Dynamic Planet
... a) the part of California west of the San Andreas fault that is moving into the Pacific Ocean. b) the period of geologic history that predates modern life forms. c) a rift valley in east Africa where a new ocean is forming. d) the name of a previous supercontinent thought to have broken into several ...
... a) the part of California west of the San Andreas fault that is moving into the Pacific Ocean. b) the period of geologic history that predates modern life forms. c) a rift valley in east Africa where a new ocean is forming. d) the name of a previous supercontinent thought to have broken into several ...
Document
... • Please IGNORE these….. • They are based on outdated information and will be marked wrong in geology exams • They often also show continental crust floating on oceanic crust, this is also incorrect. ...
... • Please IGNORE these….. • They are based on outdated information and will be marked wrong in geology exams • They often also show continental crust floating on oceanic crust, this is also incorrect. ...
Tectonic Snacks
... cracker and fruit roll up from the frosting asthenosphere (you can eat or discard the fruit roll up). Place one edge of both crackers into the glass of water for just a few seconds. Place the crackers on the frosting with the wet edges next to each other. Slowly push the graham crackers towards each ...
... cracker and fruit roll up from the frosting asthenosphere (you can eat or discard the fruit roll up). Place one edge of both crackers into the glass of water for just a few seconds. Place the crackers on the frosting with the wet edges next to each other. Slowly push the graham crackers towards each ...
How to make an Earth Layer`s Study Guide
... a.___________________________________________________________________ b.___________________________________________________________________ c.___________________________________________________________________ d.___________________________________________________________________ 7. The crust and the ...
... a.___________________________________________________________________ b.___________________________________________________________________ c.___________________________________________________________________ d.___________________________________________________________________ 7. The crust and the ...
Top driven asymmetric mantle convection
... The role of the decoupling in the low-velocity zone is crucial for understanding the mechanisms governing plate tectonics and mantle convection. Mantle convection models fail to integrate plate kinematics and thermodynamics of the mantle. We computed the volume of the plates lost along subduction zo ...
... The role of the decoupling in the low-velocity zone is crucial for understanding the mechanisms governing plate tectonics and mantle convection. Mantle convection models fail to integrate plate kinematics and thermodynamics of the mantle. We computed the volume of the plates lost along subduction zo ...
What are plate tectonics and what causes it?
... • The mantle rock close to Earth's core is hot and has some properties of a thick liquid. • The mantle rock farther from the core is cooler. • The hot mantle rock rises. The cooler mantle rock sinks. • As the cooler rock moves closer to the core, it heats up and rises. • The plates are carried along ...
... • The mantle rock close to Earth's core is hot and has some properties of a thick liquid. • The mantle rock farther from the core is cooler. • The hot mantle rock rises. The cooler mantle rock sinks. • As the cooler rock moves closer to the core, it heats up and rises. • The plates are carried along ...
types of plate boundaries 2014-2015
... • Scientists found a close link between deep-focus earthquakes and ocean trenches. • The absence of deep-focus earthquakes along the oceanic ridge system was shown to be consistent with the new theory. ...
... • Scientists found a close link between deep-focus earthquakes and ocean trenches. • The absence of deep-focus earthquakes along the oceanic ridge system was shown to be consistent with the new theory. ...
Name Date ______ Period ____ Plate Tectonics Web
... Subduction Zones and Volcanoes At some convergent boundaries, an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate. Oceanic crust tends to be __denser__________ and ______thinner_______ than continental crust, so the denser oceanic crust gets bent and pulled under, or ___subducted_____________, beneat ...
... Subduction Zones and Volcanoes At some convergent boundaries, an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate. Oceanic crust tends to be __denser__________ and ______thinner_______ than continental crust, so the denser oceanic crust gets bent and pulled under, or ___subducted_____________, beneat ...
Plate tectonics.notebook
... Oceanic plate sinks into the lithosphere Subduction Zone c. Oceanic Oceanic One plate will sink under the other 3. Transform Boundary plates slide past one another horizontally strike slip fault causes earthquakes What is behind all this? Convection current cycle of heating, rising, cooling ...
... Oceanic plate sinks into the lithosphere Subduction Zone c. Oceanic Oceanic One plate will sink under the other 3. Transform Boundary plates slide past one another horizontally strike slip fault causes earthquakes What is behind all this? Convection current cycle of heating, rising, cooling ...
The Restless Earth
... Possible Causes of Tectonic Plate Motion • Ridge Push – at mid-ocean ridges, the oceanic lithosphere is higher than it is where it sinks into the asthenosphere. Because of the ridge push, the oceanic lithosphere slides downhill under the force of gravity • Convection – hot rock from deep within the ...
