Volcanoes
... Why do volcanoes erupt? Hot, melted rock (magma) deep within the earth becomes lighter as it heats up. Because it is lighter than solid rock it rises until it pushes to the surface of the earth. A volcanic eruption occurs! ...
... Why do volcanoes erupt? Hot, melted rock (magma) deep within the earth becomes lighter as it heats up. Because it is lighter than solid rock it rises until it pushes to the surface of the earth. A volcanic eruption occurs! ...
Composition Physical Properties
... One unusual type is a carbonaceous chondrite, which can contain up to 5% organic carbon, i.e. hydrocarbons, amino acids. ...
... One unusual type is a carbonaceous chondrite, which can contain up to 5% organic carbon, i.e. hydrocarbons, amino acids. ...
Tyler Levy notes - Mark W. Williams, Ph.D
... o It is well known that the axis of the magnetic field is tipped with respect to the rotation axis of the Earth. o Thus, true north (defined by the direction to the north rotational pole) does not coincide with magnetic north (defined by the direction to the north magnetic pole) and compass directio ...
... o It is well known that the axis of the magnetic field is tipped with respect to the rotation axis of the Earth. o Thus, true north (defined by the direction to the north rotational pole) does not coincide with magnetic north (defined by the direction to the north magnetic pole) and compass directio ...
Ch 8 Earth Resources Content
... Currently, the United States is losing three billion tons of nutrient-rich topsoil each year. Growing corn and soy for animal feed using conventional methods causes a significant amount of this soil loss. Compared with row crops, pasture reduces soil loss by as much as 93 percent. [Ontario Ministry ...
... Currently, the United States is losing three billion tons of nutrient-rich topsoil each year. Growing corn and soy for animal feed using conventional methods causes a significant amount of this soil loss. Compared with row crops, pasture reduces soil loss by as much as 93 percent. [Ontario Ministry ...
Document
... b. piece of lithosphere with a unique geologic history c. crack in the center of a mid-ocean ridge d. supercontinent formed about 300 million years ago e. residual magnetism of rock f. process by which new sea floor forms g. layer that forms the thin outer shell of Earth h. cycle in which heated mat ...
... b. piece of lithosphere with a unique geologic history c. crack in the center of a mid-ocean ridge d. supercontinent formed about 300 million years ago e. residual magnetism of rock f. process by which new sea floor forms g. layer that forms the thin outer shell of Earth h. cycle in which heated mat ...
Density and Earth`s Layers Review Answer Key
... Part 2: Deposition and Earth’s Layers 1. What is deposition? The settling of sediments out of wind or water 2. What are the two main factors that affect deposition? Particle density and particle size 3. Explain the deposition in the following diagram: ...
... Part 2: Deposition and Earth’s Layers 1. What is deposition? The settling of sediments out of wind or water 2. What are the two main factors that affect deposition? Particle density and particle size 3. Explain the deposition in the following diagram: ...
CRT Science Review #8 Earth Science
... processes. These processes can be constructive or destructive and occur over geologic time scales. Indicators & Item Specifications: E.8.C.1 Students know sedimentary rocks and fossils provide evidence for changing environments and the constancy of geologic processes. E/S • Understand why most fossi ...
... processes. These processes can be constructive or destructive and occur over geologic time scales. Indicators & Item Specifications: E.8.C.1 Students know sedimentary rocks and fossils provide evidence for changing environments and the constancy of geologic processes. E/S • Understand why most fossi ...
Chapter 1 Review answers
... 1. compressional force: occurs when plates move towards each other, sqeezing together which causes rock layers to bend, warp, or be pushed upwards. 2. tensional force: occurs when plates break apart, moving away from or past each other, which sometimes forms a trench as one plate drops downward. ...
... 1. compressional force: occurs when plates move towards each other, sqeezing together which causes rock layers to bend, warp, or be pushed upwards. 2. tensional force: occurs when plates break apart, moving away from or past each other, which sometimes forms a trench as one plate drops downward. ...
Earth Science Vocabulary Chapter 9: Plate Tectonics Section 9.1
... Volcanic Island Arc- a chain of volcanic islands generally located a few hundred kilometers from a trench where subduction of one oceanic slab beneath another is occurring Section 9.4: Paleomagnetism- the study of changes in Earth’s magnetic field, as shown by patterns of magnetism in rocks that hav ...
... Volcanic Island Arc- a chain of volcanic islands generally located a few hundred kilometers from a trench where subduction of one oceanic slab beneath another is occurring Section 9.4: Paleomagnetism- the study of changes in Earth’s magnetic field, as shown by patterns of magnetism in rocks that hav ...
Chapter 12.1 Notes
... He used evidence to come up with his theory: The continents looked as though they might fit together like puzzle pieces. (The continental shelves actually fit together even better) There were matching geologic features and rocks on different continents. There were matching fossils, like Mesosaurus, ...
... He used evidence to come up with his theory: The continents looked as though they might fit together like puzzle pieces. (The continental shelves actually fit together even better) There were matching geologic features and rocks on different continents. There were matching fossils, like Mesosaurus, ...
Chapter 2 – Planet Earth GRA Section Summary
... Areas near the equator receive direct rays from the sun all year and have warm temperatures. Higher latitudes receive fewer direct rays and are cooler. THE SEASONS Many locations on Earth have four seasons: winter, spring, summer, and fall. These are based on temperature and how long the days are. T ...
... Areas near the equator receive direct rays from the sun all year and have warm temperatures. Higher latitudes receive fewer direct rays and are cooler. THE SEASONS Many locations on Earth have four seasons: winter, spring, summer, and fall. These are based on temperature and how long the days are. T ...
