pressure calcite fluorite geologists gypsum
... a dense, fine-grained, rock formed by compression of shales or other rocks that splits readily into thin layers or ...
... a dense, fine-grained, rock formed by compression of shales or other rocks that splits readily into thin layers or ...
intrusive rock
... Extrusive rocks • When magma reaches the earth’s surface it is called lava • Lava cools and forms extrusive rock • Cools quickly so does not have many crystals (fine-grain texture) ...
... Extrusive rocks • When magma reaches the earth’s surface it is called lava • Lava cools and forms extrusive rock • Cools quickly so does not have many crystals (fine-grain texture) ...
Earth Science!!!!!! Chapter 1 – Intro to Earth Science Section 1.1
... o Water and soil, metallic, and nonmetal minerals o Very important factor in Earth science o Forms the foundation of modern civilization o Earth science deals with occurrence and formation as well as maintaining these supplies and the environmental impact of their use. o Renewable resources can be r ...
... o Water and soil, metallic, and nonmetal minerals o Very important factor in Earth science o Forms the foundation of modern civilization o Earth science deals with occurrence and formation as well as maintaining these supplies and the environmental impact of their use. o Renewable resources can be r ...
Words of the Day
... 28). Liquid: A state of matter that DOES NOT have a definite shape, but does have a definite volume. ...
... 28). Liquid: A state of matter that DOES NOT have a definite shape, but does have a definite volume. ...
Environmental Geochemistry I.
... - soil is the basic natural resource (Aldo Leopold) - important process is weathering (decomposition and desintegration) - two types of weathering: mechanical and chemical ...
... - soil is the basic natural resource (Aldo Leopold) - important process is weathering (decomposition and desintegration) - two types of weathering: mechanical and chemical ...
31.3 Sedimentary Rocks Blanket Most of the Earth`s Surface
... of small fragments of other rocks Three most abundant: shale, sandstone, conglomerate Limestone and evaporitesare also sedimentary rocks Sedimentary rock contain fossils ...
... of small fragments of other rocks Three most abundant: shale, sandstone, conglomerate Limestone and evaporitesare also sedimentary rocks Sedimentary rock contain fossils ...
Earth`s Magnetic Field, Atmosphere and Geology
... “bow shock”, just like a boat pushes some water out of the way at its bow as it sails forward. ...
... “bow shock”, just like a boat pushes some water out of the way at its bow as it sails forward. ...
Mountain Building - Hicksville Public Schools
... "standstill") is a term used in geology to refer to the state of gravitational equilibrium between the earth's lithosphere and asthenosphere such that the tectonic plates "float" at an elevation which depends on their thickness and density. – Parts of the crust will rise or subside (sink) until stab ...
... "standstill") is a term used in geology to refer to the state of gravitational equilibrium between the earth's lithosphere and asthenosphere such that the tectonic plates "float" at an elevation which depends on their thickness and density. – Parts of the crust will rise or subside (sink) until stab ...
Document
... A single fold is a hinge defined by the maximum curvature of the beds. The hinge line joins the points of maximum bending along a bed. The axial surface, or plane, passes through the hinges of successive beds, while the axis of the fold is any line on the bed which is parallel to the hinge line. Whe ...
... A single fold is a hinge defined by the maximum curvature of the beds. The hinge line joins the points of maximum bending along a bed. The axial surface, or plane, passes through the hinges of successive beds, while the axis of the fold is any line on the bed which is parallel to the hinge line. Whe ...
(b) examine the chemical, physical, and thermal structure of Earth`s
... warming is changing the density of these polar oceans due to glacial and ice-cap melt, this current could stop. Ultimately, this could alter the temperatures over the continents by as much as 10˚C. Global warming could cause continental cooling in the Northern Hemisphere! ...
... warming is changing the density of these polar oceans due to glacial and ice-cap melt, this current could stop. Ultimately, this could alter the temperatures over the continents by as much as 10˚C. Global warming could cause continental cooling in the Northern Hemisphere! ...
crust
... giant landmass called Pangaea which broke up about 180 M years ago and formed 2 big pieces called Laurasia and Gondwanaland. Then, about 65 MYA, these broke up and formed the continents that we know today. ...
... giant landmass called Pangaea which broke up about 180 M years ago and formed 2 big pieces called Laurasia and Gondwanaland. Then, about 65 MYA, these broke up and formed the continents that we know today. ...
Planet Earth Test Review
... 22. Write the letter of the tectonic plate next to the corresponding name below. ...
... 22. Write the letter of the tectonic plate next to the corresponding name below. ...
Earth Systems Science Core Curriculum
... Science provides evidence that the universe is more than 10 billion years old. The most accepted science theory states that the universe expanded explosively from a hot, dense chaotic mass. Gravity causes clouds of the lightest elements to condense into massive bodies. The mass and density of these ...
