Earth Science Introduction
... • 35 minutes to birth of Christ • 1 hour+ to pyramids • 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin • 12 days = 1 million years • 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs • 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment • 31 years = 1 billion years ...
... • 35 minutes to birth of Christ • 1 hour+ to pyramids • 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin • 12 days = 1 million years • 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs • 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment • 31 years = 1 billion years ...
Chapter 20 The Origin and Evolution of Life
... Chapter 20 The Origin and Evolution of Life In the beginning… Explain the big bang theory ...
... Chapter 20 The Origin and Evolution of Life In the beginning… Explain the big bang theory ...
7.1.2 Study: The Mantle and Crust
... Main Idea #1: Scientists can collect information on the surface of Earth that gives them a hint as to what is below the surface. ...
... Main Idea #1: Scientists can collect information on the surface of Earth that gives them a hint as to what is below the surface. ...
Review for Earth Science Test
... material; Crust: layer of rock 3. What is a mineral? A mineral is a naturally occurring inorganic solid that has a crystal structure and definite chemical composition. 4. What are the characteristics of a mineral? a. Inorganic b. Solid c. Crystal structure d. Definite chemical composition e. Found i ...
... material; Crust: layer of rock 3. What is a mineral? A mineral is a naturally occurring inorganic solid that has a crystal structure and definite chemical composition. 4. What are the characteristics of a mineral? a. Inorganic b. Solid c. Crystal structure d. Definite chemical composition e. Found i ...
Lecture 7 Geologic Time
... Now you only have 50% (1/2) of the K remaining ….which continues to decay After another 1.3 Ga elapses, 50% or ½ of the remaining K will decay Note: (50% or ½ of the remaining K is equal to 25% or ¼ of what was there initially) Therefore…. 50% + another 25% = 75% or ¾ of the original K decays t ...
... Now you only have 50% (1/2) of the K remaining ….which continues to decay After another 1.3 Ga elapses, 50% or ½ of the remaining K will decay Note: (50% or ½ of the remaining K is equal to 25% or ¼ of what was there initially) Therefore…. 50% + another 25% = 75% or ¾ of the original K decays t ...
A1,A2 and A3 : Introduction to Geophysics
... ●The crust and mantle have distinct chemical compositions and are separated by the Mohorovicic discontinuity (or Moho for short). ●The crust is composed of silicate minerals such as feldspars (CaAl2,Si2O8, NaAlSi3O8, KAlSi3O8) and is enriched in lighter elements relative to mantle. The crust is comp ...
... ●The crust and mantle have distinct chemical compositions and are separated by the Mohorovicic discontinuity (or Moho for short). ●The crust is composed of silicate minerals such as feldspars (CaAl2,Si2O8, NaAlSi3O8, KAlSi3O8) and is enriched in lighter elements relative to mantle. The crust is comp ...
What is radiometrics?
... Radioactive elements occur naturally in the crystals of particular minerals. The abundance of minerals changes across the earth’s surface with variations in rock and soil type. Because the energy of gamma rays is related to the source radioactive element, they can be used to measure the abundance of ...
... Radioactive elements occur naturally in the crystals of particular minerals. The abundance of minerals changes across the earth’s surface with variations in rock and soil type. Because the energy of gamma rays is related to the source radioactive element, they can be used to measure the abundance of ...
1 a) Why is it difficult to determine Earth`s inner structure? It is so
... 1 b) How are seismic waves used to provide evidence about Earth’s interior? Seismic waves are used to provide evidence about Earth’s interior because by studying how they travel, we can detect what the Earth’s interior is really like. The waves’ speed and path provide us with details about the Earth ...
... 1 b) How are seismic waves used to provide evidence about Earth’s interior? Seismic waves are used to provide evidence about Earth’s interior because by studying how they travel, we can detect what the Earth’s interior is really like. The waves’ speed and path provide us with details about the Earth ...
Plate Tectonics Crossword - Science
... 3. The zone below the lithosphere. It is more 'plastic' than the lithosphere so it is easier to bend and move. ...
... 3. The zone below the lithosphere. It is more 'plastic' than the lithosphere so it is easier to bend and move. ...
Plate Tectonics Crossword
... It is more 'plastic' than the lithosphere so it is easier to bend and move. ...
... It is more 'plastic' than the lithosphere so it is easier to bend and move. ...
plate tectonics crossword
... 3. The zone below the lithosphere. It is more 'plastic' than the lithosphere so it is easier to bend and move. ...
... 3. The zone below the lithosphere. It is more 'plastic' than the lithosphere so it is easier to bend and move. ...
Fast Changes to the Earth`s Surface
... As the wave reached the shore, it slowed down, but grew taller. The first wave was over 9 meters (30 feet) tall when it crashed on shore. When the wall of water slammed onto the coast, property was destroyed and more than 200,000 people died. ...
... As the wave reached the shore, it slowed down, but grew taller. The first wave was over 9 meters (30 feet) tall when it crashed on shore. When the wall of water slammed onto the coast, property was destroyed and more than 200,000 people died. ...
Earth and Space Science Part 3
... • Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into continent sized slabs called plates. Plates move very slowly across Earth’s surface. (A few centimeters a year) ...
... • Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into continent sized slabs called plates. Plates move very slowly across Earth’s surface. (A few centimeters a year) ...
Fast Changes to the Earth`s Surface
... As the wave reached the shore, it slowed down, but grew taller. The first wave was over 9 meters (30 feet) tall when it crashed on shore. When the wall of water slammed onto the coast, property was destroyed and more than 200,000 people died. ...
... As the wave reached the shore, it slowed down, but grew taller. The first wave was over 9 meters (30 feet) tall when it crashed on shore. When the wall of water slammed onto the coast, property was destroyed and more than 200,000 people died. ...
Earth`s Interior
... solid inner core to spin at a slightly faster rate than the spinning of the whole Earth. • Earth’s magnetic field – Caused by the core movement – Causes the planet to act like a giant bar magnet ...
... solid inner core to spin at a slightly faster rate than the spinning of the whole Earth. • Earth’s magnetic field – Caused by the core movement – Causes the planet to act like a giant bar magnet ...
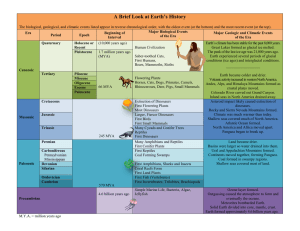
A Brief Look at Earth`s History
... Climate was much warmer than today. Shallow seas covered much of North America. Atlantic Ocean formed. North America and Africa moved apart. Pangaea began to break up. Land became drier. Basins were larger so water drained into them. Ural and Appalachian Mountains formed. Continents moved together, ...
... Climate was much warmer than today. Shallow seas covered much of North America. Atlantic Ocean formed. North America and Africa moved apart. Pangaea began to break up. Land became drier. Basins were larger so water drained into them. Ural and Appalachian Mountains formed. Continents moved together, ...
Tectonic Plates - Louis Pasteur MS 67 Science Department Resources
... Literacy Fusion Article: “Earth's tectonic plates have doubled their speed” SO MUCH for slowing down as you age. Earth's tectonic plates are moving faster now than at any point in the last 2 billion years, according to the latest study of plate movements. But the result is controversial, since previ ...
... Literacy Fusion Article: “Earth's tectonic plates have doubled their speed” SO MUCH for slowing down as you age. Earth's tectonic plates are moving faster now than at any point in the last 2 billion years, according to the latest study of plate movements. But the result is controversial, since previ ...
Study Guide
... Absolute Age: using the half life of radioactive material to find the exact age of a rock or fossil. This can only be used on igneous or metamorphic rocks. A half life is the amount if time it takes HALF a sample to decay from a radioactive parent material into a stable daughter material. Isotopes o ...
... Absolute Age: using the half life of radioactive material to find the exact age of a rock or fossil. This can only be used on igneous or metamorphic rocks. A half life is the amount if time it takes HALF a sample to decay from a radioactive parent material into a stable daughter material. Isotopes o ...
The Layers of the Earth
... Geologists have found rocks on earth’s surface that they believe were originally formed INSIDE the earth. These rocks are at the surface of the earth NOW…. but millions of years ago, they existed _______ ________ the earth. ...
... Geologists have found rocks on earth’s surface that they believe were originally formed INSIDE the earth. These rocks are at the surface of the earth NOW…. but millions of years ago, they existed _______ ________ the earth. ...
Lesson 1 - Humanities.Com
... 2. What is the crust broken up into? 3. How many plates can you name? 4. What evidence is there to tell us that the continents once joined together? 5. Why do the plates move? 6. How quickly do the plates move? ...
... 2. What is the crust broken up into? 3. How many plates can you name? 4. What evidence is there to tell us that the continents once joined together? 5. Why do the plates move? 6. How quickly do the plates move? ...
The Earth`s Structure
... External geologic processes • Generally wear down the earth’s surface • Driven directly or indirectly by sun and gravity • Weathering • Physical, Chemical, and Biological ...
... External geologic processes • Generally wear down the earth’s surface • Driven directly or indirectly by sun and gravity • Weathering • Physical, Chemical, and Biological ...
Long-Term and Short-Term Changes in Climate
... Long-Term Changes are due to: Continental Drift • According to plate tectonics, all of the continents have been moving and are continuing to shift their position on the Earth’s surface • How it impacts climate? ▫ Changes ocean currents and wind patterns ▫ Changes how land masses are distributed whi ...
... Long-Term Changes are due to: Continental Drift • According to plate tectonics, all of the continents have been moving and are continuing to shift their position on the Earth’s surface • How it impacts climate? ▫ Changes ocean currents and wind patterns ▫ Changes how land masses are distributed whi ...
4 layers of Earth and Plate Activity notes
... Milky Way- cut in half • Chocolate- crust- thinnest layer made of rocks and soil (land we walk on and under the sea) • Caramel- mantle- holt molten rock, what would come out of a volcano • Light brown layer- outer core- liquid iron • Bottom layer of chocolate- inner core, solid iron and is the hott ...
... Milky Way- cut in half • Chocolate- crust- thinnest layer made of rocks and soil (land we walk on and under the sea) • Caramel- mantle- holt molten rock, what would come out of a volcano • Light brown layer- outer core- liquid iron • Bottom layer of chocolate- inner core, solid iron and is the hott ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.