Honors Marine Biology
... Since we see deposits like these in areas that do not currently have glaciers, we have to assume that glaciers did exist in those areas at one time. ...
... Since we see deposits like these in areas that do not currently have glaciers, we have to assume that glaciers did exist in those areas at one time. ...
Observations explained by “Snowball Earth”
... Snow-free glacier ice exposed in the subtropics. This ice will resemble the snowfree “blue ice” surfaces found near Antarctic mountains. This ice has a high albedo (about 0.6) because it contains numerous bubbles, since its origin was compression of snow. Frozen seawater exposed at the equator. If t ...
... Snow-free glacier ice exposed in the subtropics. This ice will resemble the snowfree “blue ice” surfaces found near Antarctic mountains. This ice has a high albedo (about 0.6) because it contains numerous bubbles, since its origin was compression of snow. Frozen seawater exposed at the equator. If t ...
Geology of Washington
... Timeline approximately 200 million years Terrane Belts: Small crustal plates that combine with larger crust ...
... Timeline approximately 200 million years Terrane Belts: Small crustal plates that combine with larger crust ...
chapter 17 - Geoclassroom Home
... as well as Antarctica, and thousands of small glaciers were in mountain valleys on all continents. Sea level fell and rose during the several Pleistocene advances and retreats of glaciers, depending on how much water from the ocean was frozen on land. The tremendous weight of continental glacier ...
... as well as Antarctica, and thousands of small glaciers were in mountain valleys on all continents. Sea level fell and rose during the several Pleistocene advances and retreats of glaciers, depending on how much water from the ocean was frozen on land. The tremendous weight of continental glacier ...
Class Notes: Introduction to Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Tectonic
... Class Opener: Do mapping activity and answer the following questions once complete A. Are all the earthquakes and volcanoes evenly spaced randomly across earth’s surface? If not, describe where there appear to be the most… B. Look at the “Earth’s fractured surface” map and read the introduction (bac ...
... Class Opener: Do mapping activity and answer the following questions once complete A. Are all the earthquakes and volcanoes evenly spaced randomly across earth’s surface? If not, describe where there appear to be the most… B. Look at the “Earth’s fractured surface” map and read the introduction (bac ...
Section 1 - kjpederson
... 6. karst topography: a region in which a layer of limestone close to the surface creates deep valleys, caverns and sinkholes 7. meander: a looplike bend in the course of a river 8. oxbow lake: a meander cut off from a river 9. rill: a tiny groove in soil made by flowing water 10. runoff: water that ...
... 6. karst topography: a region in which a layer of limestone close to the surface creates deep valleys, caverns and sinkholes 7. meander: a looplike bend in the course of a river 8. oxbow lake: a meander cut off from a river 9. rill: a tiny groove in soil made by flowing water 10. runoff: water that ...
Science Vocabulary Constructive and Destructive Forces Lava
... Lava: Molten rock that flows from a volcano onto the earth’s surface. Sand Dune: A hill of sand made and shaped by the wind. Topography: Surface landforms of an area. Erosion: The process of moving sediment by wind, moving water, or ice. Delta: An area of new land at the mouth of a river formed from ...
... Lava: Molten rock that flows from a volcano onto the earth’s surface. Sand Dune: A hill of sand made and shaped by the wind. Topography: Surface landforms of an area. Erosion: The process of moving sediment by wind, moving water, or ice. Delta: An area of new land at the mouth of a river formed from ...
1) THIS IS THE WARMEST CLIMATE ZONE ON EARTH, AND THE
... b) warm air contains less moisture than cold air d) cold air contains less moisture than warm air ...
... b) warm air contains less moisture than cold air d) cold air contains less moisture than warm air ...
Isostatic Rebound-Actvity writeup.pages
... that allow it to act as a membrane that encases the planet. It will sink under a load and will rebound when the load is removed due to the viscoelas1c proper1es of the Earth beneath it. The ...
... that allow it to act as a membrane that encases the planet. It will sink under a load and will rebound when the load is removed due to the viscoelas1c proper1es of the Earth beneath it. The ...
Energy and Waves Review Sheet/Study Guide
... 9. The layers of earth from question 7 make up the __lithosphere_______. ...
... 9. The layers of earth from question 7 make up the __lithosphere_______. ...
Earth`s Changing Surface Review
... the convection currents move, they move the crust above them. ...
... the convection currents move, they move the crust above them. ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... the convection currents move, they move the crust above them. ...
... the convection currents move, they move the crust above them. ...
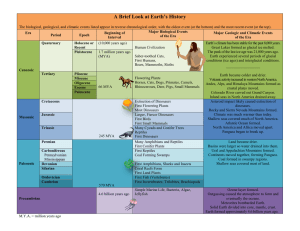
A Brief Look at Earth`s History
... Climate was much warmer than today. Shallow seas covered much of North America. Atlantic Ocean formed. North America and Africa moved apart. Pangaea began to break up. Land became drier. Basins were larger so water drained into them. Ural and Appalachian Mountains formed. Continents moved together, ...
... Climate was much warmer than today. Shallow seas covered much of North America. Atlantic Ocean formed. North America and Africa moved apart. Pangaea began to break up. Land became drier. Basins were larger so water drained into them. Ural and Appalachian Mountains formed. Continents moved together, ...
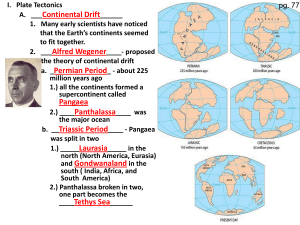
Notes: Plate Tectonics - Riverdale Middle School
... 2.) found in areas that vary greatly in climate, scientists believe these regions once were connected and had similar climates c. Fossils of warm weather plants were found in Arctic Ocean Islands d. Glacial deposits have been found where no glaciers exist today ...
