Earth`s Interior
... The deepest man has dug into the Earth is 5 km in the South African gold mines. (This is within the crust.) Here the temperature increases by 10 to 15 ˚C for every kilometer down. We have not actually been to the center of the Earth. So how can we infer what the composition of the Earth’s interior i ...
... The deepest man has dug into the Earth is 5 km in the South African gold mines. (This is within the crust.) Here the temperature increases by 10 to 15 ˚C for every kilometer down. We have not actually been to the center of the Earth. So how can we infer what the composition of the Earth’s interior i ...
137 Amazing Facts of Earth Science
... 47. Ground water layers from the surface down would include zone of aeration, water table, & zone of saturation. 48. An Aquifer is a layer of rock that transports groundwater freely. Largest aquifer in VA is ground water filled from rain. 49. A spring is an area where the water table reaches the l ...
... 47. Ground water layers from the surface down would include zone of aeration, water table, & zone of saturation. 48. An Aquifer is a layer of rock that transports groundwater freely. Largest aquifer in VA is ground water filled from rain. 49. A spring is an area where the water table reaches the l ...
Layers of the Earth Investigation 2
... what the layers are made up of, or physically, based on how the layers behave. When divided up chemically, there are 4 main layers of the Earth: the crust, the mantle and the outer and inner core. The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth. It is the layer that we walk on when we step outside. Th ...
... what the layers are made up of, or physically, based on how the layers behave. When divided up chemically, there are 4 main layers of the Earth: the crust, the mantle and the outer and inner core. The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth. It is the layer that we walk on when we step outside. Th ...
Layers of Earth Notes On-Level
... LAYERS OF THE EARTH • GEOLOGY – STUDY OF PLANET EARTH • INCLUDING SURFACE & INTERIOR • GEOLOGISTS – A PERSON WHO STUDIES INSIDE THE EARTH, TEMP, PRESSURE, HOW THEY AFFECT THE SURFACE OF THE EARTH. ...
... LAYERS OF THE EARTH • GEOLOGY – STUDY OF PLANET EARTH • INCLUDING SURFACE & INTERIOR • GEOLOGISTS – A PERSON WHO STUDIES INSIDE THE EARTH, TEMP, PRESSURE, HOW THEY AFFECT THE SURFACE OF THE EARTH. ...
Geologic Time Scale - CVHS Chicklas
... Climate changes were caused by increased volcanic activity. Volcanic output would block sun as well and same process would follow. ...
... Climate changes were caused by increased volcanic activity. Volcanic output would block sun as well and same process would follow. ...
Earth`s Structure Test
... rock, which of the following can be inferred from the rock cycle diagram? A Fossils may be found in any type of rock. B Fossils are resistant to the heating and pressure inside the Earth. C Many fossils that form are destroyed when sedimentary rocks melt. D Sedimentary rocks are the only type of roc ...
... rock, which of the following can be inferred from the rock cycle diagram? A Fossils may be found in any type of rock. B Fossils are resistant to the heating and pressure inside the Earth. C Many fossils that form are destroyed when sedimentary rocks melt. D Sedimentary rocks are the only type of roc ...
Geologic Time Scale
... Climate changes were caused by increased volcanic activity. Volcanic output would block sun as well and same process would follow. ...
... Climate changes were caused by increased volcanic activity. Volcanic output would block sun as well and same process would follow. ...
The Earth-Moon System - Academic Computer Center
... • There are two theories about the origin of Earth’s atmosphere: – Through volcanic eruptions or from impacts gases were released from rocks on Earth. – Impacts from comets brought gases to Earth. ...
... • There are two theories about the origin of Earth’s atmosphere: – Through volcanic eruptions or from impacts gases were released from rocks on Earth. – Impacts from comets brought gases to Earth. ...
TEORIES OF MASS EXTINCTION
... • Meteors (shooting stars) burn and glow when they enter earth’s atmosphere. • Most disintegrate into ashes and debris. • Some remain intact, known as Meteorites, to create craters on earth. • Can destroy life forms by shutting off sunlight for months / years. ...
... • Meteors (shooting stars) burn and glow when they enter earth’s atmosphere. • Most disintegrate into ashes and debris. • Some remain intact, known as Meteorites, to create craters on earth. • Can destroy life forms by shutting off sunlight for months / years. ...
Earth`s 4 main Layers
... The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball sm ...
... The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball sm ...
New Title - TeacherWeb
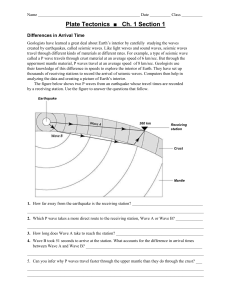
... travel through different kinds of materials at different rates. For example, a type of seismic wave called a P wave travels through crust material at an average speed of 6 km/sec. But through the uppermost mantle material, P waves travel at an average speed of 8 km/sec. Geologists use their knowledg ...
