volcanoes
... boundaries, such as the mid-ocean ridge, or in subduction zones around the edges of oceans. • But some volcanoes form at “hot spots” far from the boundaries of continental or oceanic plates. Such as Hawaii • One major volcanic belt is the Ring of Fire, formed by the many volcanoes that rim the Pacif ...
... boundaries, such as the mid-ocean ridge, or in subduction zones around the edges of oceans. • But some volcanoes form at “hot spots” far from the boundaries of continental or oceanic plates. Such as Hawaii • One major volcanic belt is the Ring of Fire, formed by the many volcanoes that rim the Pacif ...
Earth`s Oceans
... What causes the Mid Ocean Ridge? • Parts of Earth’s crust—which are called crustal plates—are constantly moving. • When these plates spread apart, they allow the hot magma to enter the ocean floor. • As it enters the ocean and cools, it solidifies, and forms new ocean floor. ...
... What causes the Mid Ocean Ridge? • Parts of Earth’s crust—which are called crustal plates—are constantly moving. • When these plates spread apart, they allow the hot magma to enter the ocean floor. • As it enters the ocean and cools, it solidifies, and forms new ocean floor. ...
Chapter 4 2004.ppt
... Continental plate – continental plate convergence • Two continents may approach each other and collide. • As the sea floor that lies between them is subducted, the ocean becomes narrower and narrower until the continents collide with each other. • One continent may slide a short distance beneath a ...
... Continental plate – continental plate convergence • Two continents may approach each other and collide. • As the sea floor that lies between them is subducted, the ocean becomes narrower and narrower until the continents collide with each other. • One continent may slide a short distance beneath a ...
Chapter4.pdf
... Continental plate – continental plate convergence • Two continents may approach each other and collide. • As the sea floor that lies between them is subducted, the ocean becomes narrower and narrower until the continents collide with each other. • One continent may slide a short distance beneath an ...
... Continental plate – continental plate convergence • Two continents may approach each other and collide. • As the sea floor that lies between them is subducted, the ocean becomes narrower and narrower until the continents collide with each other. • One continent may slide a short distance beneath an ...
Plate tectonics - s3.amazonaws.com
... • Oceanic lithosphere subducts underneath the continental lithosphere • Oceanic lithosphere heats and melts forming magma • The magma rises forming volcanic mountains. • Ex. The Andes (S. America) ...
... • Oceanic lithosphere subducts underneath the continental lithosphere • Oceanic lithosphere heats and melts forming magma • The magma rises forming volcanic mountains. • Ex. The Andes (S. America) ...
Chapter 2 Review KEY - Perry Local Schools
... What is the average rate of sea floor spreading? How about the Mid Atlantic Ridge? How about the East Pacific Rise? 1. 5 cm/yr on average 2. Mid Atlantic Ridge 2 cm/yr 3. East Pacific Rise 15+ cm/yr List 4 facts that characterize the oceanic ridge system. 1. Most divergent plate margins are associat ...
... What is the average rate of sea floor spreading? How about the Mid Atlantic Ridge? How about the East Pacific Rise? 1. 5 cm/yr on average 2. Mid Atlantic Ridge 2 cm/yr 3. East Pacific Rise 15+ cm/yr List 4 facts that characterize the oceanic ridge system. 1. Most divergent plate margins are associat ...
Plate Tectonics – Unit 8 – Study Guide
... 42. At convergent boundaries oceanic plates will go under continental plates because oceanic crust is more dense than continental crust. 43. Oceanic-continental convergent boundaries can form mountains. 44. At convergent plate boundaries known as subduction zones, a trench and deep earthquakes mark ...
... 42. At convergent boundaries oceanic plates will go under continental plates because oceanic crust is more dense than continental crust. 43. Oceanic-continental convergent boundaries can form mountains. 44. At convergent plate boundaries known as subduction zones, a trench and deep earthquakes mark ...
INTRODUCTION TO MARINE ECOLOGY
... • Larger pelagic organisms can swim against currents and often migrate long distances • Nektonic organisms include: – Squid – Fish – Marine mammals ...
... • Larger pelagic organisms can swim against currents and often migrate long distances • Nektonic organisms include: – Squid – Fish – Marine mammals ...
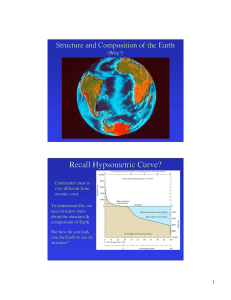
Recall Hypsometric Curve?
