Inside Earth – Chapter 1
... massive ranges that extends 2,500 kilometers across South Asia north of India. The Himalayas cover all or part of the countries of Tibet, Nepal, and Bhutan. ...
... massive ranges that extends 2,500 kilometers across South Asia north of India. The Himalayas cover all or part of the countries of Tibet, Nepal, and Bhutan. ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics
... Continental Drift was proven by: • Certain fossils are on different continents – Example: Mesosaurus – reptile that lived about 270 mya, fossils found only in parts of South America and Africa – could have only happened when the 2 continents were once joined). ...
... Continental Drift was proven by: • Certain fossils are on different continents – Example: Mesosaurus – reptile that lived about 270 mya, fossils found only in parts of South America and Africa – could have only happened when the 2 continents were once joined). ...
Growth and mixing dynamics of mantle wedge plumes
... Recent work suggests that hydrated partially molten thermal-chemical plumes that originate from subducted slab as a consequence of Rayleigh-Taylor instability are responsible for the heterogeneous composition of the mantle wedge. We use a two-dimensional ultrahighresolution numerical simulation invo ...
... Recent work suggests that hydrated partially molten thermal-chemical plumes that originate from subducted slab as a consequence of Rayleigh-Taylor instability are responsible for the heterogeneous composition of the mantle wedge. We use a two-dimensional ultrahighresolution numerical simulation invo ...
File
... where two tectonic plates are moving toward each other. One type of convergent boundaries is when continental crust converges and collides with another continental crust. Because continental rocks are too buoyant to be forced into the mantle, the colliding edges of the continents are crumpled and up ...
... where two tectonic plates are moving toward each other. One type of convergent boundaries is when continental crust converges and collides with another continental crust. Because continental rocks are too buoyant to be forced into the mantle, the colliding edges of the continents are crumpled and up ...
Ocean-Continent Convergent Plate Boundaries Quiz
... To make the Cascade volcanoes in Northeaster California, the Juan de Fuca plate collides with the a) North American Plate ...
... To make the Cascade volcanoes in Northeaster California, the Juan de Fuca plate collides with the a) North American Plate ...
Geological slant on plates
... Africa moving towards Europe to form the Alps Intra-plate volcanism Volcanic activity away from plate boundaries “Jets” of hot mantle or mantle plumes called hot spots can pierce the crust away from the plate boundaries and cause intra-plate volcanoes such as those at Hawaii. They also occur in cont ...
... Africa moving towards Europe to form the Alps Intra-plate volcanism Volcanic activity away from plate boundaries “Jets” of hot mantle or mantle plumes called hot spots can pierce the crust away from the plate boundaries and cause intra-plate volcanoes such as those at Hawaii. They also occur in cont ...
Plate Tectonics
... 6. seafloor spreading- the process by which new oceanic crust forms when magma rises up and solidifies at the mid-ocean ridges. The newer crust pushes the older crust out to each side, which is why the age of the sea floor increases with distance away from the mid-ocean ridges. ...
... 6. seafloor spreading- the process by which new oceanic crust forms when magma rises up and solidifies at the mid-ocean ridges. The newer crust pushes the older crust out to each side, which is why the age of the sea floor increases with distance away from the mid-ocean ridges. ...
12.002 Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets
... Problem 2. Heat Loss by Plate Tectonics The Earth’s oceanic lithosphere is created along mid-ocean ridges and consumed in subduction zones. Between these two events, it cools conductively as a function of age. Suppose we have a rectangular ocean that is being created at a half-spreading uniform rate ...
... Problem 2. Heat Loss by Plate Tectonics The Earth’s oceanic lithosphere is created along mid-ocean ridges and consumed in subduction zones. Between these two events, it cools conductively as a function of age. Suppose we have a rectangular ocean that is being created at a half-spreading uniform rate ...
Plate Tectonics Webquest - Ms. Murray`s Class Website
... How long ago did the Earths crust solidify?_______________________ Is the crust a solid shell? No Yes ...
... How long ago did the Earths crust solidify?_______________________ Is the crust a solid shell? No Yes ...
PDF sample
... If volcanoes in subduction zones emerge in the sea, they form a curving line of volcanic islands called an island arc. Beyond this arc is the back-arc basin, an area of shallow sea that slowly fills up with sediments. As a subducting plate sinks, the continental plate scrapes sediments off the ocean ...
... If volcanoes in subduction zones emerge in the sea, they form a curving line of volcanic islands called an island arc. Beyond this arc is the back-arc basin, an area of shallow sea that slowly fills up with sediments. As a subducting plate sinks, the continental plate scrapes sediments off the ocean ...
