Document
... Diode termination works as follows. Since the impedance of a diode changes dynamically with current, it is possible to dynamically match the impedance of a transmission line. In practice, however, diode termination can be difficult to implement. Very fast diodes are required and nonlinear effects ca ...
... Diode termination works as follows. Since the impedance of a diode changes dynamically with current, it is possible to dynamically match the impedance of a transmission line. In practice, however, diode termination can be difficult to implement. Very fast diodes are required and nonlinear effects ca ...
1422-1 Resonance and Filters - Cleveland Institute of Electronics
... Record the value in the Exp. 4, data table NOTE: Under the best of laboratory conditions, the impedance at resonance is difficult to measure. A realistic ratio between the calculated impedance and the impedance measured above is ...
... Record the value in the Exp. 4, data table NOTE: Under the best of laboratory conditions, the impedance at resonance is difficult to measure. A realistic ratio between the calculated impedance and the impedance measured above is ...
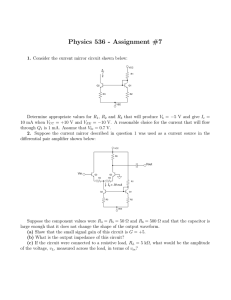
Physics 536 - Assignment #6 - Due March 19
... .MODEL ANOTHERJFET NJF(VTO=-4V IS=1NA BETA=0.00125 CGS=2P CGD=2P) which has IDSS ≈ 20 mA and VP = −4 V. The voltage source, Vin (t) has a peak-to-peak amplitude of 10 mV and a frequency of 10 kHz, modelled using VIN 5 0 DC 0 SIN(0 0.01V 10KHZ) and where R1 = 10 kΩ represents the large output impedan ...
... .MODEL ANOTHERJFET NJF(VTO=-4V IS=1NA BETA=0.00125 CGS=2P CGD=2P) which has IDSS ≈ 20 mA and VP = −4 V. The voltage source, Vin (t) has a peak-to-peak amplitude of 10 mV and a frequency of 10 kHz, modelled using VIN 5 0 DC 0 SIN(0 0.01V 10KHZ) and where R1 = 10 kΩ represents the large output impedan ...
Physics 160 Lecture 6
... The output should be biased at roughly half of the supply voltage. Assume a 1 kohm source impedance. Design to a 2.5 mA quiescent current. Check that the gain with the stated source impedance is at least 95%. ...
... The output should be biased at roughly half of the supply voltage. Assume a 1 kohm source impedance. Design to a 2.5 mA quiescent current. Check that the gain with the stated source impedance is at least 95%. ...
High Frequency Pulse Generator
... two output signals proportional to unit volume while maintaining a mechanical meter-to-register link. Signal outputs are electrically 90° out-of-phase and are used primarily for pulse security. Although designed for use in meter proving, the Dual Phase Generator can be used on any application requir ...
... two output signals proportional to unit volume while maintaining a mechanical meter-to-register link. Signal outputs are electrically 90° out-of-phase and are used primarily for pulse security. Although designed for use in meter proving, the Dual Phase Generator can be used on any application requir ...
5 Model Input power requirements Output Voltage / Current ranges
... Voltage Sense: Measured between Voltage Sense and Return, reads actual voltage. Not energized until TEST button is pressed. Reads voltages up to 1000V. Channels C, D, E and F. Note: Voltage sense terminals are inoperative for the ITU-T Power Induction Test circuit. Voltage readings must be made at t ...
... Voltage Sense: Measured between Voltage Sense and Return, reads actual voltage. Not energized until TEST button is pressed. Reads voltages up to 1000V. Channels C, D, E and F. Note: Voltage sense terminals are inoperative for the ITU-T Power Induction Test circuit. Voltage readings must be made at t ...
Line Diagrams And The Per Unit System
... transformer, capacitors, bus bars, and conductors are shown by standized schematic symbols. Instead of representing each of three phases with a separate line or terminal, only one conductor is represented. It is a form of block diagram graphically depicting the paths for power flow between entities ...
... transformer, capacitors, bus bars, and conductors are shown by standized schematic symbols. Instead of representing each of three phases with a separate line or terminal, only one conductor is represented. It is a form of block diagram graphically depicting the paths for power flow between entities ...
Lab 4 - ece.unm.edu
... and common drain (CD) configurations. These two circuits are shown in Figures 14-1 and 14-2 respectively. The common source and common drain amplifiers, like all MOSFET amplifiers, have the characteristic of high input impedance. The value of the input impedance for both amplifiers is basically limi ...
... and common drain (CD) configurations. These two circuits are shown in Figures 14-1 and 14-2 respectively. The common source and common drain amplifiers, like all MOSFET amplifiers, have the characteristic of high input impedance. The value of the input impedance for both amplifiers is basically limi ...
RF Transmission Lines and Antennas
... 1. Regardless of their lengths, all transmission lines have resistance, inductance and capacitance. These can be combined and are called impedance. Resistance is simply the DC resistance of wire. Inductance is resistance to an AC voltage. Capacitance is resistance to AC current. These definitions ar ...
... 1. Regardless of their lengths, all transmission lines have resistance, inductance and capacitance. These can be combined and are called impedance. Resistance is simply the DC resistance of wire. Inductance is resistance to an AC voltage. Capacitance is resistance to AC current. These definitions ar ...
Transistor Switch and Emitter Follower Phys 3610/6610 Lab 18 Student: TA:
... Transistor Switch and Emitter Follower Use a 0 to 5 V, 1 kHz square wave as input for your circuit in this lab. Task 1: Using a npn-transistor, a simple transistor switch can be constructed as in : +5V ...
... Transistor Switch and Emitter Follower Use a 0 to 5 V, 1 kHz square wave as input for your circuit in this lab. Task 1: Using a npn-transistor, a simple transistor switch can be constructed as in : +5V ...
ee4222
... Familiarity with generation of positive, negative, and zero sequence bus impedance matrices. ...
... Familiarity with generation of positive, negative, and zero sequence bus impedance matrices. ...
Nominal impedance
Nominal impedance in electrical engineering and audio engineering refers to the approximate designed impedance of an electrical circuit or device. The term is applied in a number of different fields, most often being encountered in respect of:The nominal value of the characteristic impedance of a cable or other form of transmission line.The nominal value of the input, output or image impedance of a port of a network, especially a network intended for use with a transmission line, such as filters, equalisers and amplifiers.The nominal value of the input impedance of a radio frequency antennaThe actual impedance may vary quite considerably from the nominal figure with changes in frequency. In the case of cables and other transmission lines, there is also variation along the length of the cable, if it is not properly terminated. It is usual practice to speak of nominal impedance as if it were a constant resistance, that is, it is invariant with frequency and has a zero reactive component, despite this often being far from the case. Depending on the field of application, nominal impedance is implicitly referring to a specific point on the frequency response of the circuit under consideration. This may be at low-frequency, mid-band or some other point and specific applications are discussed in the sections below.In most applications, there are a number of values of nominal impedance that are recognised as being standard. The nominal impedance of a component or circuit is often assigned one of these standard values, regardless of whether the measured impedance exactly corresponds to it. The item is assigned the nearest standard value.