... – Top Marked by decrease in seismic velocity – no defined base (here it is 700 km or base of transition zone) – This is plastic region that lithosphere plates ride on ...
... – Top Marked by decrease in seismic velocity – no defined base (here it is 700 km or base of transition zone) – This is plastic region that lithosphere plates ride on ...
Ocean Floor and Chemistry Directed Reading
... a. The amount of dissolved salts in a liquid b. The amount of sodium in a liquid c. The amount of water that has evaporated d. The amount of solids in a liquid ...
... a. The amount of dissolved salts in a liquid b. The amount of sodium in a liquid c. The amount of water that has evaporated d. The amount of solids in a liquid ...
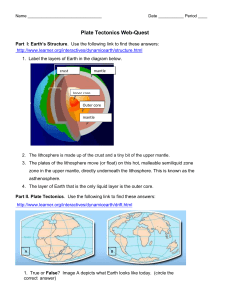
Plate Tectonics Webquest
... Subduction Zones and Volcanoes At some convergent boundaries, an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate. Oceanic crust tends to be denser and thinner than continental crust, so the denser oceanic crust gets bent and pulled under, or subducted, beneath the lighter and thicker continental cru ...
... Subduction Zones and Volcanoes At some convergent boundaries, an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate. Oceanic crust tends to be denser and thinner than continental crust, so the denser oceanic crust gets bent and pulled under, or subducted, beneath the lighter and thicker continental cru ...
plate tectonics example diagrams
... - rock is being pushed - the force of this crumples the crust because the plates are going against each other 7.Where would new crust be forming? - X, ridge 8.Explain how this diagram can be said to show how the Earth’s crust can be “recycled". - at Y the rock is melting into magma and at X it’s be ...
... - rock is being pushed - the force of this crumples the crust because the plates are going against each other 7.Where would new crust be forming? - X, ridge 8.Explain how this diagram can be said to show how the Earth’s crust can be “recycled". - at Y the rock is melting into magma and at X it’s be ...
Ch 3 Seafloor - San Diego Mesa College
... These faults display both strike-slip, horizontal motion (represented by the “+” and “-“ signs indicating out of [+] and into [-] the plane of the page) and dip-slip, vertical motion (represented by the block arrows). In effect, the continental borderland is broken up into a series of uplifted and d ...
... These faults display both strike-slip, horizontal motion (represented by the “+” and “-“ signs indicating out of [+] and into [-] the plane of the page) and dip-slip, vertical motion (represented by the block arrows). In effect, the continental borderland is broken up into a series of uplifted and d ...
The Layers of the Earth
... The next time you heat anything like soup or water in a pan you can watch the convection currents move in the liquid. When the convection currents flow in the asthenosphere they also move the crust. The crust gets a free ride with these currents, like the cork in this illustration. ...
... The next time you heat anything like soup or water in a pan you can watch the convection currents move in the liquid. When the convection currents flow in the asthenosphere they also move the crust. The crust gets a free ride with these currents, like the cork in this illustration. ...
Crust - www .alexandria .k12 .mn .us
... The next time you heat anything like soup or water in a pan you can watch the convection currents move in the liquid. When the convection currents flow in the asthenosphere they also move the crust. The crust gets a free ride with these currents, like the cork in this illustration. ...
... The next time you heat anything like soup or water in a pan you can watch the convection currents move in the liquid. When the convection currents flow in the asthenosphere they also move the crust. The crust gets a free ride with these currents, like the cork in this illustration. ...
Crust - MentorMob
... The next time you heat anything like soup or water in a pan you can watch the convection currents move in the liquid. When the convection currents flow in the asthenosphere they also move the crust. The crust gets a free ride with these currents, like the cork in this illustration. ...
... The next time you heat anything like soup or water in a pan you can watch the convection currents move in the liquid. When the convection currents flow in the asthenosphere they also move the crust. The crust gets a free ride with these currents, like the cork in this illustration. ...
PLATE TECTONICS - New Jersey City University
... New sea floor added to trailing edge of plate – e.g. North American plate growing at midAtlantic ridge Oceanic plate might get smaller as continetal plate overrides it – e.g. Eastward moving Nazca plate subducted beneath westward moving South American plate ...
... New sea floor added to trailing edge of plate – e.g. North American plate growing at midAtlantic ridge Oceanic plate might get smaller as continetal plate overrides it – e.g. Eastward moving Nazca plate subducted beneath westward moving South American plate ...
Earth’s Interior PowerPoint - Marcia's Science Teaching
... The next time you heat anything like soup or water in a pan you can watch the convection currents move in the liquid. When the convection currents flow in the asthenosphere they also move the crust. The crust gets a free ride with these currents, like the cork in this illustration. ...
