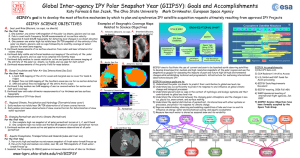
powerpoint poster - International Polar Year
... 2) Understand sea ice sufficiently to predict its response to and influence on global climate change and biological processes 3) Understand glaciers and ice caps in the context of hydrologic and biologic systems and their contributions to global sea level rise 4) Understand the interactions between ...
... 2) Understand sea ice sufficiently to predict its response to and influence on global climate change and biological processes 3) Understand glaciers and ice caps in the context of hydrologic and biologic systems and their contributions to global sea level rise 4) Understand the interactions between ...
Constructive and Destructive Forces on Earth vocb
... sediments as it flows into a lake or an ocean 13 .Floodplain land that has been formed by the deposition of sediments that occurs when the river floods 14 .Constructive processes that build up Earth's material (ex. Deposition) 15 .Destructive processes that break down Earth's material (ex. Erosion) ...
... sediments as it flows into a lake or an ocean 13 .Floodplain land that has been formed by the deposition of sediments that occurs when the river floods 14 .Constructive processes that build up Earth's material (ex. Deposition) 15 .Destructive processes that break down Earth's material (ex. Erosion) ...
Click on image to content
... formed rocks are then carried either East or West of the Mid-Ocean ridge. The floor of the Atlantic Ocean is thus an Age sequence with newly formed rock appearing at the Mid Atlantic Ridge and the oldest rocks being at the North American and European Coastlines. The time of transport from the mid At ...
... formed rocks are then carried either East or West of the Mid-Ocean ridge. The floor of the Atlantic Ocean is thus an Age sequence with newly formed rock appearing at the Mid Atlantic Ridge and the oldest rocks being at the North American and European Coastlines. The time of transport from the mid At ...
An active chain of volcanoes at p boundaries is called the Ring of F
... The rock at the Earth’s surface forms a nearly continuous shell around earth called the lithosphere. The lithosphere consists of the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle. It is believed to float on the “plastic” asthenosphere that is found just beneath it. Analysis of earthquake wave data (vib ...
... The rock at the Earth’s surface forms a nearly continuous shell around earth called the lithosphere. The lithosphere consists of the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle. It is believed to float on the “plastic” asthenosphere that is found just beneath it. Analysis of earthquake wave data (vib ...
F M2502 PAPER – II EARTH SCIENCES
... Amount of the sun’s energy that is absorbed by the earth’s surface, clouds, and atmosphere causes warming in percentage ...
... Amount of the sun’s energy that is absorbed by the earth’s surface, clouds, and atmosphere causes warming in percentage ...
Plate Tectonics (Chap. 3)
... Mantle: composed of Fe/Mg- rich silicates (olivine, pyroxene) Crust: continental – 20–90 km thick (old) Ocean crust- 5–10 km thick (young) Lithosphere: crust + upper mantle = “Plates” Asthenosphere: partially molten upper mantle Mantle: convection due to radioactive heating 3 types of plate boundary ...
... Mantle: composed of Fe/Mg- rich silicates (olivine, pyroxene) Crust: continental – 20–90 km thick (old) Ocean crust- 5–10 km thick (young) Lithosphere: crust + upper mantle = “Plates” Asthenosphere: partially molten upper mantle Mantle: convection due to radioactive heating 3 types of plate boundary ...
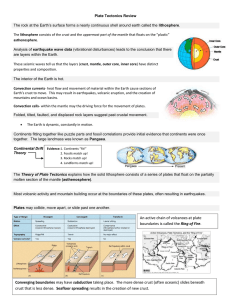
Plate Tectonics Review The rock at the Earth`s surface forms a
... These seismic waves tell us that the layers (crust, mantle, outer core, inner core) have distinct properties and composition. The interior of the Earth is hot. Convection currents- heat flow and movement of material within the Earth cause sections of Earth’s crust to move. This may result in earthqu ...
... These seismic waves tell us that the layers (crust, mantle, outer core, inner core) have distinct properties and composition. The interior of the Earth is hot. Convection currents- heat flow and movement of material within the Earth cause sections of Earth’s crust to move. This may result in earthqu ...
