as ash particles that join together in the eruptive plume and fall as cobble-sized objects 68. ________ magma is the most abundant type of magma erupted at oceanic spreading centers. A) Basaltic B) Granitic C) Andesitic D) Pegmatitic 69. Why would a plume of solid silicate rock rising slowly from ...
Chapter 6.2: Igneous Rocks
... • Magma rises slowly through the crust before erupting to the surface – Within the crust, large crystals can grow – On the surface, cooling stops any more crystals from growing ...
... • Magma rises slowly through the crust before erupting to the surface – Within the crust, large crystals can grow – On the surface, cooling stops any more crystals from growing ...
Rock Cycle Slideshow
... Extrusive Igneous Rocks • Form above the surface • Lava cools quickly when exposed to air • Forms small crystal • Fine grained texture • Frothy texture • Glassy texture • Examples: Basalt and Obsidian ...
... Extrusive Igneous Rocks • Form above the surface • Lava cools quickly when exposed to air • Forms small crystal • Fine grained texture • Frothy texture • Glassy texture • Examples: Basalt and Obsidian ...
Bedrock Geology Glossary
... Shale: A deposit of clay, silt, or mud solidified into more or less a solid rock. Siltstone: A sedimentary rock made primarily of sand. ...
... Shale: A deposit of clay, silt, or mud solidified into more or less a solid rock. Siltstone: A sedimentary rock made primarily of sand. ...
Geology Review Sheet
... 2. Explain the steps of the rock cycle, how each type of rock forms, and the processes that form different types of rocks. Be able to describe how one rock transforms into another. 3. Explain the relationships between the type of plate boundary and the likely depth, magnitude, and intensity of an ea ...
... 2. Explain the steps of the rock cycle, how each type of rock forms, and the processes that form different types of rocks. Be able to describe how one rock transforms into another. 3. Explain the relationships between the type of plate boundary and the likely depth, magnitude, and intensity of an ea ...
Volcano Lab 16-17 File
... Igneous rock was once melted and cooled to form a solid. The faster the rock cools, the smaller the crystals in the rock. When rock cools very inside the earth slowly we call it intrusive. The crystals that form grow to large sizes like the granite in our lab desk tops. When rocks cool quickly, near ...
... Igneous rock was once melted and cooled to form a solid. The faster the rock cools, the smaller the crystals in the rock. When rock cools very inside the earth slowly we call it intrusive. The crystals that form grow to large sizes like the granite in our lab desk tops. When rocks cool quickly, near ...
Phases of activity and geochemistry of basaltic dike systems in
... K – Ar dates, petrographic and chemical data were obtained from representative samples from three NW –SE trending basaltic dikes in the Harrat Ash Shaam Volcanic Field, northeast Jordan. Compared with other NE – SW trending dikes in Jordan, three phases of activity were determined for the studied di ...
... K – Ar dates, petrographic and chemical data were obtained from representative samples from three NW –SE trending basaltic dikes in the Harrat Ash Shaam Volcanic Field, northeast Jordan. Compared with other NE – SW trending dikes in Jordan, three phases of activity were determined for the studied di ...
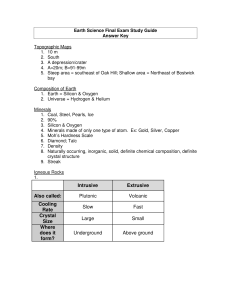
Final Exam Study Guide Answer Key
... 3. Silicon & Oxygen 4. Minerals made of only one type of atom. Ex: Gold, Silver, Copper 5. Moh’s Hardness Scale 6. Diamond; Talc 7. Density 8. Naturally occurring, inorganic, solid, definite chemical composition, definite crystal structure 9. Streak Igneous Rocks ...
... 3. Silicon & Oxygen 4. Minerals made of only one type of atom. Ex: Gold, Silver, Copper 5. Moh’s Hardness Scale 6. Diamond; Talc 7. Density 8. Naturally occurring, inorganic, solid, definite chemical composition, definite crystal structure 9. Streak Igneous Rocks ...
Review for Earth Science Test
... It is the shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth’s surface. 6. What is streak? It is the color of a mineral’s powder. 7. What is Mohs’ Hardness Scale? It is the scale used by scientists to classify minerals according to their hardness. 8. What is the rock cycle? It is a series ...
... It is the shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth’s surface. 6. What is streak? It is the color of a mineral’s powder. 7. What is Mohs’ Hardness Scale? It is the scale used by scientists to classify minerals according to their hardness. 8. What is the rock cycle? It is a series ...
Obtaining information about inside the earth.
... causes strong weathering and that’s how the rivers were formed. Sandstone is the breakdown of granite ...
