Dual Credit Major Topics for Studying
... Dual Credit Major Topics for Studying Plate Tectonics Earth’s structure: Layers and properties (i.e. crust, mantle core) Names of plates Continental Drift Types of volcanoes; magma types (felsic and maffic) Features of volcanoes Lava types Seismic waves, earthquakes liquefaction 20 ...
... Dual Credit Major Topics for Studying Plate Tectonics Earth’s structure: Layers and properties (i.e. crust, mantle core) Names of plates Continental Drift Types of volcanoes; magma types (felsic and maffic) Features of volcanoes Lava types Seismic waves, earthquakes liquefaction 20 ...
A Mountain Fact Sheet: Is A Mountain a volcano
... lava leaves the volcano it flows outward or explodes upward depending on its viscosity (thickness) and water content (explosivity). The bubbles, rough texture, and outlines of distinct flows show us that the lava that formed the basalt at the base of A Mountain was non-explosive as it flowed from th ...
... lava leaves the volcano it flows outward or explodes upward depending on its viscosity (thickness) and water content (explosivity). The bubbles, rough texture, and outlines of distinct flows show us that the lava that formed the basalt at the base of A Mountain was non-explosive as it flowed from th ...
Geology of Lava Beds National Monument
... Any errors or omissions, however, are solely the responsibility of the author. Location and Geologic Setting LBNM is located in the in eastern Siskiyou County just south of the Oregon border and southwest of the town of Tulelake (Fig. 1). The monument was established in 1935 to preserve a diverse su ...
... Any errors or omissions, however, are solely the responsibility of the author. Location and Geologic Setting LBNM is located in the in eastern Siskiyou County just south of the Oregon border and southwest of the town of Tulelake (Fig. 1). The monument was established in 1935 to preserve a diverse su ...
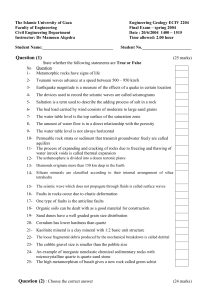
Question (1) (25 marks) State whether the following statements are
... 16- Faults in rocks occur due to elastic deformation 17- One type of faults is the anticline faults 18- Organic soils can be dealt with as a good material for construction 19- Sand dunes have a well graded grain size distribution 20- Corndum has lower hardness than quartz 21- Kaolinite mineral is a ...
... 16- Faults in rocks occur due to elastic deformation 17- One type of faults is the anticline faults 18- Organic soils can be dealt with as a good material for construction 19- Sand dunes have a well graded grain size distribution 20- Corndum has lower hardness than quartz 21- Kaolinite mineral is a ...
KEY
... ridges, such eruptions are known as FISSURE eruptions. 13. The contractions of cooing lava may produce polygonal columns know as COLUMNAR JOINTING. ...
... ridges, such eruptions are known as FISSURE eruptions. 13. The contractions of cooing lava may produce polygonal columns know as COLUMNAR JOINTING. ...
TYPES OF CRUSTAL MATERIAL
... is composed of two basic types of crustal material. We refer to these as continental crust and oceanic crust. These types of crust differ in several ways. While both are made mostly of igneous rocks (that is, rocks that solidify from molten material), they have different compositions. Ocean crust is ...
... is composed of two basic types of crustal material. We refer to these as continental crust and oceanic crust. These types of crust differ in several ways. While both are made mostly of igneous rocks (that is, rocks that solidify from molten material), they have different compositions. Ocean crust is ...
Chapter 12 - Fill-in-the
... An unusually hot area between the __________ & core that forces melted rock upward to form __________ in the middle of tectonic plates. Plate moves as the hot spot is __________. Volcanic __________ • The __________ of a volcano depends on: ...
... An unusually hot area between the __________ & core that forces melted rock upward to form __________ in the middle of tectonic plates. Plate moves as the hot spot is __________. Volcanic __________ • The __________ of a volcano depends on: ...
Introduction
... Taranaki began erupting about 130,000 years ago, with large eruptions occurring on average every 500 years and smaller eruptions about 90 years apart. An explosive mediumsized ash eruption occurred around 1755 AD and minor volcanic events (creation of a lava dome in the crater and its collapse) occu ...
... Taranaki began erupting about 130,000 years ago, with large eruptions occurring on average every 500 years and smaller eruptions about 90 years apart. An explosive mediumsized ash eruption occurred around 1755 AD and minor volcanic events (creation of a lava dome in the crater and its collapse) occu ...
Word format
... flows the fastest and furthest? A. felsic B. intermediate C. mafic D. magma E. ketchup When lava erupts and cools, if may form a groundmass of small crystals occurring together with larger phenocrysts that grew in the magma while it was still inside the Earth. The resultant type of igneous rock text ...
... flows the fastest and furthest? A. felsic B. intermediate C. mafic D. magma E. ketchup When lava erupts and cools, if may form a groundmass of small crystals occurring together with larger phenocrysts that grew in the magma while it was still inside the Earth. The resultant type of igneous rock text ...
Chapter 12 PowerPoint
... –The steep-walled depression around a volcano’s vent is called the crater. ...
... –The steep-walled depression around a volcano’s vent is called the crater. ...
GEOL 2312 IGNEOUS AND METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY Lecture
... of a 2-layer dynamic mantle model in which the 660 km transition is a sufficient density barrier to separate lower mantle convection (arrows represent flow patterns) from upper mantle flow, largely a response to plate separation. The only significant things that can penetrate this barrier are vigoro ...
... of a 2-layer dynamic mantle model in which the 660 km transition is a sufficient density barrier to separate lower mantle convection (arrows represent flow patterns) from upper mantle flow, largely a response to plate separation. The only significant things that can penetrate this barrier are vigoro ...