... Possible Causes of Tectonic Plate Motion • Ridge Push – at mid-ocean ridges, the oceanic lithosphere is higher than it is where it sinks into the asthenosphere. Because of the ridge push, the oceanic lithosphere slides downhill under the force of gravity • Convection – hot rock from deep within the ...
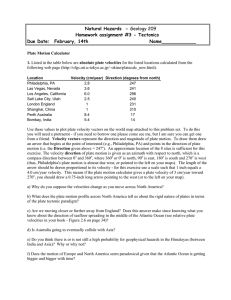
Natural Hazards - Geology 209 Homework assignment #3
... (thus, Philadelphia's plate motion is almost due west, or pointed to the left on your maps). The length of the arrow should be drawn proportional to its velocity - for this exercise use a scale such that 1 inch equals a 4.0 cm/year velocity. This means if the plate motion calculator gives a plate ve ...
... (thus, Philadelphia's plate motion is almost due west, or pointed to the left on your maps). The length of the arrow should be drawn proportional to its velocity - for this exercise use a scale such that 1 inch equals a 4.0 cm/year velocity. This means if the plate motion calculator gives a plate ve ...
PLATE TECTONICS - Part I
... spreading Basaltic magmas arise from decompression melting of hot ascending asthenosphere beneath the mid ocean ridge As new oceanic lithosphere is constructed at the mid ocean ridge, older plate material passively moves off and away from both sides of ridge Most oceanic lithosphere will event ...
... spreading Basaltic magmas arise from decompression melting of hot ascending asthenosphere beneath the mid ocean ridge As new oceanic lithosphere is constructed at the mid ocean ridge, older plate material passively moves off and away from both sides of ridge Most oceanic lithosphere will event ...
File
... Subduction Zones and Volcanoes At some convergent boundaries, an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate. Oceanic crust tends to be denser and thinner than continental crust, so the denser oceanic crust gets bent and pulled under, or subducted, beneath the lighter and thicker continental cru ...
... Subduction Zones and Volcanoes At some convergent boundaries, an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate. Oceanic crust tends to be denser and thinner than continental crust, so the denser oceanic crust gets bent and pulled under, or subducted, beneath the lighter and thicker continental cru ...
Plate Boundaries
... O-O Convergent Boundary • When two oceanic plates collide, one runs over the other which causes it to sink into the mantle forming a subduction zone. • The subducting plate is bent downward to form a very deep depression in the ocean floor called a trench. • The worlds deepest parts of the ocean ar ...
... O-O Convergent Boundary • When two oceanic plates collide, one runs over the other which causes it to sink into the mantle forming a subduction zone. • The subducting plate is bent downward to form a very deep depression in the ocean floor called a trench. • The worlds deepest parts of the ocean ar ...
BGI Academy - University of Colorado Boulder
... Earth’s oceans cover 72 percent of the planet’s surface but constitute only 0.025 percent of its mass. It is possible that deep reservoirs of water incorporated as hydroxyl into solid silicate minerals of the Earth’s interior contain the majority of the planet’s hydrogen and have acted as buffers to ...
... Earth’s oceans cover 72 percent of the planet’s surface but constitute only 0.025 percent of its mass. It is possible that deep reservoirs of water incorporated as hydroxyl into solid silicate minerals of the Earth’s interior contain the majority of the planet’s hydrogen and have acted as buffers to ...
Directed Reading
... a. the solid outer layer of Earth, that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle ...
... a. the solid outer layer of Earth, that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle ...
APS Continental Crust RLR.pptx
... Figure 15. Four tectonic settings for continental refining via relamination. In all cases, the relaminating layer may be thrust directly beneath existing crust, rise en bloc, perhaps in a "subduction channel", or rise as diapirs through the mantle wedge, depending on physical conditions. In all case ...
... Figure 15. Four tectonic settings for continental refining via relamination. In all cases, the relaminating layer may be thrust directly beneath existing crust, rise en bloc, perhaps in a "subduction channel", or rise as diapirs through the mantle wedge, depending on physical conditions. In all case ...
pHet Worksheet
... Experiment with making your own crust using the sliders in the center of the screen. Note that the middle crust sample will turn blue or green depending on whether it is considered oceanic or continental crust. 2. See what happens when you adjust the thickness of the crust. What kind of crust is ver ...
... Experiment with making your own crust using the sliders in the center of the screen. Note that the middle crust sample will turn blue or green depending on whether it is considered oceanic or continental crust. 2. See what happens when you adjust the thickness of the crust. What kind of crust is ver ...
