GEOL 1403 Physical Geology Lecture Topics
... Physical Geology Lecture Topics This course is designed to introduce the science of geology, emphasizing plate tectonics, rocks, minerals, geological processes, structural geology, and landforms. The following is a list of topics that should be covered as part of the lecture component of the course. ...
... Physical Geology Lecture Topics This course is designed to introduce the science of geology, emphasizing plate tectonics, rocks, minerals, geological processes, structural geology, and landforms. The following is a list of topics that should be covered as part of the lecture component of the course. ...
August 2008
... Which is a formal statement in which a natural phenomena is described under given conditions? (A) (B) (C) (D) ...
... Which is a formal statement in which a natural phenomena is described under given conditions? (A) (B) (C) (D) ...
Earth,Notes,RevQs,Ch12
... 14. Heat flow is not evenly distributed from Earth’s surface because it is highest where magma is rising towards the surface (at mid-ocean ridges) or in regions where high levels of radioactive isotopes exist. 15. Earth apparently increased in heat during its early formation because of several facto ...
... 14. Heat flow is not evenly distributed from Earth’s surface because it is highest where magma is rising towards the surface (at mid-ocean ridges) or in regions where high levels of radioactive isotopes exist. 15. Earth apparently increased in heat during its early formation because of several facto ...
Changes to Earth`s Surface Chapter 9
... When a tree or other plant grows, its roots may grow in small openings of rocks and cause the rock to break. Earthworms and other animals break these small ...
... When a tree or other plant grows, its roots may grow in small openings of rocks and cause the rock to break. Earthworms and other animals break these small ...
LESSON 5 - PANGEA STAGE ONE: Lesson is designed to be taught
... done before?) Students will have learned about the properties This lesson will be followed by the first in a of the mantle and crust during previous series of lectures on plate tectonics. lectures. Anticipated student strengths/obstacles/difficulties Strengths – Students will have knowledge about th ...
... done before?) Students will have learned about the properties This lesson will be followed by the first in a of the mantle and crust during previous series of lectures on plate tectonics. lectures. Anticipated student strengths/obstacles/difficulties Strengths – Students will have knowledge about th ...
Changes to Earth`s Surface Chapter 9
... When magma finds a vent (opening) between the plates it sometimes pushes through to Earth’s surface. The magma that flows onto Earth’s surface turn into lava. ...
... When magma finds a vent (opening) between the plates it sometimes pushes through to Earth’s surface. The magma that flows onto Earth’s surface turn into lava. ...
Unit 5 Review
... The object’s weight will be more The object’s weight will be less * **mass does not take gravity into account** *weight will change depending on the amount of gravity* Greater mass of planet=greater gravitational force ...
... The object’s weight will be more The object’s weight will be less * **mass does not take gravity into account** *weight will change depending on the amount of gravity* Greater mass of planet=greater gravitational force ...
Chapter 1
... 3) T or F: The doctrine of uniformitarianism implies that the current forces and processes shaping the Earth have been operating for a very long time. True 5) T or F: The currently accepted age of Earth is approximately 4.5 million years. False 6) T or F: A scientific theory is a tentative or untest ...
... 3) T or F: The doctrine of uniformitarianism implies that the current forces and processes shaping the Earth have been operating for a very long time. True 5) T or F: The currently accepted age of Earth is approximately 4.5 million years. False 6) T or F: A scientific theory is a tentative or untest ...
The Ocean Takes Shape
... The early Earth was a dry, cratered ball. It had no life, no ocean and no continents. It was a horribly hot and violent place. Many asteroids, comets, and other debris were left over from the solar system's formation. This debris continually bombarded Earth, releasing huge amounts of heat. Radioacti ...
... The early Earth was a dry, cratered ball. It had no life, no ocean and no continents. It was a horribly hot and violent place. Many asteroids, comets, and other debris were left over from the solar system's formation. This debris continually bombarded Earth, releasing huge amounts of heat. Radioacti ...
A possible result of plates moving along a transform boundary is
... where does the hanging wall more relative to the footwall? ...
... where does the hanging wall more relative to the footwall? ...
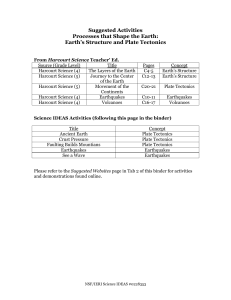
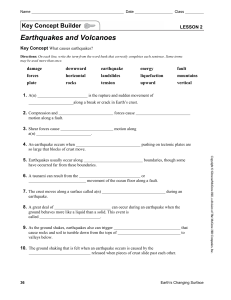
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... Directions: On each line, write the term or statement from the word bank that correctly completes each causeand-effect sentence. Each term or statement is used only once. ...