GEOL1010 Hour Exam 1 Sample
... 34. A sedimentary rock composed of rounded sand-, pebble-, and cobble-sized particles is a: a) sandstone b) breccia c) conglomerate d)cobblestone e)shale 35. The most abundant mineral in most shale is: a) calcite b)clay c) quartz ...
... 34. A sedimentary rock composed of rounded sand-, pebble-, and cobble-sized particles is a: a) sandstone b) breccia c) conglomerate d)cobblestone e)shale 35. The most abundant mineral in most shale is: a) calcite b)clay c) quartz ...
1 Eons, Eras, Periods and Epochs Dating by radioactive isotopes
... Half-life: time for ½ of unstable isotopes to decay “Absolute time” ...
... Half-life: time for ½ of unstable isotopes to decay “Absolute time” ...
The habitability of vesicles in martian basalt
... may outline large polygonal columns. This layer cooled more slowly and so is dominantly crystalline with very few vesicles, although large (5–30 cm) cavities can form when gas is trapped below the earlier-solidifying upper crust. The basal zone is mostly glassy with sparse vesicles that become more ...
... may outline large polygonal columns. This layer cooled more slowly and so is dominantly crystalline with very few vesicles, although large (5–30 cm) cavities can form when gas is trapped below the earlier-solidifying upper crust. The basal zone is mostly glassy with sparse vesicles that become more ...
Igneous Rock PPT notes
... rock cools above ground. Usually they are formed after the material has been erupted by a volcano. 1. This molten material cools quickly. 2. No crystals are visible to the eye. ...
... rock cools above ground. Usually they are formed after the material has been erupted by a volcano. 1. This molten material cools quickly. 2. No crystals are visible to the eye. ...
Document
... 10. Although cement, brick, 11. Generally, a rock is 12. Texture is the size, steel, and glass all come made up of a mixture of shape, and pattern of the from substances found in _______ and other rock’s __________. Earth’s crust, they are not ___________. classified as minerals because they ______ ...
... 10. Although cement, brick, 11. Generally, a rock is 12. Texture is the size, steel, and glass all come made up of a mixture of shape, and pattern of the from substances found in _______ and other rock’s __________. Earth’s crust, they are not ___________. classified as minerals because they ______ ...
PDF
... nonmare igneous rocks have been classified into the following four types: (1) ferroan anorthosite (FAN) or ferroan anorthositic-suite (FAS), (2) magnesian suite (Mg-suites), (3) alkali-anorthosite-suite and (4) KREEP basalt and possibly related rocks such as quartz-monzogabbro (QMG) /monzodiorite (Q ...
... nonmare igneous rocks have been classified into the following four types: (1) ferroan anorthosite (FAN) or ferroan anorthositic-suite (FAS), (2) magnesian suite (Mg-suites), (3) alkali-anorthosite-suite and (4) KREEP basalt and possibly related rocks such as quartz-monzogabbro (QMG) /monzodiorite (Q ...
How old is our Earth
... 15. Magmatism in the subduction zone is a result of melting in the mantle due to _________ *A) introduction of water, B) reduction of pressure, C) increase of temperature D) mantle plumes 16. Which of the following represents a rock sample from the mantle? *A) Peridotite B) Komatitite C) Gabbro D) D ...
... 15. Magmatism in the subduction zone is a result of melting in the mantle due to _________ *A) introduction of water, B) reduction of pressure, C) increase of temperature D) mantle plumes 16. Which of the following represents a rock sample from the mantle? *A) Peridotite B) Komatitite C) Gabbro D) D ...
REVISED EXAM 3 STUDY GUIDE – PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY
... Can you define and give an example of each of the three types of volcanoes? Shield - Stratovolcano (composite, plug dome) - Cinder Cone How are they different from each other? Which one is the least explosive? Which one is the most explosive? Which ones have fluid basalt flows? Which ones have littl ...
... Can you define and give an example of each of the three types of volcanoes? Shield - Stratovolcano (composite, plug dome) - Cinder Cone How are they different from each other? Which one is the least explosive? Which one is the most explosive? Which ones have fluid basalt flows? Which ones have littl ...
Igneous rocks lecture
... • Ignis (Latin for fire) – these rocks were crystallized from a molten state. They are not formed by sediment accumulation. ...
... • Ignis (Latin for fire) – these rocks were crystallized from a molten state. They are not formed by sediment accumulation. ...
igneous rocks
... • Ignis (Latin for fire) – these rocks were crystallized from a molten state. They are not formed by sediment accumulation. ...
... • Ignis (Latin for fire) – these rocks were crystallized from a molten state. They are not formed by sediment accumulation. ...
Chapter 14
... Lava eruptions at the Earth’s surface form volcanoes and lava flows. Stratovolcanoes form from the eruption of thick, gassy, felsic lavas and are most common along the converging plate boundaries of the Pacific rim. They have steep sides and often produce explosive eruptions that form calderas ...
... Lava eruptions at the Earth’s surface form volcanoes and lava flows. Stratovolcanoes form from the eruption of thick, gassy, felsic lavas and are most common along the converging plate boundaries of the Pacific rim. They have steep sides and often produce explosive eruptions that form calderas ...
Basalt

Basalt (pronounced /bəˈsɔːlt/, /ˈbæsɒlt/, /ˈbæsɔːlt/, or /ˈbeɪsɔːlt/)is a common extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock formed from the rapid cooling of basaltic lava exposed at or very near the surface of a planet or moon. Flood basalt describes the formation in a series of lava basalt flows.