PROTEIN-LIPID AND PROTEIN-CARBOHYDRATE INTERACTIONS
... and ionic groups of the polypeptide chain. Fractionation and reconstitution studies have shown that starch tailings fraction, although contributing to water absorption and dough-fell, is not essential for optimum loaf volume (HosENEY et al., 1971). KHAN - BUSHUK (1979) investigated the carbohydrate- ...
... and ionic groups of the polypeptide chain. Fractionation and reconstitution studies have shown that starch tailings fraction, although contributing to water absorption and dough-fell, is not essential for optimum loaf volume (HosENEY et al., 1971). KHAN - BUSHUK (1979) investigated the carbohydrate- ...
Coarse-Grained Modeling of ProteinDynamics
... 2000). Mechanical unfolding of a number of proteins has been also probed by allatom simulations with implicit solvent (Paci and Karplus 2000). The major shortcoming of all-atom MD simulations is that the pulling speed is about 6 orders of magnitude higher than that used in AFM experiments. It is unc ...
... 2000). Mechanical unfolding of a number of proteins has been also probed by allatom simulations with implicit solvent (Paci and Karplus 2000). The major shortcoming of all-atom MD simulations is that the pulling speed is about 6 orders of magnitude higher than that used in AFM experiments. It is unc ...
Thermal unfolding of proteins at high pH range studied by UV
... The UV absorbance changes following tyrosyl ionization can be used to monitor protein unfolding. Buried tyrosine residues are not affected by the pH. The unfolding of the protein molecule leads to the exposure of these residues at the protein surface and therefore tyrosyl ionization is detected. In ...
... The UV absorbance changes following tyrosyl ionization can be used to monitor protein unfolding. Buried tyrosine residues are not affected by the pH. The unfolding of the protein molecule leads to the exposure of these residues at the protein surface and therefore tyrosyl ionization is detected. In ...
Lipids as hormones and second messengers
... Nearly all of the possible products of these cleavage reactions (i.e. phospholipid headgroups, lysophospholipids, DAGs, PA and fatty acids) have been implicated in signal transduction. For example, release of lysophospholipids and fatty acids via phospholipase A2 provides compounds that serve as pre ...
... Nearly all of the possible products of these cleavage reactions (i.e. phospholipid headgroups, lysophospholipids, DAGs, PA and fatty acids) have been implicated in signal transduction. For example, release of lysophospholipids and fatty acids via phospholipase A2 provides compounds that serve as pre ...
Identification and Characterization of Two Temperature
... The present study was performed to identify stress-induced putative virulence proteins of Streptococcus suis. For this, protein expression patterns of streptococci grown at 32, 37, and 42°C were compared by one- and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Temperature shifts from 32 and 37 to 42°C induc ...
... The present study was performed to identify stress-induced putative virulence proteins of Streptococcus suis. For this, protein expression patterns of streptococci grown at 32, 37, and 42°C were compared by one- and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Temperature shifts from 32 and 37 to 42°C induc ...
Information Content in Genetics:
... groups of organisms in all eukaryote kingdoms use elongation factor-like protein (EFL) for the same purpose.] It brings the tRNA-AA complex to the large ribosome subunit Aminoacyl (A) site for the tRNA anticodon to pair with the mRNA codon. Once pairing of complementary bases occurs, the EF-1α GTPas ...
... groups of organisms in all eukaryote kingdoms use elongation factor-like protein (EFL) for the same purpose.] It brings the tRNA-AA complex to the large ribosome subunit Aminoacyl (A) site for the tRNA anticodon to pair with the mRNA codon. Once pairing of complementary bases occurs, the EF-1α GTPas ...
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors
... [1]. The fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFr) is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) involved in many biological processes like Angiogenesis, embryo development, and homeostasis of adult body tissues. The fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) family consists of five highly related genes (FGFR1-4 ...
... [1]. The fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFr) is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) involved in many biological processes like Angiogenesis, embryo development, and homeostasis of adult body tissues. The fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) family consists of five highly related genes (FGFR1-4 ...
The Nterminal region of the bacterial DNA polymerase PolC features
... structures of DnaE and PolC, corresponding OB domains occupy positions that are much closer in space than might be expected from their distinct location in sequence. This suggests that the OB domain may play a similar role in binding the incoming template in both PolC and DnaE. The ability to bind s ...
... structures of DnaE and PolC, corresponding OB domains occupy positions that are much closer in space than might be expected from their distinct location in sequence. This suggests that the OB domain may play a similar role in binding the incoming template in both PolC and DnaE. The ability to bind s ...
Red blood cells: proteomics, physiology and metabolism
... lipidomics is still is in its infancy and faces a number of technological challenges. A first attempt to characterise phospholipid exchange by lipidomics used embryonic fibroblasts (10). In future this approach may help unravel poorly abundant membrane lipids with important physiological functions, ...
