1. What is the difference between a compositional layer and a
... Convention is the movement of matter that results from differences in density caused by variations in temperatures. As rock in the lower mantle is super heated, it becomes less dense and rises up through the mantle. Once it reaches the upper portion of the mantle it forces the cooler, more dense roc ...
... Convention is the movement of matter that results from differences in density caused by variations in temperatures. As rock in the lower mantle is super heated, it becomes less dense and rises up through the mantle. Once it reaches the upper portion of the mantle it forces the cooler, more dense roc ...
(1 point
... this layer they ______________ _____, indicating the inner core is solid. g) At about ____________ , the inner core is the ____________________ part of Earth. h) The inner core, at the center of the Earth, also experiences the greatest amount of _____________________. i) The inner core makes up abou ...
... this layer they ______________ _____, indicating the inner core is solid. g) At about ____________ , the inner core is the ____________________ part of Earth. h) The inner core, at the center of the Earth, also experiences the greatest amount of _____________________. i) The inner core makes up abou ...
The Big MELT
... of the axis. Since there are also many more seaan excellent surrounding source of seismic waves, mounts on the western, or Pacific Plate, side of the since earthquakes frequently occur in these zones, axis, the asymmetry may be related to melting and where the seafloor created at the East Pacific Ri ...
... of the axis. Since there are also many more seaan excellent surrounding source of seismic waves, mounts on the western, or Pacific Plate, side of the since earthquakes frequently occur in these zones, axis, the asymmetry may be related to melting and where the seafloor created at the East Pacific Ri ...
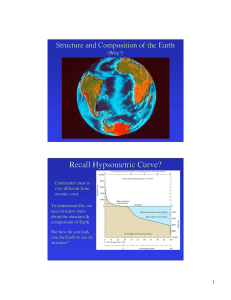
Recall Hypsometric Curve?
... – Includes crust and rigid upper mantle – This is the rigid plate in plate tectonics – Base is defined by 1200º 1200ºC boundary ...
... – Includes crust and rigid upper mantle – This is the rigid plate in plate tectonics – Base is defined by 1200º 1200ºC boundary ...
Earth is made of hard rock
... I’m sure you’re thinking (you! Yes, you! Don’t play the innocent!) that, like a goof number of your fellows, that Earth is an ocean of magma (so liquid) where some little ships are floating (so solid) which are tectonic plates. Sorry to tell you you’re totally wrong! As you already know (or don’t ;- ...
... I’m sure you’re thinking (you! Yes, you! Don’t play the innocent!) that, like a goof number of your fellows, that Earth is an ocean of magma (so liquid) where some little ships are floating (so solid) which are tectonic plates. Sorry to tell you you’re totally wrong! As you already know (or don’t ;- ...
File
... S-waves show that the outer core is liquid. Evidence for a fluid outer core includes observations from seismology which shows that seismic shear-waves are not transmitted through the outer core. The Inner Core The Earth's inner core is the Earth's innermost part. It is believed to be primarily a sol ...
... S-waves show that the outer core is liquid. Evidence for a fluid outer core includes observations from seismology which shows that seismic shear-waves are not transmitted through the outer core. The Inner Core The Earth's inner core is the Earth's innermost part. It is believed to be primarily a sol ...
Tectonic History - Illinois State Geological Survey
... geological structures, migration of groundwater and hydrocarbons, and contemporary earthquake activity in Illinois are a direct result of these processes. Because Illinois lies far removed from ancient and modern deformed plate margins, the succession of sedimentary rocks is mostly flat-lying or gen ...
... geological structures, migration of groundwater and hydrocarbons, and contemporary earthquake activity in Illinois are a direct result of these processes. Because Illinois lies far removed from ancient and modern deformed plate margins, the succession of sedimentary rocks is mostly flat-lying or gen ...
Earth Science Unit 2 Review Worksheet Name Block Circle the letter
... 10. The driving force of tectonic plates are related to convection currents in Earth’s a. Crust b. Mantle c. Inner core d. Outer core 11. Convergent boundaries are classified according to the a. Types of fossils found at the boundaries b. Rate at which the plates collide c. Compass direction of move ...
