Earth - edl.io
... with the space that was created being filled with molten magma from below. Can create massive fault zones in the oceanic ridge system-frequent oceanic earthquakes Example- Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the East Pacific Rise ...
... with the space that was created being filled with molten magma from below. Can create massive fault zones in the oceanic ridge system-frequent oceanic earthquakes Example- Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the East Pacific Rise ...
amazing_earth_science_facts
... Most waves are generated by wind. Sea level rises when ice caps melt. Features of the seafloor that are related to plate tectonic process include mid-ocean ridges and trenches. Other major topographic features are continental shelves, continental slopes, abyssal plains, and seamounts. ...
... Most waves are generated by wind. Sea level rises when ice caps melt. Features of the seafloor that are related to plate tectonic process include mid-ocean ridges and trenches. Other major topographic features are continental shelves, continental slopes, abyssal plains, and seamounts. ...
Lecture Packet#1
... surface up to the bottom of the stratosphere. It has decreasing temperature with height (at an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather ...
... surface up to the bottom of the stratosphere. It has decreasing temperature with height (at an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather ...
divergent boundary - Brighten AcademyMiddle School
... • Which layer of the earth is filled with many different solid minerals? ...
... • Which layer of the earth is filled with many different solid minerals? ...
The Earth`s Atmosphere
... surface up to the bottom of the stratosphere. It has decreasing temperature with height (at an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather ...
... surface up to the bottom of the stratosphere. It has decreasing temperature with height (at an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather ...
ocks in the lithosphere
... Rivers, oceans, winds, and rain runoff all have the ability to carry the particles washed off of eroding rocks. Such material, called detritus, consists of fragments of rocks and minerals. When the energy of the transporting current is not strong enough to carry these particles, the particles dro ...
... Rivers, oceans, winds, and rain runoff all have the ability to carry the particles washed off of eroding rocks. Such material, called detritus, consists of fragments of rocks and minerals. When the energy of the transporting current is not strong enough to carry these particles, the particles dro ...
Weathering and Erosion - geography-bbs
... a processes called oxidation • The product of oxidation is rust ...
... a processes called oxidation • The product of oxidation is rust ...
Plate tectonics
... • Earthquakes: as plates grind or slip past each other at a fault, the earth shakes or trembles. • Seismograph: Measures size of waves created by earthquake. • Epicenter: -Location on the earth where earthquake begins. ...
... • Earthquakes: as plates grind or slip past each other at a fault, the earth shakes or trembles. • Seismograph: Measures size of waves created by earthquake. • Epicenter: -Location on the earth where earthquake begins. ...
Jeopardy - Central Lyon CSD
... Subduction occurs when the Earth’s crust is recycled underneath another plate. What feature would be likely to form where the plate begins to subduct? ...
... Subduction occurs when the Earth’s crust is recycled underneath another plate. What feature would be likely to form where the plate begins to subduct? ...
Geography Lesson Tectonics Tuesday * The largest earthquakes
... vi. Andesitic volcanoes (Andes Mountains) which are also composite volcanoes. ...
... vi. Andesitic volcanoes (Andes Mountains) which are also composite volcanoes. ...
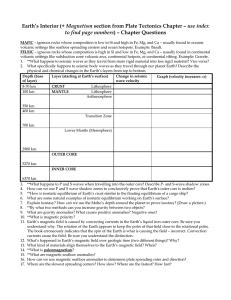
Earth`s Interior (+ Magnetism section from Plate Tectonics Chapter
... volcanic settings like seafloor spreading centers and ocean hotspots. Example: Basalt. FELSIC – igneous rocks whose composition is high in Si and low in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in continental volcanic settings like subduction zone volcanic arcs, continental hotpots, or continental rifting. Ex ...
... volcanic settings like seafloor spreading centers and ocean hotspots. Example: Basalt. FELSIC – igneous rocks whose composition is high in Si and low in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in continental volcanic settings like subduction zone volcanic arcs, continental hotpots, or continental rifting. Ex ...
The Role of the Bacterioneuston in Air
... potential to impact the cycling of reactive trace gases and the exchange rate of these gases across the air-sea boundary • Using a combination of molecular ecology techniques and an understanding of gas exchange, the knowledge of this unique and dynamic environment ...
... potential to impact the cycling of reactive trace gases and the exchange rate of these gases across the air-sea boundary • Using a combination of molecular ecology techniques and an understanding of gas exchange, the knowledge of this unique and dynamic environment ...
Question (1) (25 marks) State whether the following statements are
... 16- Faults in rocks occur due to elastic deformation 17- One type of faults is the anticline faults 18- Organic soils can be dealt with as a good material for construction 19- Sand dunes have a well graded grain size distribution 20- Corndum has lower hardness than quartz 21- Kaolinite mineral is a ...
... 16- Faults in rocks occur due to elastic deformation 17- One type of faults is the anticline faults 18- Organic soils can be dealt with as a good material for construction 19- Sand dunes have a well graded grain size distribution 20- Corndum has lower hardness than quartz 21- Kaolinite mineral is a ...
Chapter 17 Vocabulary
... tectonic plates are moving apart; is associated with volcanism, earthquakes, and high heat flow, and is found primarily on the seafloor. Rift Valley (p. 456) Long, narrow depression that forms when continental crust begins to separate at a divergent boundary. Subduction (p. 457) Process by which one ...
... tectonic plates are moving apart; is associated with volcanism, earthquakes, and high heat flow, and is found primarily on the seafloor. Rift Valley (p. 456) Long, narrow depression that forms when continental crust begins to separate at a divergent boundary. Subduction (p. 457) Process by which one ...
Study Guide Chapter 3 – Plate Tectonics GPS: S6E5. Students will
... a. Compare and contrast the Earth’s crust, mantle, and core including temperature, density, and composition. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposit ...
... a. Compare and contrast the Earth’s crust, mantle, and core including temperature, density, and composition. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposit ...
Science 8th Grade - Holy Family School | Phoenixville, PA
... from one kind to another over long periods of time: all rocks are igneous in origin but can be changed to sedimentary or metamorphic in any order 1.crytalization : solidification 2.metamorphism : changing as a result of heat, pressure, or chemical reaction 3.lithification : changing into rock ...
... from one kind to another over long periods of time: all rocks are igneous in origin but can be changed to sedimentary or metamorphic in any order 1.crytalization : solidification 2.metamorphism : changing as a result of heat, pressure, or chemical reaction 3.lithification : changing into rock ...
Plate Tectonics Matching
... asthenosphere plastic-like, denser, semi-molten layer of Earth convection circular path of heating and current cooling moves the tectonic plates Pangaea continents were joined similar rocks and fossils on separate continents similar mountain ranges divergent boundary between two plates bou ...
... asthenosphere plastic-like, denser, semi-molten layer of Earth convection circular path of heating and current cooling moves the tectonic plates Pangaea continents were joined similar rocks and fossils on separate continents similar mountain ranges divergent boundary between two plates bou ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.