Earth Science Common Assessment #8
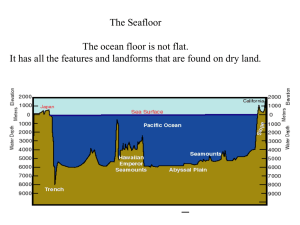
... • The shape of the ocean floor is known to scientists as submarine topography. The floor contains mountains, plains, canyons, plateaus, basins, and other topographic features that are found on land. Usually, the ocean bottom is divided into three major zones: the continental margin*, the ocean-basin ...
... • The shape of the ocean floor is known to scientists as submarine topography. The floor contains mountains, plains, canyons, plateaus, basins, and other topographic features that are found on land. Usually, the ocean bottom is divided into three major zones: the continental margin*, the ocean-basin ...
exploring_the_ocean
... • Home of many ocean plants and animals because sunlight reaches the bottom. ...
... • Home of many ocean plants and animals because sunlight reaches the bottom. ...
Ocean Waters and the Ocean Floor
... The Vast World Oceans • 81% of the Southern Hemisphere is covered by oceans • 61% of the Northern Hemisphere is covered by oceans • 71% of the Earth is covered by oceans and marginal seas ...
... The Vast World Oceans • 81% of the Southern Hemisphere is covered by oceans • 61% of the Northern Hemisphere is covered by oceans • 71% of the Earth is covered by oceans and marginal seas ...
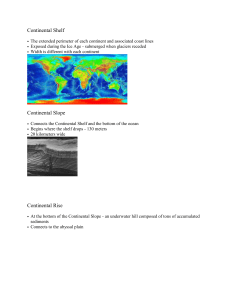
Continental Shelf • The extended perimeter of each continent and
... • The extended perimeter of each continent and associated coast lines • Exposed during the Ice Age - submerged when glaciers receded • Width is different with each continent ...
... • The extended perimeter of each continent and associated coast lines • Exposed during the Ice Age - submerged when glaciers receded • Width is different with each continent ...
Mid ocean ridge worksheet
... Mid-Ocean Ridges 1. In what year did scientists discover mid-ocean ridges? 213 ________________________________ 2. Summarize how scientists were able to map out the ocean floor. 213 ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ...
... Mid-Ocean Ridges 1. In what year did scientists discover mid-ocean ridges? 213 ________________________________ 2. Summarize how scientists were able to map out the ocean floor. 213 ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ...
8_Ocean126_2006
... Peru-Chile trench – oldest at the S end (shallower because its full of sediments) and vice versa Feature of active margin/subduction zone ...
... Peru-Chile trench – oldest at the S end (shallower because its full of sediments) and vice versa Feature of active margin/subduction zone ...
Ocean Features Abyssal currents Abyssal plains
... other undersea geomorphologic features such as the continental shelves, the deep ocean trenches, and the undersea mountain ranges (for example, the mid-Atlantic ridge) which are not considered to be part of the ocean basins; while hydrologically, oceanic basins include the flanking continental shelv ...
... other undersea geomorphologic features such as the continental shelves, the deep ocean trenches, and the undersea mountain ranges (for example, the mid-Atlantic ridge) which are not considered to be part of the ocean basins; while hydrologically, oceanic basins include the flanking continental shelv ...
Ocean Basins (Chapter 19) - Ms. Whitt's Science Classes
... sent underwater that can do a various of jobs like taking photographs, collecting mineral samples. ...
... sent underwater that can do a various of jobs like taking photographs, collecting mineral samples. ...
Chapter 3.4 - 3.5 Marine Provinces
... Any features on the abyssal plain are covered with LAYERS of sediment that have been deposited over MILLIONS of years. ...
... Any features on the abyssal plain are covered with LAYERS of sediment that have been deposited over MILLIONS of years. ...
Mapping the Ocean Floor
... water's surface, and thus is not an island. these are typically formed from extinct volcanoes, that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from a seafloor of 1,000–4,000 metres depth ...
