Geological Timescale Tables
... Group 3: You have been assigned the Mesozoic. Please plot the major Period boundaries and the following events: Event Paleozoic-Mesozoic boundary First crocodiles Rifting that eventually led to opening of the Atlantic Ocean begins (Triassic/Jurassic rift basins- local examples are Newark and Hartfo ...
... Group 3: You have been assigned the Mesozoic. Please plot the major Period boundaries and the following events: Event Paleozoic-Mesozoic boundary First crocodiles Rifting that eventually led to opening of the Atlantic Ocean begins (Triassic/Jurassic rift basins- local examples are Newark and Hartfo ...
Geologic Time: Group 1: You have been assigned the entire
... Group 3: You have been assigned the Mesozoic. Please plot the major Period boundaries and the following events: Event Paleozoic-Mesozoic boundary First crocodiles Rifting that eventually led to opening of the Atlantic Ocean begins (Triassic/Jurassic rift basins- local examples are Newark and Hartfo ...
... Group 3: You have been assigned the Mesozoic. Please plot the major Period boundaries and the following events: Event Paleozoic-Mesozoic boundary First crocodiles Rifting that eventually led to opening of the Atlantic Ocean begins (Triassic/Jurassic rift basins- local examples are Newark and Hartfo ...
The Four Spheres of Earth and Their Influence - geography-bbs
... The lithosphere, which evolved about 4.6 billion years ago, is composed of an outermost layer of hard rock. This outer rock layer is made up of the crust and the first hard layer of mantle. The lithosphere includes various landforms such as mountains and valleys, as well as rocks, minerals and soil. ...
... The lithosphere, which evolved about 4.6 billion years ago, is composed of an outermost layer of hard rock. This outer rock layer is made up of the crust and the first hard layer of mantle. The lithosphere includes various landforms such as mountains and valleys, as well as rocks, minerals and soil. ...
Name______________________ due date ______ period
... 9. In which era did dinosaurs become extinct? ___________________________________________ 10. In which era did the great extinction on earth take place? _______________________________ 11. Which statement best explains why no Permian age bedrock is found in New York State? (1) The extinction of many ...
... 9. In which era did dinosaurs become extinct? ___________________________________________ 10. In which era did the great extinction on earth take place? _______________________________ 11. Which statement best explains why no Permian age bedrock is found in New York State? (1) The extinction of many ...
What is Inquiry-Based Science?
... Throughout these units, students participate in a variety of activities involving observation, measurement, identification of properties, and controlled experiments that uncover important concepts in the life, physical, and earth sciences. The children’s own questions often lead them to investigatio ...
... Throughout these units, students participate in a variety of activities involving observation, measurement, identification of properties, and controlled experiments that uncover important concepts in the life, physical, and earth sciences. The children’s own questions often lead them to investigatio ...
Growing or
... supporting the ideas of platetectonics,a convective process where new lithosphere is created and equally efficiently destroyed.The motions are fast intermsofearth history.Touse John Elder's expression.the "roll-over" time of the crust is short, a few hundred million years. Elder's (1972) model of co ...
... supporting the ideas of platetectonics,a convective process where new lithosphere is created and equally efficiently destroyed.The motions are fast intermsofearth history.Touse John Elder's expression.the "roll-over" time of the crust is short, a few hundred million years. Elder's (1972) model of co ...
01 - Raimondi Science
... b. Earth changes only at certain times and only after certain events. c. Earth is uniform and unchanging; it has always been as it is now. d. the same geologic processes have been at work throughout Earth’s history. 3. Which of the following processes was NOT observed by Hutton when he developed the ...
... b. Earth changes only at certain times and only after certain events. c. Earth is uniform and unchanging; it has always been as it is now. d. the same geologic processes have been at work throughout Earth’s history. 3. Which of the following processes was NOT observed by Hutton when he developed the ...
Are the continents moving? What are plate tectonics?
... had once been joined, and over time had drifted apart. Pangaea was a supercontinent that included all the world's landmasses in the late Paleozoic and, according to the theory of plate tectonics. ...
... had once been joined, and over time had drifted apart. Pangaea was a supercontinent that included all the world's landmasses in the late Paleozoic and, according to the theory of plate tectonics. ...
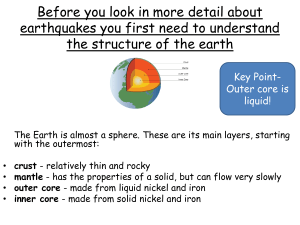
Earth’s Layers
... • Soft – can bend like plastic, layer in the upper portion of the mantle • It is located right below the Lithosphere. Lithosphere floats on this layer (like jello) ...
... • Soft – can bend like plastic, layer in the upper portion of the mantle • It is located right below the Lithosphere. Lithosphere floats on this layer (like jello) ...
Plate Tectonics Vocabulary Words
... The crust makes up less than 1% of the Earth’s mass. • We are on the Crust right now. ...
