Study Guide
... 1. Know the answers to all of the questions you answered in the journal. Which are listed below. a. Provide definitions for the following terms: core, crust, mantle, magma, pangea, ring of fire, lithospheric plates, igneous rocks, tsunami, fault, and earthquake. b. Briefly discuss the Theory of Plat ...
... 1. Know the answers to all of the questions you answered in the journal. Which are listed below. a. Provide definitions for the following terms: core, crust, mantle, magma, pangea, ring of fire, lithospheric plates, igneous rocks, tsunami, fault, and earthquake. b. Briefly discuss the Theory of Plat ...
Book F Chapter 3 Section 5
... These rock layers represent almost half, or nearly 2 billion years, of Earth’s history. ...
... These rock layers represent almost half, or nearly 2 billion years, of Earth’s history. ...
landform
... below. You may not use your book. (Use at least 5 words) You may use your imaginations! What do you think these words could mean when thinking about ways that the earths surface could be changed? ...
... below. You may not use your book. (Use at least 5 words) You may use your imaginations! What do you think these words could mean when thinking about ways that the earths surface could be changed? ...
Plate Tectonics Study guide - Grants Pass School District 7
... ________ The lithosphere contains two types of crust, oceanic and continental. ...
... ________ The lithosphere contains two types of crust, oceanic and continental. ...
SAI109 Dealing 4 Dynamic Response Earths Surface
... Which layers of the earth are composed primarily of rocky material? ...
... Which layers of the earth are composed primarily of rocky material? ...
11 Test Review - The Planet Earth
... 4. Earthquakes, volcanoes and mountains often appear where two tectonic plates meet and press against one another. 5. An idea proposed by James Lovelock - All living things on Earth (biosphere) function as one SUPERorganism that changes its environment to create conditions that best meet its needs, ...
... 4. Earthquakes, volcanoes and mountains often appear where two tectonic plates meet and press against one another. 5. An idea proposed by James Lovelock - All living things on Earth (biosphere) function as one SUPERorganism that changes its environment to create conditions that best meet its needs, ...
Book F Ch. 2 L4 NOTES
... Foliated: the texture of metamorphic rock in which the mineral grains are arranged in planes or bands Nonfoliated: the texture of metamorphic rock in which the mineral grains are not arranged in planes or bands Metamorphism: Rocks undergo the process of metamorphism when exposed to high heat (temp ...
... Foliated: the texture of metamorphic rock in which the mineral grains are arranged in planes or bands Nonfoliated: the texture of metamorphic rock in which the mineral grains are not arranged in planes or bands Metamorphism: Rocks undergo the process of metamorphism when exposed to high heat (temp ...
2.(and other) Natural Hazard physical event that happens naturally
... Fold mountains are usually formed from sedimentary rocks and are usually found along the edges continents. This is because the thickest deposits of sedimentary rock generally accumulate along the edges of continents. When plates and the continents riding on them collide, the accumulated layers o ...
... Fold mountains are usually formed from sedimentary rocks and are usually found along the edges continents. This is because the thickest deposits of sedimentary rock generally accumulate along the edges of continents. When plates and the continents riding on them collide, the accumulated layers o ...
Notes: Plate Tectonics
... B. The three main layers of Earth are the crust, mantle and core. 1.) The layers vary greatly in size, composition, temperature, and pressure. 2.) The deeper down inside Earth, the greater the pressure. 3.) The temperature inside earth increases as depth increases. C. The Layers of the Earth 1.) Cru ...
... B. The three main layers of Earth are the crust, mantle and core. 1.) The layers vary greatly in size, composition, temperature, and pressure. 2.) The deeper down inside Earth, the greater the pressure. 3.) The temperature inside earth increases as depth increases. C. The Layers of the Earth 1.) Cru ...
Earth`s Systems and Resources Unit Test
... C. 2 B. 3 D. 1 36. Forecasting the time of, location, and magnitude of a seismic event does not prevent the event from happening, but it can help us reduce the destruction caused by A. earthquakes. C. hurricanes. B. flooding. D. volcanoes. 37. What scientific instrument can be used to detect and rec ...
... C. 2 B. 3 D. 1 36. Forecasting the time of, location, and magnitude of a seismic event does not prevent the event from happening, but it can help us reduce the destruction caused by A. earthquakes. C. hurricanes. B. flooding. D. volcanoes. 37. What scientific instrument can be used to detect and rec ...
10 Things to Know About Plate Tectonics
... 2. Movement occurs because of convection currents in the asthenosphere, which move the lithosphere on top. Mantle heats up as it approaches the core, so it rises to the top, where it cools and cycles back down toward the core, and so on and so forth. 3. Divergent plate boundaries – two plates moving ...
... 2. Movement occurs because of convection currents in the asthenosphere, which move the lithosphere on top. Mantle heats up as it approaches the core, so it rises to the top, where it cools and cycles back down toward the core, and so on and so forth. 3. Divergent plate boundaries – two plates moving ...