Bill Nye Earthquake Video Notes
... I hope that this building doesn't fall down Rumble, rumble An earthquake sure can make you humble I wonder what's happening with the Earth's crust Rawr, rawr ...
... I hope that this building doesn't fall down Rumble, rumble An earthquake sure can make you humble I wonder what's happening with the Earth's crust Rawr, rawr ...
Thursday 1-31 ps - elyceum-beta
... • His book caused so much stir in USA, was never reprinted (in part that he was not a geologist) ...
... • His book caused so much stir in USA, was never reprinted (in part that he was not a geologist) ...
Happy Lesson
... 5. What happens when these plates move? • [A] They can collide. (correct answer) • [B] They can move apart. (correct answer) • [C] They can slide past each other. (correct answer) • [D] They can combine to form one plate ...
... 5. What happens when these plates move? • [A] They can collide. (correct answer) • [B] They can move apart. (correct answer) • [C] They can slide past each other. (correct answer) • [D] They can combine to form one plate ...
Textbook Powerpoint
... The rock cycle. The rock cycle slowly but continuously forms new rock and breaks down old rock. Three types of rock are created in the rock cycle: Igneous rock is formed from magma; sedimentary rock is formed by the compression of sedimentary materials; and metamorphic rock is created when rocks are ...
... The rock cycle. The rock cycle slowly but continuously forms new rock and breaks down old rock. Three types of rock are created in the rock cycle: Igneous rock is formed from magma; sedimentary rock is formed by the compression of sedimentary materials; and metamorphic rock is created when rocks are ...
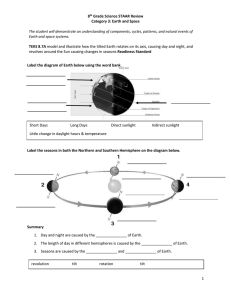
8th Grade Science STAAR Review Category 3: Earth and Space
... 1. Label the 2 pictures above as either spring or neap tide. 2. What 2 moons phases do spring tides occur during? ____________________________________ 3. What 2 moons phases do neap tides occur during? _____________________________________ 4. What is the tidal range for spring tides? _______________ ...
... 1. Label the 2 pictures above as either spring or neap tide. 2. What 2 moons phases do spring tides occur during? ____________________________________ 3. What 2 moons phases do neap tides occur during? _____________________________________ 4. What is the tidal range for spring tides? _______________ ...
Exam Review with Answers
... a. Independent Variable – the variable you are testing. It is the variable that the researcher changes. Also called the manipulated variable. b. Dependent Variable– the variable that you are measuring. It is also called the responding variable. 3. How many variables should be tested during an experi ...
... a. Independent Variable – the variable you are testing. It is the variable that the researcher changes. Also called the manipulated variable. b. Dependent Variable– the variable that you are measuring. It is also called the responding variable. 3. How many variables should be tested during an experi ...
Getting to Know: Plate Tectonics
... Earth’s crust is divided into several large tectonic plates that ride on top of slowly moving rock in the Earth’s mantle. Convection in the mantle causes these plates to move. Tectonic plates move at extremely slow rates, which is why we cannot feel them moving. However, we can witness their effects ...
... Earth’s crust is divided into several large tectonic plates that ride on top of slowly moving rock in the Earth’s mantle. Convection in the mantle causes these plates to move. Tectonic plates move at extremely slow rates, which is why we cannot feel them moving. However, we can witness their effects ...
Unit 4
... fundamental question raised by his critics: what kind of forces could be strong enough to move such large masses of solid rock over such great distances? E After Wegener`s death in 1930, new evidence from ocean floor exploration and other studies rekindled interest in his theory, ultimately leading, ...
... fundamental question raised by his critics: what kind of forces could be strong enough to move such large masses of solid rock over such great distances? E After Wegener`s death in 1930, new evidence from ocean floor exploration and other studies rekindled interest in his theory, ultimately leading, ...
the geosphere - Blinklearning
... Minerals are solid substances. They cannot be liquid or gaseous. They are inorganic. They have not been produced by living things. They are natural, not made by humans. They have a definite chemical composition; they are composed of chemical elements that are always combined in the same proportion t ...
... Minerals are solid substances. They cannot be liquid or gaseous. They are inorganic. They have not been produced by living things. They are natural, not made by humans. They have a definite chemical composition; they are composed of chemical elements that are always combined in the same proportion t ...
Slide 1
... While this may not seem significant, the cycling of nitrogen on Earth is essential for life. It is found in amino acids, proteins, and genetic material. Nitrogen is the most abundant element in the atmosphere (~78%). However, gaseous nitrogen must be 'fixed' into another form so that it can be used ...
... While this may not seem significant, the cycling of nitrogen on Earth is essential for life. It is found in amino acids, proteins, and genetic material. Nitrogen is the most abundant element in the atmosphere (~78%). However, gaseous nitrogen must be 'fixed' into another form so that it can be used ...
Deforming the Earth`s Crust
... mountains form. • The layers of the crust break and drop in elevation compared to surrounding layers. • The Tetons are an ...
... mountains form. • The layers of the crust break and drop in elevation compared to surrounding layers. • The Tetons are an ...
When drilling stopped in 1994, the hole was over seven miles deep
... Council for the Study of the Earth’s Interior and Superdeep Drilling, which spent years preparing for the historic project. It was started in parallel to the Space Race, a period of intense competition between the U.S. and U.S.S.R. The survey to find a suitable drill site was completed in 1965 when ...
... Council for the Study of the Earth’s Interior and Superdeep Drilling, which spent years preparing for the historic project. It was started in parallel to the Space Race, a period of intense competition between the U.S. and U.S.S.R. The survey to find a suitable drill site was completed in 1965 when ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.