Dr. Thorsten Becker, UT Austin Abstract: Plate tectonics can be
... layer of Earth's mantle which is convecting over timescales of millions of years. However, how forces are transmitted depends on the flow strength of rocks (viscosity). For example, the low viscosity of the region underneath the plates, the asthenosphere, matters greatly for plate dynamics, and migh ...
... layer of Earth's mantle which is convecting over timescales of millions of years. However, how forces are transmitted depends on the flow strength of rocks (viscosity). For example, the low viscosity of the region underneath the plates, the asthenosphere, matters greatly for plate dynamics, and migh ...
Rocks and The Earth`s Interior
... • Lower mantle region between the asthenosphere and the outer core • It is the largest layer of the earth • This region, also called the lower mantle, is named in order to differentiate from the lithosphere and asthenosphere portions of the mantle • Higher pressure makes the mesosphere more solid th ...
... • Lower mantle region between the asthenosphere and the outer core • It is the largest layer of the earth • This region, also called the lower mantle, is named in order to differentiate from the lithosphere and asthenosphere portions of the mantle • Higher pressure makes the mesosphere more solid th ...
Lecture 6 - Rocks and The Earth`s Interior
... • Lower mantle region between the asthenosphere and the outer core • It is the largest layer of the earth • This region, also called the lower mantle, is named in order to differentiate from the lithosphere and asthenosphere portions of the mantle • Higher pressure makes the mesosphere more solid th ...
... • Lower mantle region between the asthenosphere and the outer core • It is the largest layer of the earth • This region, also called the lower mantle, is named in order to differentiate from the lithosphere and asthenosphere portions of the mantle • Higher pressure makes the mesosphere more solid th ...
rocks and the earth`s interior - FAU
... • Lower mantle region between the asthenosphere and the outer core • It is the largest layer of the earth • This region, also called the lower mantle, is named in order to differentiate from the lithosphere and asthenosphere portions of the mantle • Higher pressure makes the mesosphere more solid th ...
... • Lower mantle region between the asthenosphere and the outer core • It is the largest layer of the earth • This region, also called the lower mantle, is named in order to differentiate from the lithosphere and asthenosphere portions of the mantle • Higher pressure makes the mesosphere more solid th ...
Earthquake Notes
... Intraplate quakes occur far from plate edges and happen when stress builds up and the Earth's crust is stretched or squeezed together until it rips. ...
... Intraplate quakes occur far from plate edges and happen when stress builds up and the Earth's crust is stretched or squeezed together until it rips. ...
Plate Tectonic/Rock Cycle Crossward Puzzle
... 7. the uppermost mantle, along with the overlying crust, that behaves as a strong layer 9. forms when sediment is eventually compacted and cemented 10. molten material that forms deep beneath earth's surface 11. two plates grind past each other without harming the lithosphere 15. and thereby produce ...
... 7. the uppermost mantle, along with the overlying crust, that behaves as a strong layer 9. forms when sediment is eventually compacted and cemented 10. molten material that forms deep beneath earth's surface 11. two plates grind past each other without harming the lithosphere 15. and thereby produce ...
CHAPTER 3 TECTONICS Vatnajokull Glacier- Iceland
... Da Vinci, Bacon- fit of the continents Evidence: 1. Glassopteris 3. Glaciers 2. Rocks 4. Climate Pangea, Panthalassa Wadati-1935- earthquakes/ volcanoes may be associated with the continental drift Benioff-1940-revealed Pacific Ring of Fire Hess-1960s- Seafloor Spreading >Ocean Crust is young (less ...
... Da Vinci, Bacon- fit of the continents Evidence: 1. Glassopteris 3. Glaciers 2. Rocks 4. Climate Pangea, Panthalassa Wadati-1935- earthquakes/ volcanoes may be associated with the continental drift Benioff-1940-revealed Pacific Ring of Fire Hess-1960s- Seafloor Spreading >Ocean Crust is young (less ...
107-Wegner-Plates
... • Then he noticed that there were fossils that were found on opposite sides of the ocean! BUT – these animals could not swim long distances!!! • Plant fossils, Animal Fossils, Coal Beds, and some mountain ranges that looked very much alike. • This lead to the idea of Continental Drift ...
