IGNEOUS
... *Form when rocks weather, erode, deposit, compact and cement together. *Have thicker layers that are loosely compacted. *Often dull in luster and can break easily. *Can have fossils in them. *Clastic- made of rock fragments / sediment. *Organic- made of remains of plants and animals *Chemical- made ...
... *Form when rocks weather, erode, deposit, compact and cement together. *Have thicker layers that are loosely compacted. *Often dull in luster and can break easily. *Can have fossils in them. *Clastic- made of rock fragments / sediment. *Organic- made of remains of plants and animals *Chemical- made ...
Shifting Continents and Climates S
... levels of carbon dioxide and other greenrupted atmospheric circulation and trigthe rise of the Asian monsoons. house gases in the atmosphere (at least until gered a cascade of other climate changes. the anomalous and very recent post-Industrial “Understanding the links between solid and Revolution e ...
... levels of carbon dioxide and other greenrupted atmospheric circulation and trigthe rise of the Asian monsoons. house gases in the atmosphere (at least until gered a cascade of other climate changes. the anomalous and very recent post-Industrial “Understanding the links between solid and Revolution e ...
Restless Continents
... the magnetic field of the Earth. • As the magnetic field reverses and the ocean and new ocean floor is formed it leaves a record of this change. ...
... the magnetic field of the Earth. • As the magnetic field reverses and the ocean and new ocean floor is formed it leaves a record of this change. ...
Plate Tectonics - Faculty Perry, Oklahoma
... The layer in Earth’s upper mantle and directly under the lithosphere in which rock is soft and weak because it is close to melting. ...
... The layer in Earth’s upper mantle and directly under the lithosphere in which rock is soft and weak because it is close to melting. ...
Inside the Earth - Londonderry NH School District
... • Parts are semimolten (silly putty) • 1800 miles thick • Mantle rock is more dense than crustal rock • Flows in sluggish currents • Between crust and outer core ...
... • Parts are semimolten (silly putty) • 1800 miles thick • Mantle rock is more dense than crustal rock • Flows in sluggish currents • Between crust and outer core ...
mp1grade5wkst18
... Mercury is the closest planet to the sun . Mercury is a very small planet. There is no life on Mercury. http://www.schoollasti cs.com ...
... Mercury is the closest planet to the sun . Mercury is a very small planet. There is no life on Mercury. http://www.schoollasti cs.com ...
Grade 7
... Students explain interactions between the Earth’s lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. Describe the interior composition of the Earth, including its core, mantle, and crust. Examine how the formation, weathering, sedimentation and reformation of rock constitute a continuing rock ...
... Students explain interactions between the Earth’s lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. Describe the interior composition of the Earth, including its core, mantle, and crust. Examine how the formation, weathering, sedimentation and reformation of rock constitute a continuing rock ...
BUGS Rocks Station 1 Plate Tectonics and the Rock Cycle
... plates bump into each other (subduction, collision, seafloor spreading, and transform fault have the students do the hand motions as you define these terms). Explain how these plates bump into each other helps the earth to move the rock around. The earth is a great rock recycler. Using the rock cycl ...
... plates bump into each other (subduction, collision, seafloor spreading, and transform fault have the students do the hand motions as you define these terms). Explain how these plates bump into each other helps the earth to move the rock around. The earth is a great rock recycler. Using the rock cycl ...
section 1 - image identification
... The catastrophic earthquake that hit Izmit, Turkey on August 17, 1999 – which claimed the lives of over 18,000 people – was caused by movement of a nearby ________. Does mountain glaciation tend to produce smooth, rounded mountain peaks? Do meandering rivers make stable and unchanging boundari ...
... The catastrophic earthquake that hit Izmit, Turkey on August 17, 1999 – which claimed the lives of over 18,000 people – was caused by movement of a nearby ________. Does mountain glaciation tend to produce smooth, rounded mountain peaks? Do meandering rivers make stable and unchanging boundari ...
Article - Cross Section of the Earth
... dense rock basalt. Continental plates and the continents themselves contain large amounts of granite. Below the lithosphere is the asthenosphere, a partly molten layer in the upper mantle. The temperature of the asthenosphere varies throughout. Geologists believe that this is because large quantitie ...