... water's surface, and thus is not an island. these are typically formed from extinct volcanoes, that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from a seafloor of 1,000–4,000 metres depth ...
Study Notes for Chapter 19: The Ocean Basins Directions: Use the
... 14. The continental shelf has a gentle slope and usually has less than 100 meters of water above it. 15. Erosion from turbidity currents creates submarine canyons and the continental rise. 16. Sediments from rivers spread over the deep-ocean basins by means of turbidity currents. 17. The Mariana Tre ...
... 14. The continental shelf has a gentle slope and usually has less than 100 meters of water above it. 15. Erosion from turbidity currents creates submarine canyons and the continental rise. 16. Sediments from rivers spread over the deep-ocean basins by means of turbidity currents. 17. The Mariana Tre ...
Chapter 4
... Continents can drift apart from one another and have done so in the past Pangea Greek word meaning “All Earth” Name for the single land mass that is the separate continents of today Panthelassa Name for the single ocean of the world that is the separate oceans of the world today. Sea-Floor S ...
... Continents can drift apart from one another and have done so in the past Pangea Greek word meaning “All Earth” Name for the single land mass that is the separate continents of today Panthelassa Name for the single ocean of the world that is the separate oceans of the world today. Sea-Floor S ...
chapter in perspective
... margins and deep ocean basins. The continental margin, the relatively shallow ocean floor nearest the shore, consists of the continental shelf and the continental slope. The continental margin shares the structure of the adjacent continents, but the deep-ocean floor away from land has a much differe ...
... margins and deep ocean basins. The continental margin, the relatively shallow ocean floor nearest the shore, consists of the continental shelf and the continental slope. The continental margin shares the structure of the adjacent continents, but the deep-ocean floor away from land has a much differe ...
Geological and Physical Factors of the Marine
... vii. Rifts – cracks that are found generally by the ridges c. Mid Ocean Ridges – formed when material rising from below the mantle pushes up on the oceanic crust i. Central Rift Valley – a great gap or depression caused by the plates pulling apart at the center of the ridge ii. Hydrothermal Vents – ...
... vii. Rifts – cracks that are found generally by the ridges c. Mid Ocean Ridges – formed when material rising from below the mantle pushes up on the oceanic crust i. Central Rift Valley – a great gap or depression caused by the plates pulling apart at the center of the ridge ii. Hydrothermal Vents – ...
process of forming new oceanic crust from magma rising to the
... Which process adds new crust to the surface? ______Sea Floor ...
... Which process adds new crust to the surface? ______Sea Floor ...
File
... Occur along active margins (present-day plate boundaries) where subduction is taking place deepest part of the ocean floor, typically 3 - 4 km deeper than surrounding seafloor most occur in the Pacific, mostly western Pacific, but most of the Pacific is surrounded by trenches deepest spot in ...
... Occur along active margins (present-day plate boundaries) where subduction is taking place deepest part of the ocean floor, typically 3 - 4 km deeper than surrounding seafloor most occur in the Pacific, mostly western Pacific, but most of the Pacific is surrounded by trenches deepest spot in ...
Document
... How have earth scientists learned about the depths of the world’s oceans? HMS Challenger, 1872 throughout a 4year voyage, used rope lines to estimate ocean depths. Today we use echo sounders, devices that emit a pinging sound and record its return later in time. Knowing the speed of sound and the t ...
... How have earth scientists learned about the depths of the world’s oceans? HMS Challenger, 1872 throughout a 4year voyage, used rope lines to estimate ocean depths. Today we use echo sounders, devices that emit a pinging sound and record its return later in time. Knowing the speed of sound and the t ...
ch20_Oceans_online_notes
... How have earth scientists learned about the depths of the world’s oceans? HMS Challenger, 1872 throughout a 4year voyage, used rope lines to estimate ocean depths. Today we use echo sounders, devices that emit a pinging sound and record its return later in time. Knowing the speed of sound and the t ...