... • Then he noticed that there were fossils that were found on opposite sides of the ocean! BUT – these animals could not swim long distances!!! • Plant fossils, Animal Fossils, Coal Beds, and some mountain ranges that looked very much alike. • This lead to the idea of Continental Drift ...
The solid, outer layer of Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid
... The process of one tectonic plate sinking beneath another into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary ...
... The process of one tectonic plate sinking beneath another into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary ...
Science Chapter 6 Study Guide
... Important facts to remember Glaciers form when more snow falls in the winter than melts in summer. The force of gravity causes the layers of a glacier to flow downhill. The oceans DID NOT become larger during the Ice Age. It takes hundreds to thousands of years for one inch of soil to form. Seismic ...
... Important facts to remember Glaciers form when more snow falls in the winter than melts in summer. The force of gravity causes the layers of a glacier to flow downhill. The oceans DID NOT become larger during the Ice Age. It takes hundreds to thousands of years for one inch of soil to form. Seismic ...
Lecture32_webpost - UA Atmospheric Sciences
... Solar radiation variability at the North Pole over thousands of years Changes in the orbital parameters change the incoming solar radiation at the North Pole by about 15% This is likely coupled with a biological response which affects the uptake of carbon dioxide in the ocean These two effects prob ...
... Solar radiation variability at the North Pole over thousands of years Changes in the orbital parameters change the incoming solar radiation at the North Pole by about 15% This is likely coupled with a biological response which affects the uptake of carbon dioxide in the ocean These two effects prob ...
Crustal structure of the West Antarctic rift system and Marie Byrd
... The West Antarctic rift system is one of the largest zones of continental extension on Earth. However, little is known of its crustal structure owing to the vast ice sheet that dominates the region. We report on new insights gained from a recent broadband seismic experiment. The 25-km-thick crust me ...
... The West Antarctic rift system is one of the largest zones of continental extension on Earth. However, little is known of its crustal structure owing to the vast ice sheet that dominates the region. We report on new insights gained from a recent broadband seismic experiment. The 25-km-thick crust me ...
The Era
... o ________________ many dinosaurs had an __________ posture o Mass extinction terrestrial dinosaurs, most marine ___________, plants, & many other organisms why? combo of: massive ____________ (stressed climate) large ______________ impact @ end of Cretaceous (@ least 10km in diameter) o ...
... o ________________ many dinosaurs had an __________ posture o Mass extinction terrestrial dinosaurs, most marine ___________, plants, & many other organisms why? combo of: massive ____________ (stressed climate) large ______________ impact @ end of Cretaceous (@ least 10km in diameter) o ...
How has Earth`s Environment Changed Over Time?
... since slowed down. The Pacific Ring of Fire—an ocean‐girdling zone of crustal instability, volcanism, and earthquakes—is but a trace of the paroxysm that marked the onset of Pangaea's breakup (Fig. 13.5). Yet, as we saw with the tsunami in Japan in 2011, tectonic events have cost millions of humans ...
... since slowed down. The Pacific Ring of Fire—an ocean‐girdling zone of crustal instability, volcanism, and earthquakes—is but a trace of the paroxysm that marked the onset of Pangaea's breakup (Fig. 13.5). Yet, as we saw with the tsunami in Japan in 2011, tectonic events have cost millions of humans ...
Post-glacial rebound
.jpg?width=300)
Post-glacial rebound (sometimes called continental rebound) is the rise of land masses that were depressed by the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, through a process known as isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound and isostatic depression are different parts of a process known as either glacial isostasy, glacial isostatic adjustment, or glacioisostasy. Glacioisostasy is the solid Earth deformation associated with changes in ice mass distribution. The most obvious and direct affects of post-glacial rebound are readily apparent in northern Europe (especially Scotland, Estonia, Latvia, Fennoscandia, and northern Denmark), Siberia, Canada, the Great Lakes of Canada and the United States, the coastal region of the US state of Maine, parts of Patagonia, and Antarctica. However, through processes known as ocean siphoning and continental levering, the effects of post-glacial rebound on sea-level are felt globally far from the locations of current and former ice sheets.