Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Plate Tectonics
... Seismic wave speeds, and how they travel through different levels in the interior allow scientists to map out the major layers of Earth. ...
... Seismic wave speeds, and how they travel through different levels in the interior allow scientists to map out the major layers of Earth. ...
Name__________________________________________
... 11. Why? (refer to question #10) 12. How does the Sun (and all other stars) produce their energy? 13. What are the 3 ways the Earth moves? ...
... 11. Why? (refer to question #10) 12. How does the Sun (and all other stars) produce their energy? 13. What are the 3 ways the Earth moves? ...
earthquakes and volcanoes - Didattica Orizzonte Scuola
... divided into a number of blocks of rock, called plates, that cover the planet. An earthquake is a sudden, violent shaking in Earth’s crust. It happens when two of these plates, under great pressure, move past each other along a fault. The violent shaking is caused by seismic waves that travel throug ...
... divided into a number of blocks of rock, called plates, that cover the planet. An earthquake is a sudden, violent shaking in Earth’s crust. It happens when two of these plates, under great pressure, move past each other along a fault. The violent shaking is caused by seismic waves that travel throug ...
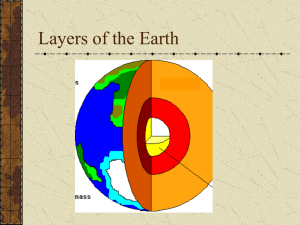
Scale Model of Earth`s Layers
... 2.Label the state of matter of each layer. 3.What elements make up the core? 4.Label the thickness of each layer. 5.Label the temperature of each layer using the numbers below. 12,000 F ...
... 2.Label the state of matter of each layer. 3.What elements make up the core? 4.Label the thickness of each layer. 5.Label the temperature of each layer using the numbers below. 12,000 F ...
Open file
... particles and so are the slower of the two. They do not transmit through liquid medium and so the inner core cannot be penetrated by S waves. S waves will however pass through the mantle this provides scientist with evidence to suggest that the outer core is not a solid structure. As S waves cannot ...
... particles and so are the slower of the two. They do not transmit through liquid medium and so the inner core cannot be penetrated by S waves. S waves will however pass through the mantle this provides scientist with evidence to suggest that the outer core is not a solid structure. As S waves cannot ...
A. WEATHERING • Weathering is the BREAKUP OF ROCK mainly
... DISINTEGRATE as it is subjected to freezing-thawing cycles, rain, and other environmental forces. The rock breaks down into parent material, which in turn breaks into smaller mineral particles. Biological material adds to the chemical breakdown of the rock material. As soil continues to develop, lay ...
... DISINTEGRATE as it is subjected to freezing-thawing cycles, rain, and other environmental forces. The rock breaks down into parent material, which in turn breaks into smaller mineral particles. Biological material adds to the chemical breakdown of the rock material. As soil continues to develop, lay ...
Natural History of Newfoundland and Labrador: Geological Formation
... years ago. These mantle rocks, normally dark green in colour, are now brown because they have been open to the atmosphere for such a long time. The soil on the Tablelands is so poor in nutrients, very little grows in this area. It has often been described as a moonscape. (9) On the east coast of New ...
... years ago. These mantle rocks, normally dark green in colour, are now brown because they have been open to the atmosphere for such a long time. The soil on the Tablelands is so poor in nutrients, very little grows in this area. It has often been described as a moonscape. (9) On the east coast of New ...
chap2 - LaffertysBiologyClass
... HOW this occurred. • What is the name of the process that explains HOW the continents drift? – Theory of Plate Tectonics ...
... HOW this occurred. • What is the name of the process that explains HOW the continents drift? – Theory of Plate Tectonics ...
Plate Tectonics 1
... Alfred Wegner came up with the Continental Drift Hypothesis. His 5 pieces of evidence were: 1) Continents seemed to fit together 2) Similar fossils on each continent 3) Rocks matched (age and composition) 4) Glacial evidence – striations (scratches in rocks matched) + deposits 5) Climate evidence – ...
... Alfred Wegner came up with the Continental Drift Hypothesis. His 5 pieces of evidence were: 1) Continents seemed to fit together 2) Similar fossils on each continent 3) Rocks matched (age and composition) 4) Glacial evidence – striations (scratches in rocks matched) + deposits 5) Climate evidence – ...
Chapter 4: Earthquakes
... – If there are two normal faults near each other, the land between could eventually drop down creating a valley. ...
... – If there are two normal faults near each other, the land between could eventually drop down creating a valley. ...
Earth`s Shifting Crust
... making it only 10,000 years ago, instead of 30,000 years. A still more startling discovery was that the first known phase of this ice age (called the "Farmdale Advance") occurred only about 25,000 yean ago, instead of more than 100,000 years before the present. Ihis discovery challenged the fundamen ...
... making it only 10,000 years ago, instead of 30,000 years. A still more startling discovery was that the first known phase of this ice age (called the "Farmdale Advance") occurred only about 25,000 yean ago, instead of more than 100,000 years before the present. Ihis discovery challenged the fundamen ...
Water Resources - Mayfield City Schools
... Talk About It Do you think the distance between the source of the nitrogen and phosphorus and the dead zones themselves makes it difficult to manage this problem? Why or why not? ...
... Talk About It Do you think the distance between the source of the nitrogen and phosphorus and the dead zones themselves makes it difficult to manage this problem? Why or why not? ...