... causes strong weathering and that’s how the rivers were formed. Sandstone is the breakdown of granite ...
Composite Volcanoes - Wallkill Valley Regional High School
... Composite Volcanoes Build up over time with alternating ash fallouts and lava flows, tendency to generate extremely violent events mixed with more moderate events. ...
... Composite Volcanoes Build up over time with alternating ash fallouts and lava flows, tendency to generate extremely violent events mixed with more moderate events. ...
11 EG SP Exam 1 Review
... What is thought to have caused the extinctions of the dinosaurs? Diagram the rock cycle Diagram the hydrologic cycle Chapter 2 Minerals Do minerals with the lowest silica content melt at the lowest temperatures? What is the definition of a mineral? Which of the following is not a rock-forming minera ...
... What is thought to have caused the extinctions of the dinosaurs? Diagram the rock cycle Diagram the hydrologic cycle Chapter 2 Minerals Do minerals with the lowest silica content melt at the lowest temperatures? What is the definition of a mineral? Which of the following is not a rock-forming minera ...
300_S2005_solid_earth
... gemstones (many have names different from their mineral names) diamond sapphire = corundum = aluminum oxide + impurities with titanium + iron (blue sapphire) with chromium (red ruby) ...
... gemstones (many have names different from their mineral names) diamond sapphire = corundum = aluminum oxide + impurities with titanium + iron (blue sapphire) with chromium (red ruby) ...
Earth Scie Intro 2016
... Gas- a state of matter where particles move quickly and are far apart from each other Lava- hot, molten rock found on the outside of a volcano Magma- hot, molten rock found on the inside of a volcano Flow- the speed at which lava moves. Flow rate depends on the thickness of the lava Land- solid pie ...
... Gas- a state of matter where particles move quickly and are far apart from each other Lava- hot, molten rock found on the outside of a volcano Magma- hot, molten rock found on the inside of a volcano Flow- the speed at which lava moves. Flow rate depends on the thickness of the lava Land- solid pie ...
diverse intrusive and volcanic rocks in the axis of the abandoned
... match OIB and EMORB well but have negative Sr anomalies (Fig.4). The intrusive rhyolite (75 wt.% SiO2) shows LREE-enrichment with a small negative Eu anomaly. The granite varies in SiO2 from 72.2 to 57.5 wt.% as it approaches the gabbro contact. The REE pattern of the granite is very ...
... match OIB and EMORB well but have negative Sr anomalies (Fig.4). The intrusive rhyolite (75 wt.% SiO2) shows LREE-enrichment with a small negative Eu anomaly. The granite varies in SiO2 from 72.2 to 57.5 wt.% as it approaches the gabbro contact. The REE pattern of the granite is very ...
Review Sheet for Exam 1
... How igneous rocks form and the two categories of igneous rocks Igneous textures & what they tell you about the rock that they make up Bowen’s Reaction Series (and the temperatures associated with the crystallization of mafic and felsic minerals) Processes that change the composition of magma ...
... How igneous rocks form and the two categories of igneous rocks Igneous textures & what they tell you about the rock that they make up Bowen’s Reaction Series (and the temperatures associated with the crystallization of mafic and felsic minerals) Processes that change the composition of magma ...
ACROSS 3 ______ is the way a mineral reflects light off it`s surface 6
... 2 ______ rock forms from cooling magma below the surface or cooling lava on the surface 4 Igneous rocks found under the surface of the Earth are known as ______ rocks 5 When a mineral does not split apart evenly it is known as ______ 10 ______ and pressure can create metamorphic rock 12 ______ is wh ...
... 2 ______ rock forms from cooling magma below the surface or cooling lava on the surface 4 Igneous rocks found under the surface of the Earth are known as ______ rocks 5 When a mineral does not split apart evenly it is known as ______ 10 ______ and pressure can create metamorphic rock 12 ______ is wh ...
Igneous Rock Classification.
... thin, widespread sheets of mafic rock. These occur either by subaerial eruption of fluid basalt at rifts within continents, or by intrusion of mafic magma as near-surface sills between layers of cooler sediments. ...
... thin, widespread sheets of mafic rock. These occur either by subaerial eruption of fluid basalt at rifts within continents, or by intrusion of mafic magma as near-surface sills between layers of cooler sediments. ...
Basalt

Basalt (pronounced /bəˈsɔːlt/, /ˈbæsɒlt/, /ˈbæsɔːlt/, or /ˈbeɪsɔːlt/)is a common extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock formed from the rapid cooling of basaltic lava exposed at or very near the surface of a planet or moon. Flood basalt describes the formation in a series of lava basalt flows.