ppt
... Rocks are volcanic in origin. Basalts similar to those on Earth, rich in iron and magnesium and containing glassy structures characteristic of rapid cooling. However, lunar basalts contain no water and a lower percentage of volatiles relative to refractories. ...
... Rocks are volcanic in origin. Basalts similar to those on Earth, rich in iron and magnesium and containing glassy structures characteristic of rapid cooling. However, lunar basalts contain no water and a lower percentage of volatiles relative to refractories. ...
Sources of information about plate tectonics
... Sources of information about plate tectonics 1. Inside the Earth (www.iris.edu/hq/inclass/animation/layers_of_the_earth) Video explaining the Earth’s structure and how the crust is often mistaken for the tectonic plates. ...
... Sources of information about plate tectonics 1. Inside the Earth (www.iris.edu/hq/inclass/animation/layers_of_the_earth) Video explaining the Earth’s structure and how the crust is often mistaken for the tectonic plates. ...
Geographic Influences on Identity
... http://study.com/academy/lesson/what-are-convection-currents-definitionexamples-quiz.html ...
... http://study.com/academy/lesson/what-are-convection-currents-definitionexamples-quiz.html ...
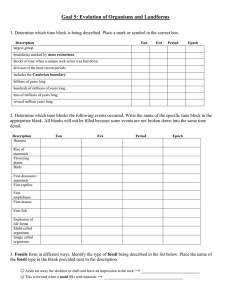
Goal 5: Evolution of Organisms and Landforms
... boundaries marked by mass extinctions blocks of time when a unique rock series was laid down division of the most recent periods includes the Cambrian boundary billions of years long hundreds of millions of years long tens of millions of years long ...
... boundaries marked by mass extinctions blocks of time when a unique rock series was laid down division of the most recent periods includes the Cambrian boundary billions of years long hundreds of millions of years long tens of millions of years long ...
Changing Earth Study Guide
... VI. How the Earth’s Surface Has Changed (C22-25) a. The Theory of ...
... VI. How the Earth’s Surface Has Changed (C22-25) a. The Theory of ...
What is the difference between geocentric and heliocentric theories?
... views of the time, he underwent many trials and tribulations, and was even sentenced to house arrest for his remaining years. • His view has withstood the test of time. • Today we talk about our Solar System, not our Earth system ...
... views of the time, he underwent many trials and tribulations, and was even sentenced to house arrest for his remaining years. • His view has withstood the test of time. • Today we talk about our Solar System, not our Earth system ...
How The Earth Works
... Precession and Orbit Variations (Ice Ages?) Galactic (250 m.y. period) Unpredictable Events – Nearby Supernovae – Meteor Impacts ...
... Precession and Orbit Variations (Ice Ages?) Galactic (250 m.y. period) Unpredictable Events – Nearby Supernovae – Meteor Impacts ...
Earth Outline
... h. Plates can crush together, scrape past each other or bend along boundaries. i. The places where the crust moves are called______________ . j. An instrument called a ____________________is used to measure the magnitude of an earthquake. The numbers on the ____________ ________ describe the magnitu ...
... h. Plates can crush together, scrape past each other or bend along boundaries. i. The places where the crust moves are called______________ . j. An instrument called a ____________________is used to measure the magnitude of an earthquake. The numbers on the ____________ ________ describe the magnitu ...
0004_EarthProcesses
... formed from the weathered material carried by water, wind, or ice most common rocks in the upper crust cover over 2/3 of the earth’s surface sandstone, shale, and limestone ...
... formed from the weathered material carried by water, wind, or ice most common rocks in the upper crust cover over 2/3 of the earth’s surface sandstone, shale, and limestone ...
Earth`s Landforms
... Continents and ocean floors form the top of these plates=move and carry continents and ocean floors with them ...
... Continents and ocean floors form the top of these plates=move and carry continents and ocean floors with them ...
Geologic Principles and Relative Dating
... a. ________________________________________________________ to the ages of other rock or events in the geological sequence b. Saying “ ________________________________________________” shows its age relative to a known. c. This means that geologists can say which layers are older than which and thus ...
... a. ________________________________________________________ to the ages of other rock or events in the geological sequence b. Saying “ ________________________________________________” shows its age relative to a known. c. This means that geologists can say which layers are older than which and thus ...
Chapter 5 Plate Tectonics-Section 1 Earth`s Interior Exploring Inside
... inside Earth where these rocks formed. In addition, forces inside Earth sometimes blast rock to the surface from depths of more than 100 kilometers. These rocks provide more information about the interior. Evidence From Seismic Waves- To study Earth’s interior, geologists use seismic waves. When ear ...