... 10. The driving force of tectonic plates are related to convection currents in Earth’s a. Crust b. Mantle c. Inner core d. Outer core 11. Convergent boundaries are classified according to the a. Types of fossils found at the boundaries b. Rate at which the plates collide c. Compass direction of move ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... more dense with distance from mid-oceanic ridge • When sufficiently cool and dense, these rocks may sink back into the mantle at subduction zones – Downward plunge of cold rocks gives rise to oceanic trenches ...
... more dense with distance from mid-oceanic ridge • When sufficiently cool and dense, these rocks may sink back into the mantle at subduction zones – Downward plunge of cold rocks gives rise to oceanic trenches ...
Thinning and Accretion of Deep Lithosphere in North China Block
... not immutable. The instability of the lithosphere may be closely related to the tremendous change in its structure, composition and rheology. The trigger and mechanism of lithospheric destabilization are the key to understanding the generation of intraplate magmatism, ore-forming processes and tecto ...
... not immutable. The instability of the lithosphere may be closely related to the tremendous change in its structure, composition and rheology. The trigger and mechanism of lithospheric destabilization are the key to understanding the generation of intraplate magmatism, ore-forming processes and tecto ...
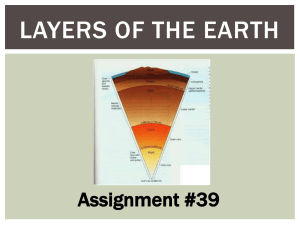
Inside Earth: Layers of the Earth
... tremendous pressure it is under from all of the other layers pushing down above it and gravity pulling all of Earth’s mass towards the center. The outer core is liquid nickel and iron. It is also extremely hot and surrounds the inner core and has an average thickness of about 2250 kilometers. Scien ...
... tremendous pressure it is under from all of the other layers pushing down above it and gravity pulling all of Earth’s mass towards the center. The outer core is liquid nickel and iron. It is also extremely hot and surrounds the inner core and has an average thickness of about 2250 kilometers. Scien ...
info
... Read through section 1c, and take down very general notes on the mantle (how it “works,” what it is made of, etc.). Use the dictionary on the left side of the screen to look up any unfamiliar terms. After completing the reading, answer one of the following two questions (do not answer both) 1. Based ...
... Read through section 1c, and take down very general notes on the mantle (how it “works,” what it is made of, etc.). Use the dictionary on the left side of the screen to look up any unfamiliar terms. After completing the reading, answer one of the following two questions (do not answer both) 1. Based ...
crust - River Dell Regional School District
... rock at the surface and partly liquid rock material below. When scientists understand the Earth’s structure, they can help predict when a geyser or a volcano will erupt, or how a river will change course over time. ...
... rock at the surface and partly liquid rock material below. When scientists understand the Earth’s structure, they can help predict when a geyser or a volcano will erupt, or how a river will change course over time. ...
Unit 3- Plate Tectonics - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... 10. Volcanic Mountain 11. Trench 12. Subduction Zone 13. Ridge/ Rise 14. Volcanic Island 15. Trench 16. Subduction Zone 17. Continental Crust 18. Oceanic Crust D ...
... 10. Volcanic Mountain 11. Trench 12. Subduction Zone 13. Ridge/ Rise 14. Volcanic Island 15. Trench 16. Subduction Zone 17. Continental Crust 18. Oceanic Crust D ...
12.710 – Problem Set 4 solutions 1. What is “the geothermal
... 11. Describe the three primary tectonic settings where volcanism occurs and discuss how differences in these settings result in different melting conditions, styles of volcanism and resulting melt compositions. Volcanism occurs at divergent margins (spreading ridges), convergent margins (subduction ...
... 11. Describe the three primary tectonic settings where volcanism occurs and discuss how differences in these settings result in different melting conditions, styles of volcanism and resulting melt compositions. Volcanism occurs at divergent margins (spreading ridges), convergent margins (subduction ...