... 2.) found in areas that vary greatly in climate, scientists believe these regions once were connected and had similar climates c. Fossils of warm weather plants were found in Arctic Ocean Islands d. Glacial deposits have been found where no glaciers exist today ...
Earth History Study Guide Answers are in RED 1) How has scientific
... 15) What drives plate tectonics? Convection currents in the mantle and ridge push/slab pull at the crust 16) What’s the difference between oceanic and continental crust? Oceanic crust is denser, usually younger, primarily made up of basalt, and thinner. Continental crust is less dense, usually older ...
... 15) What drives plate tectonics? Convection currents in the mantle and ridge push/slab pull at the crust 16) What’s the difference between oceanic and continental crust? Oceanic crust is denser, usually younger, primarily made up of basalt, and thinner. Continental crust is less dense, usually older ...
Crustal Diapirism - Neutrino Geoscience 2008
... • Predominantly vertical (diapiric) crustal tectonics in the Early Earth; but also: • Supplies metabasalts to the lower crust to form TTGs (tonalites, trondhjemites and granodiorites) • Leaves a depleted restite which can be harzburgitic to dunitic (for komatiitic volcanism), and which can accumulat ...
... • Predominantly vertical (diapiric) crustal tectonics in the Early Earth; but also: • Supplies metabasalts to the lower crust to form TTGs (tonalites, trondhjemites and granodiorites) • Leaves a depleted restite which can be harzburgitic to dunitic (for komatiitic volcanism), and which can accumulat ...
App4 GeolHistory
... The Precambrian rocks of the Belt Supergroup that underlie the Flathead Subbasin formed from sediments deposited in and near a large but shallow sea or inland lake during the middle Proterozoic (from roughly 1,600 to 800 million years ago). This large body of water, which may have been similar to to ...
... The Precambrian rocks of the Belt Supergroup that underlie the Flathead Subbasin formed from sediments deposited in and near a large but shallow sea or inland lake during the middle Proterozoic (from roughly 1,600 to 800 million years ago). This large body of water, which may have been similar to to ...
Tectonic Plates - Louis Pasteur MS 67 Science Department Resources
... Literacy Fusion Article: “Earth's tectonic plates have doubled their speed” SO MUCH for slowing down as you age. Earth's tectonic plates are moving faster now than at any point in the last 2 billion years, according to the latest study of plate movements. But the result is controversial, since previ ...
... Literacy Fusion Article: “Earth's tectonic plates have doubled their speed” SO MUCH for slowing down as you age. Earth's tectonic plates are moving faster now than at any point in the last 2 billion years, according to the latest study of plate movements. But the result is controversial, since previ ...
Earth`s Inner Layers Quiz
... 1) The ____________ makes up less than 1% of the Earth by mass. 2) Most of the Earth’s mass is located in the… a) mantle. b) inner core. c) outer core. d) none of these 3) The lithosphere is part of the… a) crust. b) mantle. c) crust and mantle. d) mantle and outer. core 4) The asthenosphere is easi ...
... 1) The ____________ makes up less than 1% of the Earth by mass. 2) Most of the Earth’s mass is located in the… a) mantle. b) inner core. c) outer core. d) none of these 3) The lithosphere is part of the… a) crust. b) mantle. c) crust and mantle. d) mantle and outer. core 4) The asthenosphere is easi ...
Earth`s Magnetic Field
... Ko`olau lavas mostly reversed in polarity, so they must be older than 700,000 yrs, but younger than 2.5 my • Lavas on Kaua`i and in Wai`anae Range show normal polarity, so they must be older than 2.5 my ...
... Ko`olau lavas mostly reversed in polarity, so they must be older than 700,000 yrs, but younger than 2.5 my • Lavas on Kaua`i and in Wai`anae Range show normal polarity, so they must be older than 2.5 my ...
Cenozoic Tectonics & Life
... • As the Farallon Plate disappeared completely under California. • North American plate came into contact with the Pacific Plate moving in different directions, the San Andreas Fault formed. • Because of this there is little volcanic activity beneath central and southern California ...
... • As the Farallon Plate disappeared completely under California. • North American plate came into contact with the Pacific Plate moving in different directions, the San Andreas Fault formed. • Because of this there is little volcanic activity beneath central and southern California ...
Unit 1 The Earth, Water, and Landforms
... underside of the crust ___________- thin layer of rock at the earth’s surface On and above earth_______________- surrounding the earth-layer of gases, oxygen, protects from radiation, space debris _______________- solid rock- some below water and forms floor of ocean _______________- 7 _____________ ...
... underside of the crust ___________- thin layer of rock at the earth’s surface On and above earth_______________- surrounding the earth-layer of gases, oxygen, protects from radiation, space debris _______________- solid rock- some below water and forms floor of ocean _______________- 7 _____________ ...
Post-glacial rebound
.jpg?width=300)
Post-glacial rebound (sometimes called continental rebound) is the rise of land masses that were depressed by the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, through a process known as isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound and isostatic depression are different parts of a process known as either glacial isostasy, glacial isostatic adjustment, or glacioisostasy. Glacioisostasy is the solid Earth deformation associated with changes in ice mass distribution. The most obvious and direct affects of post-glacial rebound are readily apparent in northern Europe (especially Scotland, Estonia, Latvia, Fennoscandia, and northern Denmark), Siberia, Canada, the Great Lakes of Canada and the United States, the coastal region of the US state of Maine, parts of Patagonia, and Antarctica. However, through processes known as ocean siphoning and continental levering, the effects of post-glacial rebound on sea-level are felt globally far from the locations of current and former ice sheets.