Earth Science Unit Review
... reaching the surface pushes plates apart. 43. Note: Have students change the wording of this question to: “Compare the formation of a composite volcano to that of a shield volcano.” Composite volcanoes form at subduction boundaries, where material from the subducting plate rises to the surface. Shie ...
... reaching the surface pushes plates apart. 43. Note: Have students change the wording of this question to: “Compare the formation of a composite volcano to that of a shield volcano.” Composite volcanoes form at subduction boundaries, where material from the subducting plate rises to the surface. Shie ...
Earth Science - Wiki-by
... water, and the gases of the atmosphere. The varied materials have different physical and chemical properties, which make them useful in different ways, for example, as building materials, (e.g., stone, clay, marble), as sources of fuel, (e.g., petroleum, natural gas) or for growing the plants we use ...
... water, and the gases of the atmosphere. The varied materials have different physical and chemical properties, which make them useful in different ways, for example, as building materials, (e.g., stone, clay, marble), as sources of fuel, (e.g., petroleum, natural gas) or for growing the plants we use ...
Vocabulary Quiz
... Vocabulary Quiz Matching: For each section, place the letter on the line which best matches each term with its’ description. Do Not draw lines! If I get confused, then it must be wrong! Part I Continental Drift _______1. Continental Drift ...
... Vocabulary Quiz Matching: For each section, place the letter on the line which best matches each term with its’ description. Do Not draw lines! If I get confused, then it must be wrong! Part I Continental Drift _______1. Continental Drift ...
Ex s16 solution
... tangling and then untangling of the solar magnetic field. The sun’s magnetic field is frozen into its gases. The differential rotation wraps this field around the sun—like a long string caught in a rotating wheel. After about 11 years of tangling, the field becomes so complex that adjacent regions o ...
... tangling and then untangling of the solar magnetic field. The sun’s magnetic field is frozen into its gases. The differential rotation wraps this field around the sun—like a long string caught in a rotating wheel. After about 11 years of tangling, the field becomes so complex that adjacent regions o ...
Earth Science
... Letter grades on all work are based on total points awarded, divided by total possible points earned. Daily work, quizzes, tests, labs, exhibitions, and projects are all graded on the total point system. It is my belief that daily work is just as important as tests in the ...
... Letter grades on all work are based on total points awarded, divided by total possible points earned. Daily work, quizzes, tests, labs, exhibitions, and projects are all graded on the total point system. It is my belief that daily work is just as important as tests in the ...
Name__________________ EARTH SCIENCE FIRST QUARTER
... 20 matching terms from Process of Science, Earth’s Systems, Plate tectonics, and Minerals units. (40 pts) 10 Multiple choice from the same units mentioned above (20 pts) 5 numbers to put in scientific notation (10 pts) 5 metric conversions (15 pts) 3 Short Answer Questions from the same units mentio ...
... 20 matching terms from Process of Science, Earth’s Systems, Plate tectonics, and Minerals units. (40 pts) 10 Multiple choice from the same units mentioned above (20 pts) 5 numbers to put in scientific notation (10 pts) 5 metric conversions (15 pts) 3 Short Answer Questions from the same units mentio ...
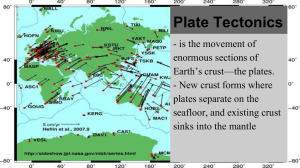
Plate Tectonics
... and violent shaking of the ground, sometimes causing great destruction, as a result of movements within the earth's crust or volcanic action. ...
... and violent shaking of the ground, sometimes causing great destruction, as a result of movements within the earth's crust or volcanic action. ...
Document
... Alfred Wegener, a German who was educated as a meteorologist and geologist, was one of the first scientists to theorize about tectonic plates. Wegener suggested that past continents had drifted apart over time to form the present continents. This rearrangement of continents is known as continental d ...
... Alfred Wegener, a German who was educated as a meteorologist and geologist, was one of the first scientists to theorize about tectonic plates. Wegener suggested that past continents had drifted apart over time to form the present continents. This rearrangement of continents is known as continental d ...
Climate Test
... D. The climate on one side of a mountain range will never be different from the climate on the other side of the mountain range. ...
... D. The climate on one side of a mountain range will never be different from the climate on the other side of the mountain range. ...
E.S. SOL Facts
... 45. Renewable resources can be replaced by nature at a rate close to the rate at which they are used. Renewable resources include vegetation, water, and soil. 46. Nonrenewable resources are renewed very slowly, or not at all. These include, coal, oil, and minerals. 47. The Earth’s water supply is re ...
... 45. Renewable resources can be replaced by nature at a rate close to the rate at which they are used. Renewable resources include vegetation, water, and soil. 46. Nonrenewable resources are renewed very slowly, or not at all. These include, coal, oil, and minerals. 47. The Earth’s water supply is re ...
Chapter 7: Plate Tectonics
... Plates may be continents, oceans or a combination, Thick continental plates displace or sink more into the asthenesphere than thin oceanic plates do. ...
... Plates may be continents, oceans or a combination, Thick continental plates displace or sink more into the asthenesphere than thin oceanic plates do. ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.