... travel through different kinds of materials at different rates. For example, a type of seismic wave called a P wave travels through crust material at an average speed of 6 km/sec. But through the uppermost mantle material, P waves travel at an average speed of 8 km/sec. Geologists use their knowledg ...
Earth Science - Ms. Harper`s Science Class
... processes that change it • Oceanography -- study of earth’s oceans ...
... processes that change it • Oceanography -- study of earth’s oceans ...
Layers of the Earth - study notes
... Ridge continues to separate. Magma seeps up from below, cools, and hardens to form new oceanic crust. The Crust is made up of 3 types of rock: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary. Igneous rock forms when magma cools. Most of the rock on Earth is igneous rock. Sometimes high temperatures and pr ...
... Ridge continues to separate. Magma seeps up from below, cools, and hardens to form new oceanic crust. The Crust is made up of 3 types of rock: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary. Igneous rock forms when magma cools. Most of the rock on Earth is igneous rock. Sometimes high temperatures and pr ...
File
... ___Crust is always being created and destroyed. Divergent boundaries allow magma to break through and cool forming new crust/lithosphere and convergent boundaries is where old crust is destroyed because the crust collides and subducts into the mantle where it is melted down Where do convection curre ...
... ___Crust is always being created and destroyed. Divergent boundaries allow magma to break through and cool forming new crust/lithosphere and convergent boundaries is where old crust is destroyed because the crust collides and subducts into the mantle where it is melted down Where do convection curre ...
Earth Revealed - Weathering and Soils
... 3. What per cent does water expand when it freezes? (a) 1% (b) 5% (c) 10% (d) 20% (e) 100% 4. Chemical weathering is fastest in what kind of environment? (a) wet & cool (b) wet & hot (c) dry & cool (d) dry & hot 5. (True/False) Only a few rock-forming minerals are stable at the Earth’s surface. 6. W ...
... 3. What per cent does water expand when it freezes? (a) 1% (b) 5% (c) 10% (d) 20% (e) 100% 4. Chemical weathering is fastest in what kind of environment? (a) wet & cool (b) wet & hot (c) dry & cool (d) dry & hot 5. (True/False) Only a few rock-forming minerals are stable at the Earth’s surface. 6. W ...
sxES_G6_RNG_ch04-A_070-073.fm
... 16. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about Earth’s inner core. a. It consists of molten metal. b. It is a thick liquid. c. It is not very dense. d. It is under extreme pressure 17. What creates Earth’s magnetic field? ...
... 16. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about Earth’s inner core. a. It consists of molten metal. b. It is a thick liquid. c. It is not very dense. d. It is under extreme pressure 17. What creates Earth’s magnetic field? ...
What are the characteristics of Earth`s interior?
... – Seismic Waves • Waves produced by earthquakes • Record the waves and study how they travel • Speed of waves and the paths they take reveal that our planet is made up of several layers ...
... – Seismic Waves • Waves produced by earthquakes • Record the waves and study how they travel • Speed of waves and the paths they take reveal that our planet is made up of several layers ...
Backward Design Learning Plan - UNC
... Earthquakes often occur along the boundaries between colliding plates, and molten rock from below creates pressure that is released by volcanic eruptions, helping to build up mountains. Under the ocean basins, molten rock may well up between separating plates to create new ocean floor. Volcanic acti ...
... Earthquakes often occur along the boundaries between colliding plates, and molten rock from below creates pressure that is released by volcanic eruptions, helping to build up mountains. Under the ocean basins, molten rock may well up between separating plates to create new ocean floor. Volcanic acti ...
Geog 101: Chapter 3 Quiz
... land formation. 2. Of what is the lithosphere composed? 3. Where are earthquakes most likely to occur? 4. What is the place where the earth’s crust actually moves in an earthquake called? 5. What factors influence the amount of ground shaking caused by earthquakes? 6. What is the nature and behavior ...
... land formation. 2. Of what is the lithosphere composed? 3. Where are earthquakes most likely to occur? 4. What is the place where the earth’s crust actually moves in an earthquake called? 5. What factors influence the amount of ground shaking caused by earthquakes? 6. What is the nature and behavior ...
Earth Systems CRT Review
... Objective 1: Explain the water cycle in terms of its reservoirs, the movement between reservoirs, and the energy to move water. Evaluate the importance of fresh water to the biosphere. Objective 2: Analyze the physical and biological dynamics of the oceans. ...
... Objective 1: Explain the water cycle in terms of its reservoirs, the movement between reservoirs, and the energy to move water. Evaluate the importance of fresh water to the biosphere. Objective 2: Analyze the physical and biological dynamics of the oceans. ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.