APS Continental Crust RLR.pptx
... Figure 15. Four tectonic settings for continental refining via relamination. In all cases, the relaminating layer may be thrust directly beneath existing crust, rise en bloc, perhaps in a "subduction channel", or rise as diapirs through the mantle wedge, depending on physical conditions. In all case ...
... Figure 15. Four tectonic settings for continental refining via relamination. In all cases, the relaminating layer may be thrust directly beneath existing crust, rise en bloc, perhaps in a "subduction channel", or rise as diapirs through the mantle wedge, depending on physical conditions. In all case ...
The India
... The India - Eurasia collision, Himalaya and the Tibetan plateau. Some important characteristics: • Very long duration of continental collision and shortening • Thickest crust and highest topography on earth ...
... The India - Eurasia collision, Himalaya and the Tibetan plateau. Some important characteristics: • Very long duration of continental collision and shortening • Thickest crust and highest topography on earth ...
Lecture 31
... If a system has experienced a decrease in U/Pb at some point in the past, its Pb isotopic composition will lie to the left of the Geochron; if its U/Pb ratio increased, its present Pb isotopic composition will lie to the right of the Geochron. U is more incompatible than Pb, so incompatible element ...
... If a system has experienced a decrease in U/Pb at some point in the past, its Pb isotopic composition will lie to the left of the Geochron; if its U/Pb ratio increased, its present Pb isotopic composition will lie to the right of the Geochron. U is more incompatible than Pb, so incompatible element ...
Chapter 3 Test Review
... continental drift? • A. the existence of convection currents • B. the matching of glacial grooves on ...
... continental drift? • A. the existence of convection currents • B. the matching of glacial grooves on ...
LECTURE-1 JEO253 PHYSICAL GEOLOGY OVERVIEW
... Transform Fault Boundaries • forms when two tectonic plates slide past one another. This type of boundary was proposed by ‘J. Tuzo Wilson’ (Canadian Geologist).There is no destruction or production of the lithosphere along a transform fault boundary. Transform faults are most common on the seafloor ...
... Transform Fault Boundaries • forms when two tectonic plates slide past one another. This type of boundary was proposed by ‘J. Tuzo Wilson’ (Canadian Geologist).There is no destruction or production of the lithosphere along a transform fault boundary. Transform faults are most common on the seafloor ...
Chapter 3
... Plate Boundaries • Convergent Plate Boundaries – Lithospheric plates move toward each other – Higher density oceanic crust overridden by low density continental crust – Subduction zone forms and produces a trench – Subduction of older oceanic crust balances the spreading seafloor equation – Subduct ...
... Plate Boundaries • Convergent Plate Boundaries – Lithospheric plates move toward each other – Higher density oceanic crust overridden by low density continental crust – Subduction zone forms and produces a trench – Subduction of older oceanic crust balances the spreading seafloor equation – Subduct ...
1 0 .
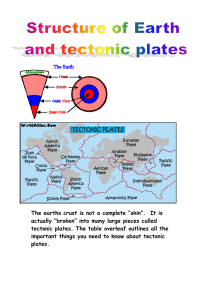
... 10. Lithosphere – Movements of Tectonic Plates The Earth’s Crust was divided into many segments – litospheric (tectonic) plates. These plates are moving. The speed of this movement is 1 – 5 cm per year. Crustal plates can converge, diverge, collide with each other, slide under each other or move hor ...
... 10. Lithosphere – Movements of Tectonic Plates The Earth’s Crust was divided into many segments – litospheric (tectonic) plates. These plates are moving. The speed of this movement is 1 – 5 cm per year. Crustal plates can converge, diverge, collide with each other, slide under each other or move hor ...
KEY
... D. polar wandering 13. Studies of past plate motions indicate that A. any two adjacent plates must move in the same direction, to avoid plates breaking up B. once they begin to move, plates always continue to move in the same direction C. plate movements have occurred for hundreds of millions, proba ...
... D. polar wandering 13. Studies of past plate motions indicate that A. any two adjacent plates must move in the same direction, to avoid plates breaking up B. once they begin to move, plates always continue to move in the same direction C. plate movements have occurred for hundreds of millions, proba ...
Geophysical and Geochemical Approaches
... continental slope. Our new data were supplemented at the landward end by data from an existing coincident wide-angle profile (Horsefield et al., 1994). Traveltime modelling of these data shows the presence of a 70 km region between thinned continental crust and anomaly 34 where velocities of 7.2-7.6 ...
... continental slope. Our new data were supplemented at the landward end by data from an existing coincident wide-angle profile (Horsefield et al., 1994). Traveltime modelling of these data shows the presence of a 70 km region between thinned continental crust and anomaly 34 where velocities of 7.2-7.6 ...
Chapter 2
... continent and as a result shows little geological activity – flat, lots of sediment, wide continental shelf ...
... continent and as a result shows little geological activity – flat, lots of sediment, wide continental shelf ...
The Layer`s Of The Earth! - Doral Academy Preparatory
... crust at the rate of 17 km3 per year, covering the ocean floor with an igneous rock called basalt. Hawaii and Iceland are two examples of the accumulation of basalt islands. • Continental crust: depth of 0-75 kilometres This is the outer part of the Earth composed essentially of crystalline rocks. T ...
... crust at the rate of 17 km3 per year, covering the ocean floor with an igneous rock called basalt. Hawaii and Iceland are two examples of the accumulation of basalt islands. • Continental crust: depth of 0-75 kilometres This is the outer part of the Earth composed essentially of crystalline rocks. T ...
Chapter 2
... Below the lithosphere, rock masses in the deeper mantle rise and fall according to differences in temperature and buoyancy. The densest lithosphere is most likely to sink back into the asthenosphere and the deeper mantle. Ocean floor and the continents are slowly moving (up to 12 cm/yr). ...