... How have earth scientists learned about the depths of the world’s oceans? HMS Challenger, 1872 throughout a 4year voyage, used rope lines to estimate ocean depths. Today we use echo sounders, devices that emit a pinging sound and record its return later in time. Knowing the speed of sound and the t ...
Mapping the Ocean Floor
... water's surface, and thus is not an island. these are typically formed from extinct volcanoes, that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from a seafloor of 1,000–4,000 metres depth ...
... water's surface, and thus is not an island. these are typically formed from extinct volcanoes, that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from a seafloor of 1,000–4,000 metres depth ...
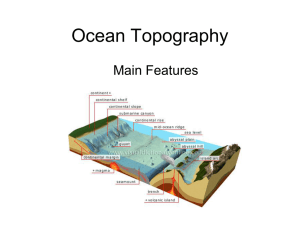
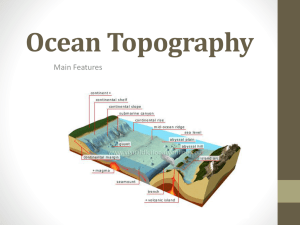
Ocean Topography
... Mid-Ocean ridge • A mid-ocean ridge is an underwater mountain range, typically having a valley known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. It is usually an oceanic spreading center, which is responsible for seafloor spreading. ...
... Mid-Ocean ridge • A mid-ocean ridge is an underwater mountain range, typically having a valley known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. It is usually an oceanic spreading center, which is responsible for seafloor spreading. ...
Ocean Topography
... • Hemispheric-scale (one hemisphere to another) long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor. ...
... • Hemispheric-scale (one hemisphere to another) long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor. ...
2.00 Bathymetry notes
... +Occur along active margins (present-day plate boundaries) where _________________________ is taking place +deepest part of the ocean floor, typically 3 - 4 km deeper than surrounding seafloor +relatively narrow, few 10’s of km wide and thousands of km long +most occur in the Pacific, mostly western ...
... +Occur along active margins (present-day plate boundaries) where _________________________ is taking place +deepest part of the ocean floor, typically 3 - 4 km deeper than surrounding seafloor +relatively narrow, few 10’s of km wide and thousands of km long +most occur in the Pacific, mostly western ...
Abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3000 and 6000 m. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins (the other elements being an elevated mid-ocean ridge and flanking abyssal hills). In addition to these elements, active oceanic basins (those that are associated with a moving plate tectonic boundary) also typically include an oceanic trench and a subduction zone.Abyssal plains were not recognized as distinct physiographic features of the sea floor until the late 1940s and, until very recently, none had been studied on a systematic basis. They are poorly preserved in the sedimentary record, because they tend to be consumed by the subduction process. The creation of the abyssal plain is the end result of spreading of the seafloor (plate tectonics) and melting of the lower oceanic crust. Magma rises from above the asthenosphere (a layer of the upper mantle) and as this basaltic material reaches the surface at mid-ocean ridges it forms new oceanic crust. This is constantly pulled sideways by spreading of the seafloor. Abyssal plains result from the blanketing of an originally uneven surface of oceanic crust by fine-grained sediments, mainly clay and silt. Much of this sediment is deposited by turbidity currents that have been channelled from the continental margins along submarine canyons down into deeper water. The remainder of the sediment is composed chiefly of pelagic sediments. Metallic nodules are common in some areas of the plains, with varying concentrations of metals, including manganese, iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper. These nodules may provide a significant resource for future mining ventures.Owing in part to their vast size, abyssal plains are currently believed to be a major reservoir of biodiversity. The abyss also exerts significant influence upon ocean carbon cycling, dissolution of calcium carbonate, and atmospheric CO2 concentrations over timescales of 100–1000 years. The structure and function of abyssal ecosystems are strongly influenced by the rate of flux of food to the seafloor and the composition of the material that settles. Factors such as climate change, fishing practices, and ocean fertilization are expected to have a substantial effect on patterns of primary production in the euphotic zone. This will undoubtedly impact the flux of organic material to the abyss in a similar manner and thus have a profound effect on the structure, function and diversity of abyssal ecosystems.