Why are Low Impedance Microphones Better Than High
... To do this we first need a circuit model (and then math model) of how a microphone works together with the amplifier it plugs into. So, first there is the microphone... whose job it is to generate a wiggling voltage... so it is a time-varying voltage source... and because it is not an ideal source i ...
... To do this we first need a circuit model (and then math model) of how a microphone works together with the amplifier it plugs into. So, first there is the microphone... whose job it is to generate a wiggling voltage... so it is a time-varying voltage source... and because it is not an ideal source i ...
EMC Components and Filters
... loss depends on source and load impedance Design performance achieved if system is matched L and C are reflective components R is Lossy, or absorptive ...
... loss depends on source and load impedance Design performance achieved if system is matched L and C are reflective components R is Lossy, or absorptive ...
RC and RL circuits. Given the following circuit with Vin = 10V sin(ωt
... against the log(ω) for ω = 10 to 109 rad/s. c) If the voltage across the capacitor is used as the output signal, Plot the gain of the circuit (Vc / Vin) against ω. The choice of log or linear is up to you, defend your choice based on the information it shows clearly. d) same question as c) but for V ...
... against the log(ω) for ω = 10 to 109 rad/s. c) If the voltage across the capacitor is used as the output signal, Plot the gain of the circuit (Vc / Vin) against ω. The choice of log or linear is up to you, defend your choice based on the information it shows clearly. d) same question as c) but for V ...
review_00
... (a) Write an expression for the incident electric field (phasor form). (b) Write an expression for the reflected electric field (phasor form) in the air. ...
... (a) Write an expression for the incident electric field (phasor form). (b) Write an expression for the reflected electric field (phasor form) in the air. ...
return loss
... We can model just about any RF transmission line situation with three components: a signal source (the output of an amp, tap, modulator), transmission medium (coaxial cable) and a termination (input to a tap, amp, cable modem, etc.). If the impedances of all three are exactly the same, all power tra ...
... We can model just about any RF transmission line situation with three components: a signal source (the output of an amp, tap, modulator), transmission medium (coaxial cable) and a termination (input to a tap, amp, cable modem, etc.). If the impedances of all three are exactly the same, all power tra ...
Lab 3: RLC Circuits - Weber State University
... identify a “final” steady state value. Instead we define the settling time (ts) to be the amount of time it takes the voltage/current to settle to within a defined error (ε) of the final value.It is approximately the time taken by Vo to reach 10% of its final value. ...
... identify a “final” steady state value. Instead we define the settling time (ts) to be the amount of time it takes the voltage/current to settle to within a defined error (ε) of the final value.It is approximately the time taken by Vo to reach 10% of its final value. ...
PowerPoint 프레젠테이션
... Control Input Impedance: 4.7kΩ to +5V (2-wire mode), >1MΩ (3-wire mode) Logic Output Voltage: 0 or +5V unloaded Logic Output Impedance: 440Ωs Logic Output Current: 10mA source, 60mA sink Watchdog Output: Phoenix/Combicon connector for failsafe control Opto Output Current: 14mA maximum Withstanding V ...
... Control Input Impedance: 4.7kΩ to +5V (2-wire mode), >1MΩ (3-wire mode) Logic Output Voltage: 0 or +5V unloaded Logic Output Impedance: 440Ωs Logic Output Current: 10mA source, 60mA sink Watchdog Output: Phoenix/Combicon connector for failsafe control Opto Output Current: 14mA maximum Withstanding V ...
7154 VFD - Cincinnati State
... terminals and acts as an impedance matching network. The snubber components are carefully selected to cause the load impedance to match the characteristic impedance of the motor cables. When the motor surge impedance is equal to the line characteristic impedance, then voltage reflection does not occ ...
... terminals and acts as an impedance matching network. The snubber components are carefully selected to cause the load impedance to match the characteristic impedance of the motor cables. When the motor surge impedance is equal to the line characteristic impedance, then voltage reflection does not occ ...
Dual impedance digital multimeters
... today for testing industrial, electrical, and electronic systems have high impedance input circuits greater than 1 megohm. In simple terms this means that when the DMM is placed across a circuit for a measurement, it will have little impact on circuit performance. This is the desired effect for ...
... today for testing industrial, electrical, and electronic systems have high impedance input circuits greater than 1 megohm. In simple terms this means that when the DMM is placed across a circuit for a measurement, it will have little impact on circuit performance. This is the desired effect for ...