... lipidomics is still is in its infancy and faces a number of technological challenges. A first attempt to characterise phospholipid exchange by lipidomics used embryonic fibroblasts (10). In future this approach may help unravel poorly abundant membrane lipids with important physiological functions, ...
Increasing Muscle Growth
... he constant struggle to put on muscle is one numerous people have been struggling with for many years. People want to see results and they want to see them fast. Some even turn to illegal or unhealthy ways to achieve these results such as steroid use or compulsive exercising. For those who decide to ...
... he constant struggle to put on muscle is one numerous people have been struggling with for many years. People want to see results and they want to see them fast. Some even turn to illegal or unhealthy ways to achieve these results such as steroid use or compulsive exercising. For those who decide to ...
P1 and P2 protein heterodimer binding to the P0 protein of
... are more important for cell growth than P1b or P2a (30). A recently described stalk assembly model attributed a leading role to the P1a/P2b pair, proposed to be the first heterodimer to bind to site A of P0. The P1b/P2a pair would play a subsidiary function, subsequently binding to site B (20,24). Th ...
... are more important for cell growth than P1b or P2a (30). A recently described stalk assembly model attributed a leading role to the P1a/P2b pair, proposed to be the first heterodimer to bind to site A of P0. The P1b/P2a pair would play a subsidiary function, subsequently binding to site B (20,24). Th ...
Phosphorylation of apoproteins in VLDL, and LDL by protein
... for apo BlOO phosphorylated by CAMP-PKcompared with AMPPK (Figure lb). This indicates that these two kinases phosphorylate different sites. This has also been suggested by reversed phase HPLC separation of tryptic peptides from apo BlOO phosphorylated by either kinase and will be confmed when these ...
... for apo BlOO phosphorylated by CAMP-PKcompared with AMPPK (Figure lb). This indicates that these two kinases phosphorylate different sites. This has also been suggested by reversed phase HPLC separation of tryptic peptides from apo BlOO phosphorylated by either kinase and will be confmed when these ...
Identification of TIpC, a novel 62 kDa MCP
... of high conservation was found to be localized within the C-terminal domain (Fig. 4), with no detectable homology in the N-terminal region. An amino acid alignment between TlpC and a representative E. coli transducer Tar showed 30.0 o/' identity in a 297 amino acid overlap (Fig. 4). The similarity b ...
... of high conservation was found to be localized within the C-terminal domain (Fig. 4), with no detectable homology in the N-terminal region. An amino acid alignment between TlpC and a representative E. coli transducer Tar showed 30.0 o/' identity in a 297 amino acid overlap (Fig. 4). The similarity b ...
Bacteria Binding by DMBT1/SAG/gp-340 Is Confined to
... interactions play a crucial role in the interaction with its negatively charged ligands (6). Group B SRCR proteins are generally involved in the regulation of cellular immune responses. In vertebrates, the group B SRCR proteins can be divided, on the basis of their structure and sequence homology, i ...
... interactions play a crucial role in the interaction with its negatively charged ligands (6). Group B SRCR proteins are generally involved in the regulation of cellular immune responses. In vertebrates, the group B SRCR proteins can be divided, on the basis of their structure and sequence homology, i ...
BMC Microbiology
... from any of two events: the release of calcium from internal stores or the increased uptake from the extracellular environment. Once the intracellular calcium concentration has increased, calcium exerts its role through a specific class of proteins known as calcium binding proteins. One of the most ...
... from any of two events: the release of calcium from internal stores or the increased uptake from the extracellular environment. Once the intracellular calcium concentration has increased, calcium exerts its role through a specific class of proteins known as calcium binding proteins. One of the most ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... • In prokaryotes, the 30S ribosome binds to a region of the mRNA (Shine-Dalgarno sequence) upstream of the initiation sequence • S-D sequence also binds to a complementary base sequence at the 3’ end of the 16S rRNA • Double-stranded RNA structure binds mRNA to the ribosome ...
... • In prokaryotes, the 30S ribosome binds to a region of the mRNA (Shine-Dalgarno sequence) upstream of the initiation sequence • S-D sequence also binds to a complementary base sequence at the 3’ end of the 16S rRNA • Double-stranded RNA structure binds mRNA to the ribosome ...
Bioinformatic Software in Web
... DNA microarray are used for genetic analysis as well as expression analysis at the mRNA level. Protein microarrays are used for expression analysis at the protein level and in the expansive field of interaction analysis. ...
... DNA microarray are used for genetic analysis as well as expression analysis at the mRNA level. Protein microarrays are used for expression analysis at the protein level and in the expansive field of interaction analysis. ...