... dense rock basalt. Continental plates and the continents themselves contain large amounts of granite. Below the lithosphere is the asthenosphere, a partly molten layer in the upper mantle. The temperature of the asthenosphere varies throughout. Geologists believe that this is because large quantitie ...
File
... Part III: Read each question carefully and then choose the BEST answer. 9. Compared to rocks in the Earth’s crust, rocks in the mantle are more what? a. Mineral-rich b. Light c. Dense 10. What are tectonic plates? a. Pieces of the lithosphere that move on top of the asthenosphere b. Broken pieces of ...
... Part III: Read each question carefully and then choose the BEST answer. 9. Compared to rocks in the Earth’s crust, rocks in the mantle are more what? a. Mineral-rich b. Light c. Dense 10. What are tectonic plates? a. Pieces of the lithosphere that move on top of the asthenosphere b. Broken pieces of ...
The Interior of Earth
... Lithosphere - Solid (Rest of mantel + crust) o Crust – silicate – least dense History o Earth was molten o More dense materials sunk below (iron and nickel – became core) o Silicate rocks were buoyed up (floated) o This process when material is separated called differentiation All planets are diff ...
... Lithosphere - Solid (Rest of mantel + crust) o Crust – silicate – least dense History o Earth was molten o More dense materials sunk below (iron and nickel – became core) o Silicate rocks were buoyed up (floated) o This process when material is separated called differentiation All planets are diff ...
Jeopardy - Newton.k12.ma.us
... of technology was available to him that helped him prove his theory? ...
... of technology was available to him that helped him prove his theory? ...
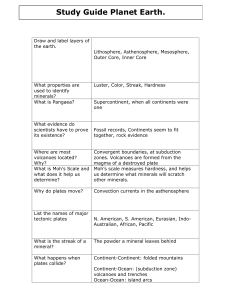
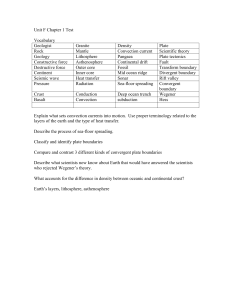
Unit F Chapter 1 Test
... Describe the process of sea-floor spreading. Classify and identify plate boundaries Compare and contrast 3 different kinds of convergent plate boundaries Describe what scientists now know about Earth that would have answered the scientists who rejected Wegener’s theory. What accounts for the differe ...
... Describe the process of sea-floor spreading. Classify and identify plate boundaries Compare and contrast 3 different kinds of convergent plate boundaries Describe what scientists now know about Earth that would have answered the scientists who rejected Wegener’s theory. What accounts for the differe ...
Energy Rich, Coal is plentiful in US, Easy to transport
... Clues from Igneous Rock: igneous rocks come from when magma or lava hardens. Lava that hardens on the surface s an extrusion. Sometimes magma pushes into rocks from below this is called an intrusion. The intrusion is younger than the rocks around it. Clues from Faults: A fault is a break in the crus ...
... Clues from Igneous Rock: igneous rocks come from when magma or lava hardens. Lava that hardens on the surface s an extrusion. Sometimes magma pushes into rocks from below this is called an intrusion. The intrusion is younger than the rocks around it. Clues from Faults: A fault is a break in the crus ...
Overview of the Big Questions in Physical Geology
... What is a rock? What is a mineral?A rock can be made of one or more minerals. An example of a singlemineral rock would be rock salt, or halite (the mineral). Most rocks are made of groups of minerals (igneous and metamorphic rocks) or particles of other rocks (sedimentary rocks). A mineral is a natu ...
... What is a rock? What is a mineral?A rock can be made of one or more minerals. An example of a singlemineral rock would be rock salt, or halite (the mineral). Most rocks are made of groups of minerals (igneous and metamorphic rocks) or particles of other rocks (sedimentary rocks). A mineral is a natu ...
Dimensions of the Earth
... The Earth bulges slightly at the equator and flattens slightly at the poles. Evidence of the Earth’s shape? Ships “sink” when moving past the horizon Satellite photographs Moon phases and lunar eclipses ...
... The Earth bulges slightly at the equator and flattens slightly at the poles. Evidence of the Earth’s shape? Ships “sink” when moving past the horizon Satellite photographs Moon phases and lunar eclipses ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.