CHAPTER 3
... joined in a single landmass called Gondwanaland. This idea was developed in a series of papers written between 1885 and 1909. - Suess believed that the ocean basins were created when large regions of Gondwanaland sank and the seas invaded the land. Thus, he did not propose a fragmentation of Gondwan ...
... joined in a single landmass called Gondwanaland. This idea was developed in a series of papers written between 1885 and 1909. - Suess believed that the ocean basins were created when large regions of Gondwanaland sank and the seas invaded the land. Thus, he did not propose a fragmentation of Gondwan ...
10-2 Directed Reading
... 53. Is ridge push the main driving force of plate motion? Along with ridge push, what did scientists study for clues about forces that drive plate motion? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _________________ ...
... 53. Is ridge push the main driving force of plate motion? Along with ridge push, what did scientists study for clues about forces that drive plate motion? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _________________ ...
6.F Post Assessment
... 1. Old oceanic crust is more dense than new oceanic crust because it is a. hot, new rock b. moving toward a deep-ocean trench c. cooled over time d. closer to the mid-ocean ridge 2. The geological theory that states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion is the theory of a. ...
... 1. Old oceanic crust is more dense than new oceanic crust because it is a. hot, new rock b. moving toward a deep-ocean trench c. cooled over time d. closer to the mid-ocean ridge 2. The geological theory that states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion is the theory of a. ...
File
... 5. The Earth’s Mantle is made up of very hot material that rises to the top of the mantle, cools, than sink, and rises up again. THIS ACTION IS KNOWIN AS CONVECTION CURRENTS. 5.1 What are CONVECTION CURRENTS? Draw a picture as well. ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... 5. The Earth’s Mantle is made up of very hot material that rises to the top of the mantle, cools, than sink, and rises up again. THIS ACTION IS KNOWIN AS CONVECTION CURRENTS. 5.1 What are CONVECTION CURRENTS? Draw a picture as well. ___________________________________________________________________ ...
Ch. 21 - Tri-City
... ¡ Narrow valley that forms where plates separate Most studied is Mid-Atlantic Ridge ¡ Most of this ridge is under water ¡ A portion of it is at sea level in Iceland ¡ Run roughly down center of Atlantic Ocean, from Arctic Ocean to southern tip of South America ...
... ¡ Narrow valley that forms where plates separate Most studied is Mid-Atlantic Ridge ¡ Most of this ridge is under water ¡ A portion of it is at sea level in Iceland ¡ Run roughly down center of Atlantic Ocean, from Arctic Ocean to southern tip of South America ...
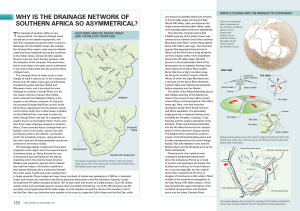
Why is the drainage network of Southern Africa so asymmetrical?
... This drainage pattern is believed to have been escarpment imprinted on the region when the supercontinent Gondwana broke up. Africa formed the core 100 million years ago of Gondwana and was flanked in the east by Antarctica and in the west by South America. The major drainages of southern Africa as ...
... This drainage pattern is believed to have been escarpment imprinted on the region when the supercontinent Gondwana broke up. Africa formed the core 100 million years ago of Gondwana and was flanked in the east by Antarctica and in the west by South America. The major drainages of southern Africa as ...
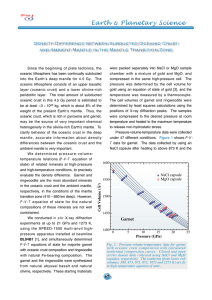
Mantle plume
A mantle plume is a mechanism proposed in 1971 to explain volcanic regions of the earth that were not thought to be explicable by the then-new theory of plate tectonics. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, for example, Hawaii. Others represent unusually large-volume volcanism, whether on plate boundaries, e.g. Iceland, or basalt floods such as the Deccan or Siberian traps.A mantle plume is posited to exist where hot rock nucleates at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle becoming a diapir in the Earth's crust. The currently active volcanic centers are known as ""hot spots"". In particular, the concept that mantle plumes are fixed relative to one another, and anchored at the core-mantle boundary, was thought to provide a natural explanation for the time-progressive chains of older volcanoes seen extending out from some such hot spots, such as the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain.The hypothesis of mantle plumes from depth is not universally accepted as explaining all such volcanism. It has required progressive hypothesis-elaboration leading to variant propositions such as mini-plumes and pulsing plumes. Another hypothesis for unusual volcanic regions is the ""Plate model"". This proposes shallower, passive leakage of magma from the mantle onto the Earth's surface where extension of the lithosphere permits it, attributing most volcanism to plate tectonic processes, with volcanoes far from plate boundaries resulting from intraplate extension.