A chemogenomic analysis of the transmembrane binding cavity of
... Key words: amino acid sequences; human G-proteincoupled receptors; transmembrane domain; bovine rhodopsin INTRODUCTION G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) constitute a large superfamily of very heterogeneous membrane receptors characterized by a typical heptahelical membrane-spanning fold usually de ...
... Key words: amino acid sequences; human G-proteincoupled receptors; transmembrane domain; bovine rhodopsin INTRODUCTION G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) constitute a large superfamily of very heterogeneous membrane receptors characterized by a typical heptahelical membrane-spanning fold usually de ...
Analysis of p75NTR-dependent apoptotic
... Although p75NTR was the first identified neurotrophin receptor, its physiological function remains poorly understood. Many studies indicate that the effects of p75NTR range from promotion of survival pathways, induction of apoptosis, modulation of cell cycle and differentiation, and facilitation or ...
... Although p75NTR was the first identified neurotrophin receptor, its physiological function remains poorly understood. Many studies indicate that the effects of p75NTR range from promotion of survival pathways, induction of apoptosis, modulation of cell cycle and differentiation, and facilitation or ...
577
... the post-synaptic membrane 7) Step (6) causes the Na+ gates to open on post synaptic membrane which starts the nerve impulse along that cell 8) Synaptic cleft is returned to normal - enzymes that destroy specific neurotransmitters - Ca2+ returned to the synaptic cleft (active transport) ...
... the post-synaptic membrane 7) Step (6) causes the Na+ gates to open on post synaptic membrane which starts the nerve impulse along that cell 8) Synaptic cleft is returned to normal - enzymes that destroy specific neurotransmitters - Ca2+ returned to the synaptic cleft (active transport) ...
Running title: Regulation of RBOHD during plant immunity
... and StCDPK5 directly phosphorylate the N-terminal region of StRBOHB in a Ca2+-dependent manner (Kobayashi et al. 2007). These CPKs phosphorylate S82 and S97 on StRBOHB, which correspond to S133 and S148 in AtRBOHD. In Arabidopsis, CPK4, CPK5, CPK6 and CPK11 (which are related to StCDPK4/5) are posit ...
... and StCDPK5 directly phosphorylate the N-terminal region of StRBOHB in a Ca2+-dependent manner (Kobayashi et al. 2007). These CPKs phosphorylate S82 and S97 on StRBOHB, which correspond to S133 and S148 in AtRBOHD. In Arabidopsis, CPK4, CPK5, CPK6 and CPK11 (which are related to StCDPK4/5) are posit ...
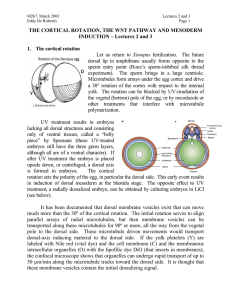
the cortical rotation, the wnt pathway
... dual-kinase mechanism. First Casein Kinase 1α (one of the first protein kinases to be discovered) phosphorylates a serine, and only then GSK-3 can phosphorylate the other Ser/Thr residurs. Once the two most amino-terminal Ser are phosphorylated, the protein is recognized by β-Trcp (Slimb in Drosophi ...
... dual-kinase mechanism. First Casein Kinase 1α (one of the first protein kinases to be discovered) phosphorylates a serine, and only then GSK-3 can phosphorylate the other Ser/Thr residurs. Once the two most amino-terminal Ser are phosphorylated, the protein is recognized by β-Trcp (Slimb in Drosophi ...
Comparison of Trypsin Immobilization Techniques With or Without a
... biological degradation. These particles of 125-177 μm with 700Å average pore size have a high surface area (35 m2/g), are thermostable and inert except at very alkaline pH. • Glutaraldehyde (25% in aqueous solution, Sigma) is a small, homoO O bifunctionnal reagent with high reactivity toward NH2 gro ...
... biological degradation. These particles of 125-177 μm with 700Å average pore size have a high surface area (35 m2/g), are thermostable and inert except at very alkaline pH. • Glutaraldehyde (25% in aqueous solution, Sigma) is a small, homoO O bifunctionnal reagent with high reactivity toward NH2 gro ...
Minimal domain of bacterial phytochrome required for chromophore binding and fluorescence
... Cys19Ser and Ile252Cys, of RpBphP1. Interestingly, the absorbance and fluorescence emission maxima of PASGAF-FP variant were similar to those found in blue-shifted two-domain (PAS-GAF) iRFPs8. The Cys19Ser substitution suggested that this FP variant was no longer able to covalently bind BV in the PA ...
... Cys19Ser and Ile252Cys, of RpBphP1. Interestingly, the absorbance and fluorescence emission maxima of PASGAF-FP variant were similar to those found in blue-shifted two-domain (PAS-GAF) iRFPs8. The Cys19Ser substitution suggested that this FP variant was no longer able to covalently bind BV in the PA ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).