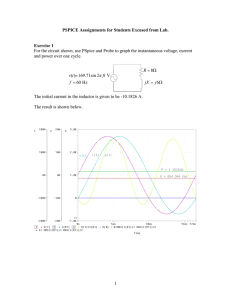
PSpiceAssignments1
... loads that are connected in parallel. The first load is Y-connected and has an impedance of 30 + j40 /phase. The second load is delta connected and has an impedance of 60 j45 /phase. The line is energized at the sending-end from a 3-phase balanced supply of line to neutral voltage Van 2000 V (r ...
... loads that are connected in parallel. The first load is Y-connected and has an impedance of 30 + j40 /phase. The second load is delta connected and has an impedance of 60 j45 /phase. The line is energized at the sending-end from a 3-phase balanced supply of line to neutral voltage Van 2000 V (r ...
Introduction to MOS Transistor
... RB must be much larger than RP, the parallel equivalent resistance Of RS. Otherwise, RB will load the input match network! ...
... RB must be much larger than RP, the parallel equivalent resistance Of RS. Otherwise, RB will load the input match network! ...
Term 2 and 3 revision notes - The Random Information Bureau
... Zpu is the aspect ratio (length-to-width ratio) of the pull-up device. Zpd is the aspect ratio of the pull-down device. VTd is the threshold voltage of the depletion mode device (pull-up) VTe is the threshold voltage of the enhancement mode device (pull-down) Vinv is the cross-over voltage of the in ...
... Zpu is the aspect ratio (length-to-width ratio) of the pull-up device. Zpd is the aspect ratio of the pull-down device. VTd is the threshold voltage of the depletion mode device (pull-up) VTe is the threshold voltage of the enhancement mode device (pull-down) Vinv is the cross-over voltage of the in ...
EL6413 Catalog Description
... transistors, biasing, and temperature compensation techniques. Physics, models, and biasing for field-effect transistors. General treatment of nonlinear controlled sources. High frequency models. Single and multistage broadband small signal amplifiers. Harmonic distortion analysis of amplifiers. Emi ...
... transistors, biasing, and temperature compensation techniques. Physics, models, and biasing for field-effect transistors. General treatment of nonlinear controlled sources. High frequency models. Single and multistage broadband small signal amplifiers. Harmonic distortion analysis of amplifiers. Emi ...
RCL Worksheet Key
... reactance of 415 Ω. The current in the circuit is 0.233 A. What is the voltage of the generator? REASONING The voltage supplied by the generator can be found from the equation: Vrms I rms Z . The value of I rms is given in the problem statement, so we must obtain the impedance of the circuit. SOLU ...
... reactance of 415 Ω. The current in the circuit is 0.233 A. What is the voltage of the generator? REASONING The voltage supplied by the generator can be found from the equation: Vrms I rms Z . The value of I rms is given in the problem statement, so we must obtain the impedance of the circuit. SOLU ...
Lab 10 - ece.unm.edu
... The common collector amplifier as shown in Figure 10-1 is one of the most useful small-signal amplifier configurations. The same biasing scheme and frequency response approximation technique as used for the common emitter amplifier can also be used for the common collector amplifier. The only change ...
... The common collector amplifier as shown in Figure 10-1 is one of the most useful small-signal amplifier configurations. The same biasing scheme and frequency response approximation technique as used for the common emitter amplifier can also be used for the common collector amplifier. The only change ...
Nominal impedance
Nominal impedance in electrical engineering and audio engineering refers to the approximate designed impedance of an electrical circuit or device. The term is applied in a number of different fields, most often being encountered in respect of:The nominal value of the characteristic impedance of a cable or other form of transmission line.The nominal value of the input, output or image impedance of a port of a network, especially a network intended for use with a transmission line, such as filters, equalisers and amplifiers.The nominal value of the input impedance of a radio frequency antennaThe actual impedance may vary quite considerably from the nominal figure with changes in frequency. In the case of cables and other transmission lines, there is also variation along the length of the cable, if it is not properly terminated. It is usual practice to speak of nominal impedance as if it were a constant resistance, that is, it is invariant with frequency and has a zero reactive component, despite this often being far from the case. Depending on the field of application, nominal impedance is implicitly referring to a specific point on the frequency response of the circuit under consideration. This may be at low-frequency, mid-band or some other point and specific applications are discussed in the sections below.In most applications, there are a number of values of nominal impedance that are recognised as being standard. The nominal impedance of a component or circuit is often assigned one of these standard values, regardless of whether the measured impedance exactly corresponds to it. The item is assigned the nearest standard value.