... The crust makes up less than 1% of the Earth’s mass. • We are on the Crust right now. ...
File
... 1) Most geological processes take place very slowly, over _______________________ or _________________________ of years, but some processes, like __________________________, ______________________________, and ___________________________________ can happen very quickly and with very little warning. ...
... 1) Most geological processes take place very slowly, over _______________________ or _________________________ of years, but some processes, like __________________________, ______________________________, and ___________________________________ can happen very quickly and with very little warning. ...
Rocks provide a timeline for Earth.
... major volcanic eruptions or the impacts of asteroids. 7.4.e Students know fossils provide evidence of how life and environmental conditions have changed. CHAPTER RESOURCES SECTION OUTLINE ...
... major volcanic eruptions or the impacts of asteroids. 7.4.e Students know fossils provide evidence of how life and environmental conditions have changed. CHAPTER RESOURCES SECTION OUTLINE ...
Document
... Continental crust is very old (typically over a billion years old) because it does not get recycled frequently. Oceanic crust is typically 100 million years old on average (fairly young). Oceanic crust is continually recycled. ...
... Continental crust is very old (typically over a billion years old) because it does not get recycled frequently. Oceanic crust is typically 100 million years old on average (fairly young). Oceanic crust is continually recycled. ...
Plate Tectonic Notes
... identify the continents that were once part of Pangaea? • Let’s find out… • http://kids.earth.nasa.gov/archive/pangaea/Pangaea_game.html ...
... identify the continents that were once part of Pangaea? • Let’s find out… • http://kids.earth.nasa.gov/archive/pangaea/Pangaea_game.html ...
Earth Science Chapter 5 - alisa25k
... • You are Harry Hess! (or Harriet Hess) • You have just concluded your research about sea-floor spreading • Prepare a speech for your science conference in which you will share your findings • Include your theory, the evidence that supports if from molten material, magnetic stripes, and drilling sam ...
... • You are Harry Hess! (or Harriet Hess) • You have just concluded your research about sea-floor spreading • Prepare a speech for your science conference in which you will share your findings • Include your theory, the evidence that supports if from molten material, magnetic stripes, and drilling sam ...
Hemingway Name: 12.1 Evidence for Continental Drift * PANGEA
... ________________ began on one continent, end on the coastline and then appear to continue on a continent across the ocean ...
... ________________ began on one continent, end on the coastline and then appear to continue on a continent across the ocean ...
Spring 2007 Earth Science
... produced by the friction of air particles released from Earth’s interior absorbed by Earth during daylight hours ...
... produced by the friction of air particles released from Earth’s interior absorbed by Earth during daylight hours ...
Name _____ Hour ______ Score Plate Tectonics Unit Objectives
... Identify the different layers of the Earth and their compositions Describe important milestones in geologic time eras Describe the movement of the Earth’s plates over geologic time Explain Alfred Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis and why it was not accepted in his time Explain the the ...
... Identify the different layers of the Earth and their compositions Describe important milestones in geologic time eras Describe the movement of the Earth’s plates over geologic time Explain Alfred Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis and why it was not accepted in his time Explain the the ...
GEOLOGY 11 EXAM I STUDY QUESTIONS What are the
... What is luster? What is cleavage? How is hardness of minerals measured? What is the most abundant atom in the rocky part of the earth? What is the most abundant mineral in the crust? What are the minerals in the mantle? What is the liquidus? What is the solidus? What are the states of rocks found at ...
... What is luster? What is cleavage? How is hardness of minerals measured? What is the most abundant atom in the rocky part of the earth? What is the most abundant mineral in the crust? What are the minerals in the mantle? What is the liquidus? What is the solidus? What are the states of rocks found at ...
Name: Graphing Seafloor Spreading Lab Objective: Using ocean
... Questions: 1) What process within Earth’s asthenosphere is responsible for plate motions? ...
... Questions: 1) What process within Earth’s asthenosphere is responsible for plate motions? ...
Changes to Earth`s Surface Chapter 9
... When magma finds a vent (opening) between the plates it sometimes pushes through to Earth’s surface. The magma that flows onto Earth’s surface turn into lava. ...
... When magma finds a vent (opening) between the plates it sometimes pushes through to Earth’s surface. The magma that flows onto Earth’s surface turn into lava. ...
Chapter 7
... • Combines the hypothesis of continental drift with the theory of sea floor spreading. • Earth’s crust and upper mantle broken into plates. • Shift on layer of molten rock. ...
... • Combines the hypothesis of continental drift with the theory of sea floor spreading. • Earth’s crust and upper mantle broken into plates. • Shift on layer of molten rock. ...
The Layer`s Of The Earth!
... 3) Using the rolling pin, roll out the red clay in a flat circular shape (represents the outer core) ...
... 3) Using the rolling pin, roll out the red clay in a flat circular shape (represents the outer core) ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.