... The next time you heat anything like soup or water in a pan you can watch the convection currents move in the liquid. When the convection currents flow in the asthenosphere they also move the crust. The crust gets a free ride with these currents, like the cork in this illustration. ...
Plate Tectonics : Different Plate Boundaries Create Different
... break/fault. As crust is stretched wider, the valley drops deeper. Eventually can lead to the creation of a new body of water if low enough. ...
... break/fault. As crust is stretched wider, the valley drops deeper. Eventually can lead to the creation of a new body of water if low enough. ...
Plate Tectonics : Different Plate Boundaries Create Different
... break/fault. As crust is stretched wider, the valley drops deeper. Eventually can lead to the creation of a new body of water if low enough. ...
... break/fault. As crust is stretched wider, the valley drops deeper. Eventually can lead to the creation of a new body of water if low enough. ...
Geology 12 Plate Boundaries
... general features of Earth Important to the prediction of volcanoes and earthquakes to help protect people Explains much of the geology of Canada, including the hills of Eskasoni and the ...
... general features of Earth Important to the prediction of volcanoes and earthquakes to help protect people Explains much of the geology of Canada, including the hills of Eskasoni and the ...
CONSTRUCTING A SEA-FLOOR SPREADING MODEL
... PURPOSE: To demonstrate processes and features at mid-ocean ridges and at trenches. BACKGROUND INFORMATION: ...
... PURPOSE: To demonstrate processes and features at mid-ocean ridges and at trenches. BACKGROUND INFORMATION: ...
When the Earth Moves: Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics
... timescale of reversals by measuring the magnetic directions in lava flows on land and determining their ages by radioactive methods. It was a painstaking process, but by 1966 researchers had charted the reversal timescale for the past 3.5 million years. At sea, meanwhile, researchers were finding an ...
... timescale of reversals by measuring the magnetic directions in lava flows on land and determining their ages by radioactive methods. It was a painstaking process, but by 1966 researchers had charted the reversal timescale for the past 3.5 million years. At sea, meanwhile, researchers were finding an ...
Q. What is the concept of plate tectonics theory?
... Q. What is the concept of plate tectonics theory? - It is a scientific theory which describes the large scale motion of Earth’s lithosphere. The theory builds on the older concepts of continental drift developed by Alfred Wegner and seafloor spreading. Where the plates are relatively moving towards ...
... Q. What is the concept of plate tectonics theory? - It is a scientific theory which describes the large scale motion of Earth’s lithosphere. The theory builds on the older concepts of continental drift developed by Alfred Wegner and seafloor spreading. Where the plates are relatively moving towards ...
Abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3000 and 6000 m. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins (the other elements being an elevated mid-ocean ridge and flanking abyssal hills). In addition to these elements, active oceanic basins (those that are associated with a moving plate tectonic boundary) also typically include an oceanic trench and a subduction zone.Abyssal plains were not recognized as distinct physiographic features of the sea floor until the late 1940s and, until very recently, none had been studied on a systematic basis. They are poorly preserved in the sedimentary record, because they tend to be consumed by the subduction process. The creation of the abyssal plain is the end result of spreading of the seafloor (plate tectonics) and melting of the lower oceanic crust. Magma rises from above the asthenosphere (a layer of the upper mantle) and as this basaltic material reaches the surface at mid-ocean ridges it forms new oceanic crust. This is constantly pulled sideways by spreading of the seafloor. Abyssal plains result from the blanketing of an originally uneven surface of oceanic crust by fine-grained sediments, mainly clay and silt. Much of this sediment is deposited by turbidity currents that have been channelled from the continental margins along submarine canyons down into deeper water. The remainder of the sediment is composed chiefly of pelagic sediments. Metallic nodules are common in some areas of the plains, with varying concentrations of metals, including manganese, iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper. These nodules may provide a significant resource for future mining ventures.Owing in part to their vast size, abyssal plains are currently believed to be a major reservoir of biodiversity. The abyss also exerts significant influence upon ocean carbon cycling, dissolution of calcium carbonate, and atmospheric CO2 concentrations over timescales of 100–1000 years. The structure and function of abyssal ecosystems are strongly influenced by the rate of flux of food to the seafloor and the composition of the material that settles. Factors such as climate change, fishing practices, and ocean fertilization are expected to have a substantial effect on patterns of primary production in the euphotic zone. This will undoubtedly impact the flux of organic material to the abyss in a similar manner and thus have a profound effect on the structure, function and diversity of abyssal ecosystems.