Plate Tectonics, Topographic Maps Test
... 8th Grade Plate Tectonics & Topographic Maps Test 1. The mid-ocean ridge is a. Another name for Pangaea b. The Rocky Mountains c. A volcano d. A huge mountain range under the ocean 2. The lithosphere includes both the crust and the solid part of theA. Inner Core B. Outer Core C. Mantle D. All of the ...
... 8th Grade Plate Tectonics & Topographic Maps Test 1. The mid-ocean ridge is a. Another name for Pangaea b. The Rocky Mountains c. A volcano d. A huge mountain range under the ocean 2. The lithosphere includes both the crust and the solid part of theA. Inner Core B. Outer Core C. Mantle D. All of the ...
Chapter 8 The Moon and Mercury
... Examination of the whole surface of the moon shows us that A. craters exist only on one side of the moon. B. the northern hemisphere is distinctly different from the southern hemisphere. C. the moon can be considered as having two distinctly different sides, that seen from Earth, and that hidden fr ...
... Examination of the whole surface of the moon shows us that A. craters exist only on one side of the moon. B. the northern hemisphere is distinctly different from the southern hemisphere. C. the moon can be considered as having two distinctly different sides, that seen from Earth, and that hidden fr ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • Earth has a thin rigid lithosphere that is underlain by a plastic asthenosphere • Seafloor crust is created along mid-ocean ridges where magma upwells from the mantle • Ocean basins are generally younger than continents • Seaflloor spreads until it encounters a trench and descends back into the ma ...
... • Earth has a thin rigid lithosphere that is underlain by a plastic asthenosphere • Seafloor crust is created along mid-ocean ridges where magma upwells from the mantle • Ocean basins are generally younger than continents • Seaflloor spreads until it encounters a trench and descends back into the ma ...
Notes for the unit
... Alaska, 1964 - one of the most violent quakes of recent times. - It lasted 7 minutes - It was felt in Texas - The ground moved up and down 6m - A giant ocean wave was set off 200km away, which rushed to shore and moved a 10,000 tonne ship on to land. Earthquakes occur along _______________. The rock ...
... Alaska, 1964 - one of the most violent quakes of recent times. - It lasted 7 minutes - It was felt in Texas - The ground moved up and down 6m - A giant ocean wave was set off 200km away, which rushed to shore and moved a 10,000 tonne ship on to land. Earthquakes occur along _______________. The rock ...
Background Info SBTaylor
... 3. Sed. rocks account for only 5% of the earth's crust/lithosphere, however they cover 75% of the earth's surface exposures. The sedimentary environment is a surface environment (at surface pressures and temperatures) 4. As geologists we can examine modern day sedimentary processes, look at depositi ...
... 3. Sed. rocks account for only 5% of the earth's crust/lithosphere, however they cover 75% of the earth's surface exposures. The sedimentary environment is a surface environment (at surface pressures and temperatures) 4. As geologists we can examine modern day sedimentary processes, look at depositi ...
Ch 7 study guide answers
... where plates are separating. The magma is pushing up through the plate boundary causing the plates to move away from each other. The youngest rock is found at the mid-ocean ridge. The rock get older as you move away from the mid ocean ridge. 7. What are subduction zones and at what type of boundary ...
... where plates are separating. The magma is pushing up through the plate boundary causing the plates to move away from each other. The youngest rock is found at the mid-ocean ridge. The rock get older as you move away from the mid ocean ridge. 7. What are subduction zones and at what type of boundary ...
Mineralogy and Petrology :: 2. Formation of minerals (and rocks)
... present in smaller quantities so far increase significantly. A crystallization depth of around 2-12 km and a very slowly changing temperature of around 600-800°C enable calm crystallization, and thus enormous crystals of even several metres may form. This early phase of the postcrystallization stage ...
... present in smaller quantities so far increase significantly. A crystallization depth of around 2-12 km and a very slowly changing temperature of around 600-800°C enable calm crystallization, and thus enormous crystals of even several metres may form. This early phase of the postcrystallization stage ...
PowerPoint Fill-in-the-Notes for Unit 2
... Why are the days longer in some parts of the year? • The Earth’s axis is at an ___________________. • In about half of the Earth’s orbit, the tilt causes a region to face toward the sun for more hours than it faces away from the sun. • _______________________. • In other regions that face away from ...
... Why are the days longer in some parts of the year? • The Earth’s axis is at an ___________________. • In about half of the Earth’s orbit, the tilt causes a region to face toward the sun for more hours than it faces away from the sun. • _______________________. • In other regions that face away from ...
Directions: Select the best answer for each item. (8.P.1A.3) Some
... ends come together the carpet bunches and folds. This model illustrates __________. a. Normal Faults b. Reverse Faults c. Strike-Slip Faults d. Uplift Faults 18. (8.E.5B.2) The land formation modeled in this demonstration is __________. a. An Earthquake b. A Mountain c. A Ridge d. A Volcano 19. (8.E ...
... ends come together the carpet bunches and folds. This model illustrates __________. a. Normal Faults b. Reverse Faults c. Strike-Slip Faults d. Uplift Faults 18. (8.E.5B.2) The land formation modeled in this demonstration is __________. a. An Earthquake b. A Mountain c. A Ridge d. A Volcano 19. (8.E ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.