Earth Science Chapter 5 - alisa25k
... • Blasts from the Earth have brought rocks from 100 ft to the surface ...
... • Blasts from the Earth have brought rocks from 100 ft to the surface ...
Numerical Simulation of the Thermal Convection and
... The Nusselt number (Nu) is defined by the ratio of the total heat transport to the conductive one through the layer. When convection occurs, heat is transported by both fluid motion and conduction, then Nu becomes more than one. Nu is the most important value for evaluating the total activity of the ...
... The Nusselt number (Nu) is defined by the ratio of the total heat transport to the conductive one through the layer. When convection occurs, heat is transported by both fluid motion and conduction, then Nu becomes more than one. Nu is the most important value for evaluating the total activity of the ...
The Earth`s Layers Foldable
... Challenge: Perhaps you have imagined digging a tunnel through the earth that comes out the other side. Figure it out ... How many kilometers would you have to dig? Show your work! ...
... Challenge: Perhaps you have imagined digging a tunnel through the earth that comes out the other side. Figure it out ... How many kilometers would you have to dig? Show your work! ...
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner
... Sonar is technology that uses sound waves to map the ocean floor. Magnetometers measure small magnetic changes in the ocean floor. The earth’s outer layer is broken into a series of large slabs of rock material called tectonic plates. These plates comprise the lithosphere, the outer most rigid layer ...
... Sonar is technology that uses sound waves to map the ocean floor. Magnetometers measure small magnetic changes in the ocean floor. The earth’s outer layer is broken into a series of large slabs of rock material called tectonic plates. These plates comprise the lithosphere, the outer most rigid layer ...
motions.of.tectonic.plates.activiity - wikifuller
... a. subduction zones c. convection currents b. transform faults d. divergent boundaries 2. The crust and upper mantle make up Earth's _____. a. lithosphere c. shield b. asthenosphere d. continents 3. The boundaries between two colliding plates are called _____. a. divergent c. a transform fault b. co ...
... a. subduction zones c. convection currents b. transform faults d. divergent boundaries 2. The crust and upper mantle make up Earth's _____. a. lithosphere c. shield b. asthenosphere d. continents 3. The boundaries between two colliding plates are called _____. a. divergent c. a transform fault b. co ...
Plate Tectonics Definition
... The volcanism stems from the unique manner at which subduction produces molten rock. Some of the ocean water trapped in the oceanic crust is brought down into the asthenosphere with it. Because of the higher temperature, the water evaporates from the oceanic crust and dissolves into the wedge of as ...
... The volcanism stems from the unique manner at which subduction produces molten rock. Some of the ocean water trapped in the oceanic crust is brought down into the asthenosphere with it. Because of the higher temperature, the water evaporates from the oceanic crust and dissolves into the wedge of as ...
Mantle plume
A mantle plume is a mechanism proposed in 1971 to explain volcanic regions of the earth that were not thought to be explicable by the then-new theory of plate tectonics. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, for example, Hawaii. Others represent unusually large-volume volcanism, whether on plate boundaries, e.g. Iceland, or basalt floods such as the Deccan or Siberian traps.A mantle plume is posited to exist where hot rock nucleates at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle becoming a diapir in the Earth's crust. The currently active volcanic centers are known as ""hot spots"". In particular, the concept that mantle plumes are fixed relative to one another, and anchored at the core-mantle boundary, was thought to provide a natural explanation for the time-progressive chains of older volcanoes seen extending out from some such hot spots, such as the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain.The hypothesis of mantle plumes from depth is not universally accepted as explaining all such volcanism. It has required progressive hypothesis-elaboration leading to variant propositions such as mini-plumes and pulsing plumes. Another hypothesis for unusual volcanic regions is the ""Plate model"". This proposes shallower, passive leakage of magma from the mantle onto the Earth's surface where extension of the lithosphere permits it, attributing most volcanism to plate tectonic processes, with volcanoes far from plate boundaries resulting from intraplate extension.