... Directions: On each line, write the term or statement from the word bank that correctly completes each causeand-effect sentence. Each term or statement is used only once. ...
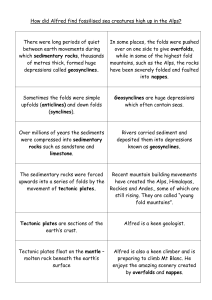
How did Alfred find fossilised sea animals high up in the Alps
... Fold mountains occur where two tectonic plates are moving towards each other. ...
... Fold mountains occur where two tectonic plates are moving towards each other. ...
S05_4359_Exam01
... A. Magnitude; B. Hypocenter, C. Epicenter, D. Focus, E. Intensity, or F. Moment. _____26. An earthquake of Moment Magnitude: A. 5-6, B. 6-7, C. 7-8, or D. 8-9 is called a Great Earthquake, can cause very serious damage to nearby buildings, and globally occurs on average about once per year. _____27. ...
... A. Magnitude; B. Hypocenter, C. Epicenter, D. Focus, E. Intensity, or F. Moment. _____26. An earthquake of Moment Magnitude: A. 5-6, B. 6-7, C. 7-8, or D. 8-9 is called a Great Earthquake, can cause very serious damage to nearby buildings, and globally occurs on average about once per year. _____27. ...
Name Youngblood, Period
... 34. Transform boundaries are located on ________________________, which are associated with this type of tectonic movement. 35. When plates slip from the __________________ position and move transversely, the sudden movement causes a(n) ____________________________________. 36. Another name for tran ...
... 34. Transform boundaries are located on ________________________, which are associated with this type of tectonic movement. 35. When plates slip from the __________________ position and move transversely, the sudden movement causes a(n) ____________________________________. 36. Another name for tran ...
File
... (if planet’s gravity is strong enough, it pulls the gases in & keeps them near surface) • Venus, Earth, Mars had gravity strong enough to hold heavy gases such as CO2. (Mars/Venus are mostly CO2) • Atmosphere moves from warmer places to cooler places. Keeps planet surface warmer & stable between day ...
... (if planet’s gravity is strong enough, it pulls the gases in & keeps them near surface) • Venus, Earth, Mars had gravity strong enough to hold heavy gases such as CO2. (Mars/Venus are mostly CO2) • Atmosphere moves from warmer places to cooler places. Keeps planet surface warmer & stable between day ...
Internal Structure of the Earth
... How do we know there are four layers? • We don’t, it’s a theory! • Using earthquake waves, they can tell whether an object is a liquid or a solid, so by using that information, they theorized about the interior layers of the Earth ...
... How do we know there are four layers? • We don’t, it’s a theory! • Using earthquake waves, they can tell whether an object is a liquid or a solid, so by using that information, they theorized about the interior layers of the Earth ...
Earth Science
... the ocean floor, and the ages of the rocks themselves. 1. Molten Material - shape of rocks – only when molten material hardens quickly under water ...
... the ocean floor, and the ages of the rocks themselves. 1. Molten Material - shape of rocks – only when molten material hardens quickly under water ...
Geology Study Guide
... The division of Earth’s history is the Geological Time Scale- from most recent to oldest time periods: Cenozoic (Age of Mammals), Mesozoic (Age of Reptiles), Paleozoic (Age of Marine Life), Proterozoic Eon (where first organism appeared), Archean Eon (where first rock appeared), and Hadean Eon.(Page ...
... The division of Earth’s history is the Geological Time Scale- from most recent to oldest time periods: Cenozoic (Age of Mammals), Mesozoic (Age of Reptiles), Paleozoic (Age of Marine Life), Proterozoic Eon (where first organism appeared), Archean Eon (where first rock appeared), and Hadean Eon.(Page ...
Plate Tectonic Test Review Answers!
... During sea-floor spreading, new crust forms when molten material from the mantle will rise up and fill in to form New Ocean Crust. The opposite edges of the boundary then become subducted. ...
... During sea-floor spreading, new crust forms when molten material from the mantle will rise up and fill in to form New Ocean Crust. The opposite edges of the boundary then become subducted. ...
Regents Earth Science – Unit 3: Measuring Earth
... Troposphere – lowest layer, temperature decreases with increasing altitude, has “weather” due to the presence of water vapor ...
... Troposphere – lowest layer, temperature decreases with increasing altitude, has “weather” due to the presence of water vapor ...
Key Ideas
... combining with other elements to form compounds, and is also being used by respiratory life. Despite this, the amount of oxygen in our atmosphere is not decreasing because it is being replenished by A. B. C. D. ...
... combining with other elements to form compounds, and is also being used by respiratory life. Despite this, the amount of oxygen in our atmosphere is not decreasing because it is being replenished by A. B. C. D. ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.