... Science provides evidence that the universe is more than 10 billion years old. The most accepted science theory states that the universe expanded explosively from a hot, dense chaotic mass. Gravity causes clouds of the lightest elements to condense into massive bodies. The mass and density of these ...
Geologic Time
... of years) on the ages of rocks and geologic time periods – Uses radioactive decay of unstable isotopes – Only possible since radioactivity was discovered in 1896 – Radioactive isotopes decay in predictable manner, giving a characteristic half-life (time it takes for a given amount of radioactive iso ...
... of years) on the ages of rocks and geologic time periods – Uses radioactive decay of unstable isotopes – Only possible since radioactivity was discovered in 1896 – Radioactive isotopes decay in predictable manner, giving a characteristic half-life (time it takes for a given amount of radioactive iso ...
The Earth`s Layers Foldable
... Challenge: Perhaps you have imagined digging a tunnel through the earth that comes out the other side. Figure it out ... How many kilometers would you have to dig? Show your work! 3. Write 4 interesting facts about the Earth's Crust. a. ________________________________________________ b. ___________ ...
... Challenge: Perhaps you have imagined digging a tunnel through the earth that comes out the other side. Figure it out ... How many kilometers would you have to dig? Show your work! 3. Write 4 interesting facts about the Earth's Crust. a. ________________________________________________ b. ___________ ...
Teacher Guide - The University of Iowa
... Water is a solvent. As it passes through the water cycle, especially as it moves on the earth’s surface and underground, it dissolves minerals and gases and carries them to the oceans, rivers, and other surface water. Natural and human forces can contribute to contamination of surface water and gro ...
... Water is a solvent. As it passes through the water cycle, especially as it moves on the earth’s surface and underground, it dissolves minerals and gases and carries them to the oceans, rivers, and other surface water. Natural and human forces can contribute to contamination of surface water and gro ...
Background
... grey to black in colour as it is made up of many dark coloured minerals. It is a crystalline rock but typically you can’t see most of the mineral crystals without using a microscope. This is due to the way in which basalt is formed. Much of the Earth’s basalt was made millions of years ago when molt ...
... grey to black in colour as it is made up of many dark coloured minerals. It is a crystalline rock but typically you can’t see most of the mineral crystals without using a microscope. This is due to the way in which basalt is formed. Much of the Earth’s basalt was made millions of years ago when molt ...
2-Unit4Part2EarthsInteriors
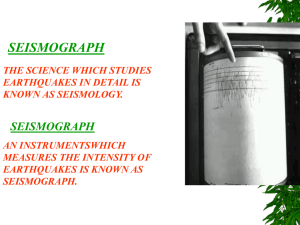
... • When the ground shakes, the base and frame of the instrument move with it • Inertia keeps the pendulum in place • It will then appear to move; relative to the shaking ground • As it moves, it records the pendulum ...
... • When the ground shakes, the base and frame of the instrument move with it • Inertia keeps the pendulum in place • It will then appear to move; relative to the shaking ground • As it moves, it records the pendulum ...
Catastrophic Events
... the core is divided into a liquid outer core and a solid inner core. I understand the crust and rigid portion of the upper mantle make up the lithosphere, which is broken into plates that move over a plastic-like portion of the mantle. I understand lithospheric plates move at a rate of 2 to 20 c ...
... the core is divided into a liquid outer core and a solid inner core. I understand the crust and rigid portion of the upper mantle make up the lithosphere, which is broken into plates that move over a plastic-like portion of the mantle. I understand lithospheric plates move at a rate of 2 to 20 c ...
Internal and External Forces that Shape the Earth
... tectonic plates spread apart and cools, forming new rock ...
... tectonic plates spread apart and cools, forming new rock ...
C1.7 Changes in Earth and atmosphere
... Describe some of the effects of tectonic plate movements, particularly at plate boundaries Describe how Wegener’s theory explained the formation of mountains described continental drift Explain why Wegener’s theory of continental drift was not generally accepted for many years, and compare it to the ...
... Describe some of the effects of tectonic plate movements, particularly at plate boundaries Describe how Wegener’s theory explained the formation of mountains described continental drift Explain why Wegener’s theory of continental drift was not generally accepted for many years, and compare it to the ...
Worksheet 046 - Nature Conservation Lewisham
... weathering and large earth movements. The rocks are gradually recycled over millions of years. This is called the rock cycle. For example sedimentary rocks can be changed into metamorphic rocks, and these can be weathered and the pieces transported away. These pieces could be deposited in lakes or s ...
... weathering and large earth movements. The rocks are gradually recycled over millions of years. This is called the rock cycle. For example sedimentary rocks can be changed into metamorphic rocks, and these can be weathered and the pieces transported away. These pieces could be deposited in lakes or s ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.