... Below the lithosphere, rock masses in the deeper mantle rise and fall according to differences in temperature and buoyancy. The densest lithosphere is most likely to sink back into the asthenosphere and the deeper mantle. Ocean floor and the continents are slowly moving (up to 12 cm/yr). ...
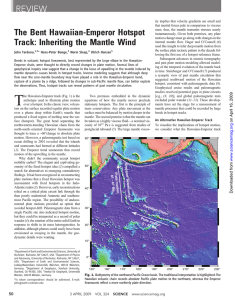
The Bent Hawaiian-Emperor Hotspot Track
... tion: Lord Howe Rise is locked to the Campbell which rifting of the lithosphere stimulates shallow contribute substantially to the mantle energy budPlateau between 84 and 47 million years ago mantle melting (20). The second is a “bottom-up” get (22). Below, we identify five physical pro(Ma). Moreove ...
... tion: Lord Howe Rise is locked to the Campbell which rifting of the lithosphere stimulates shallow contribute substantially to the mantle energy budPlateau between 84 and 47 million years ago mantle melting (20). The second is a “bottom-up” get (22). Below, we identify five physical pro(Ma). Moreove ...
Chapter 10 Volcanoes and other Igneous Activity Section 10.1
... ___________________________ plate boundaries. Some volcanoes form far from plate boundaries above ________________________ in the crust. ...
... ___________________________ plate boundaries. Some volcanoes form far from plate boundaries above ________________________ in the crust. ...
by William J. Crornie Rapidly developing technologies are
... traced such a fault 70 kilometers into the crust, slanting down to a depth of 25 kilometers. Such a situation provides an exceptionally clear look through the seismic window; geologists do not have to guess what kind of boundary reflects the seismic energy because boundary rock is exposed at the sur ...
... traced such a fault 70 kilometers into the crust, slanting down to a depth of 25 kilometers. Such a situation provides an exceptionally clear look through the seismic window; geologists do not have to guess what kind of boundary reflects the seismic energy because boundary rock is exposed at the sur ...
The origin and occurrence of
... much less than expected for oceanic lithosphere post-plume or ‘super-plume’ (Tejada et al. 2004). Seismic tomography shows a 300km tail from the OJP into the upper mantle (Ingle & Coffin, 2004). There is still however evidence for plume activity in a geochemical sense, the OJP basalts contain enough ...
... much less than expected for oceanic lithosphere post-plume or ‘super-plume’ (Tejada et al. 2004). Seismic tomography shows a 300km tail from the OJP into the upper mantle (Ingle & Coffin, 2004). There is still however evidence for plume activity in a geochemical sense, the OJP basalts contain enough ...
Interactive comment on “Energy of plate tectonics calculation and
... matter. The heat of mantle convection is what drives the tectonic plates. The following are sample paragraphs extracted from the submitted manuscript: REPLY: You are ignoring the work done to deform the mantle – this is an essential part of the energy balance of plate tectonics. AUTHOR: I respectful ...
... matter. The heat of mantle convection is what drives the tectonic plates. The following are sample paragraphs extracted from the submitted manuscript: REPLY: You are ignoring the work done to deform the mantle – this is an essential part of the energy balance of plate tectonics. AUTHOR: I respectful ...
Continental Drift
... zone of intensely shattered rock numerous shallow earthquakes connect two oceanic ridge segments and are at fracture zones ...
... zone of intensely shattered rock numerous shallow earthquakes connect two oceanic ridge segments and are at fracture zones ...
Chapter 7
... 41. The ridge in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean formed along a ____________________ boundary. (convergent or divergent) 42. Anticlines and synclines are the result of ____________________. (faults or folding) 43. The center of the Earth is called the ____________________. 44. Earth's ____________ ...
... 41. The ridge in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean formed along a ____________________ boundary. (convergent or divergent) 42. Anticlines and synclines are the result of ____________________. (faults or folding) 43. The center of the Earth is called the ____________________. 44. Earth's ____________ ...
The complicated birth of a volcano: Researchers unravel
... types of fire mountains. One type is generated where tectonic plates meet, so the earth's crust is already cracked to begin with. The other type is formed within the earth's plates. "The latter are called intraplate volcanoes. They are often found above a so-called mantle plume. Hot material rises f ...
... types of fire mountains. One type is generated where tectonic plates meet, so the earth's crust is already cracked to begin with. The other type is formed within the earth's plates. "The latter are called intraplate volcanoes. They are often found above a so-called mantle plume. Hot material rises f ...
Mantle plume
A mantle plume is a mechanism proposed in 1971 to explain volcanic regions of the earth that were not thought to be explicable by the then-new theory of plate tectonics. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, for example, Hawaii. Others represent unusually large-volume volcanism, whether on plate boundaries, e.g. Iceland, or basalt floods such as the Deccan or Siberian traps.A mantle plume is posited to exist where hot rock nucleates at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle becoming a diapir in the Earth's crust. The currently active volcanic centers are known as ""hot spots"". In particular, the concept that mantle plumes are fixed relative to one another, and anchored at the core-mantle boundary, was thought to provide a natural explanation for the time-progressive chains of older volcanoes seen extending out from some such hot spots, such as the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain.The hypothesis of mantle plumes from depth is not universally accepted as explaining all such volcanism. It has required progressive hypothesis-elaboration leading to variant propositions such as mini-plumes and pulsing plumes. Another hypothesis for unusual volcanic regions is the ""Plate model"". This proposes shallower, passive leakage of magma from the mantle onto the Earth's surface where extension of the lithosphere permits it, attributing most volcanism to plate tectonic processes, with volcanoes far from plate boundaries resulting from intraplate extension.