Clouard_new_scientis..
... line where the crust was likely to tear and form volcanic islands and it matched the position of existing islands. Norman Sleep of Stanford University in California thinks the researchers' claim for a new plate boundary is interesting, but has some doubts about the mechanism they use to make their c ...
... line where the crust was likely to tear and form volcanic islands and it matched the position of existing islands. Norman Sleep of Stanford University in California thinks the researchers' claim for a new plate boundary is interesting, but has some doubts about the mechanism they use to make their c ...
Seismic tomography - Italo Bovolenta Editore
... core-mantle boundary. Near the surface, you can clearly see the structure of plate tectonics. The low S-wave speeds caused by the upwelling of hot asthenosphere along the mid-ocean ridges are shown in warm colors; the high S-wave speeds from cold lithosphere in the old ocean basins and beneath the c ...
... core-mantle boundary. Near the surface, you can clearly see the structure of plate tectonics. The low S-wave speeds caused by the upwelling of hot asthenosphere along the mid-ocean ridges are shown in warm colors; the high S-wave speeds from cold lithosphere in the old ocean basins and beneath the c ...
Water in Motion
... It's obvious why Earth is called the "Blue Planet" as 71 percent of the surface is covered by water, 97% of which is in oceans. Oceans appeared on Earth between 3 and 4 billion years ago from which sprang life. Ancient algal formations found in the water near Australia called stromatolites are thoug ...
... It's obvious why Earth is called the "Blue Planet" as 71 percent of the surface is covered by water, 97% of which is in oceans. Oceans appeared on Earth between 3 and 4 billion years ago from which sprang life. Ancient algal formations found in the water near Australia called stromatolites are thoug ...
Plate Tectonics
... the rocks became older as they moved away from the ridge, consistent with seafloor spreading. ...
... the rocks became older as they moved away from the ridge, consistent with seafloor spreading. ...
Restless Continents
... fault plane should be labeled “footwall.” when fault blocks slide past each other horizontally The hanging wall has moved down relative to the footwall. Most mountains are the result of plate movements. Since plates move very slowly, mountains form very slowly. tension continent-ocean ...
... fault plane should be labeled “footwall.” when fault blocks slide past each other horizontally The hanging wall has moved down relative to the footwall. Most mountains are the result of plate movements. Since plates move very slowly, mountains form very slowly. tension continent-ocean ...
8.4: Plates converge or scrape past each other
... more earthquakes are likely where plates slide past each other volcanic activity where plates are sinking beneath other plates mountains will continue to rise where plates push together ...
... more earthquakes are likely where plates slide past each other volcanic activity where plates are sinking beneath other plates mountains will continue to rise where plates push together ...
Abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3000 and 6000 m. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins (the other elements being an elevated mid-ocean ridge and flanking abyssal hills). In addition to these elements, active oceanic basins (those that are associated with a moving plate tectonic boundary) also typically include an oceanic trench and a subduction zone.Abyssal plains were not recognized as distinct physiographic features of the sea floor until the late 1940s and, until very recently, none had been studied on a systematic basis. They are poorly preserved in the sedimentary record, because they tend to be consumed by the subduction process. The creation of the abyssal plain is the end result of spreading of the seafloor (plate tectonics) and melting of the lower oceanic crust. Magma rises from above the asthenosphere (a layer of the upper mantle) and as this basaltic material reaches the surface at mid-ocean ridges it forms new oceanic crust. This is constantly pulled sideways by spreading of the seafloor. Abyssal plains result from the blanketing of an originally uneven surface of oceanic crust by fine-grained sediments, mainly clay and silt. Much of this sediment is deposited by turbidity currents that have been channelled from the continental margins along submarine canyons down into deeper water. The remainder of the sediment is composed chiefly of pelagic sediments. Metallic nodules are common in some areas of the plains, with varying concentrations of metals, including manganese, iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper. These nodules may provide a significant resource for future mining ventures.Owing in part to their vast size, abyssal plains are currently believed to be a major reservoir of biodiversity. The abyss also exerts significant influence upon ocean carbon cycling, dissolution of calcium carbonate, and atmospheric CO2 concentrations over timescales of 100–1000 years. The structure and function of abyssal ecosystems are strongly influenced by the rate of flux of food to the seafloor and the composition of the material that settles. Factors such as climate change, fishing practices, and ocean fertilization are expected to have a substantial effect on patterns of primary production in the euphotic zone. This will undoubtedly impact the flux of organic material to the abyss in a similar manner and thus have a profound effect on the structure, function and diversity of abyssal ecosystems.