... inside Earth where these rocks formed. In addition, forces inside Earth sometimes blast rock to the surface from depths of more than 100 kilometers. These rocks provide more information about the interior. Evidence From Seismic Waves- To study Earth’s interior, geologists use seismic waves. When ear ...
Plate Tectonics Crossword
... 4. ______________ zones. Places where the seafloor is forced under continental plates. 5. Section of the Earth below the crust. 7. Paleontologists noticed that these were the same on different continents even though the continents were separated by oceans. 9. Source of heat in the mantle. 11. Seaflo ...
... 4. ______________ zones. Places where the seafloor is forced under continental plates. 5. Section of the Earth below the crust. 7. Paleontologists noticed that these were the same on different continents even though the continents were separated by oceans. 9. Source of heat in the mantle. 11. Seaflo ...
Plate Tectonics Journey to the center of the Earth
... 22. When a liquid or gas is heated, the particles move __________ and spread apart. Therefore, the particles occupy more space. 23. What three factors set convection current in motion? a. ____________ and ____________ of the fluid b. Changes in the fluid’s ______________ c. Force of _____________ 24 ...
... 22. When a liquid or gas is heated, the particles move __________ and spread apart. Therefore, the particles occupy more space. 23. What three factors set convection current in motion? a. ____________ and ____________ of the fluid b. Changes in the fluid’s ______________ c. Force of _____________ 24 ...
Lecture 12
... Uranium mining established in the late 1940ies. Mining for Uranium mineral Uranium Vanadate Slightly lower fraction of 235U isotope component 0.717% compared to the average of 0.720% in local deposition. A natural reactor needs an enrichment of 235U of up to 3% over a distance a 70 cm to thermalize ...
... Uranium mining established in the late 1940ies. Mining for Uranium mineral Uranium Vanadate Slightly lower fraction of 235U isotope component 0.717% compared to the average of 0.720% in local deposition. A natural reactor needs an enrichment of 235U of up to 3% over a distance a 70 cm to thermalize ...
Chapter 1-3
... o States that the crust in not an unbroken shell but consists of plates Huge slabs of rock that move Floating on liquid rock just below the crust Move in different directions ...
... o States that the crust in not an unbroken shell but consists of plates Huge slabs of rock that move Floating on liquid rock just below the crust Move in different directions ...
Evolution _2 Relative Dating
... the older rock layers end up at the bottom of the sequence and the newer ones toward the top. The arrow shows the relative order of the rock layers from earliest to most recent. ...
... the older rock layers end up at the bottom of the sequence and the newer ones toward the top. The arrow shows the relative order of the rock layers from earliest to most recent. ...
Note Packet
... Life and Evolution: Variations in Fossils and Environments •Evidence from the ______________________ (preserved in sedimentary rocks) shows that a wide variety of life forms have lived in Earth’s changing environments over time. •The comparisons of fossil remains and ______________________________ e ...
... Life and Evolution: Variations in Fossils and Environments •Evidence from the ______________________ (preserved in sedimentary rocks) shows that a wide variety of life forms have lived in Earth’s changing environments over time. •The comparisons of fossil remains and ______________________________ e ...
Chapter 1.2-Spheres
... 6th : Once your piles are set, raise your hand and I will come over to check your work. 7th: When all groups are finished you will receive ...
... 6th : Once your piles are set, raise your hand and I will come over to check your work. 7th: When all groups are finished you will receive ...
Quiz # 7
... d. earthquakes are caused by huge waves that come up from inside the molten core of the Earth e. slow motions within the mantle of the Earth slowly move large sections of the crust around __E__ 2. The most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere is a. oxygen b. ozone c. water vapor d. argon e. nitrog ...
... d. earthquakes are caused by huge waves that come up from inside the molten core of the Earth e. slow motions within the mantle of the Earth slowly move large sections of the crust around __E__ 2. The most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere is a. oxygen b. ozone c. water vapor d. argon e. nitrog ...
Test Review Quiz B
... A series of processes on Earth’s surface and interior that slowly changes rocks from one kind to another is called a. Erosion c. Crystallization b. Deposition d. The rock cycle Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of minerals? a. Definite crystalline structure. b. Solid c. Naturally occurr ...
... A series of processes on Earth’s surface and interior that slowly changes rocks from one kind to another is called a. Erosion c. Crystallization b. Deposition d. The rock cycle Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of minerals? a. Definite crystalline structure. b. Solid c. Naturally occurr ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.