The Sec61p Complex Mediates the Integration of a Membrane
... see Matlack et al., 1998). In the case of a signal sequence, the hydrophobic segment binds in an NcytClum (cyt, cytosol; lum, lumenal) orientation to a specific site at the interface between the channel and lipid formed by both the Sec61p complex and the TRAM protein, another component of the transl ...
... see Matlack et al., 1998). In the case of a signal sequence, the hydrophobic segment binds in an NcytClum (cyt, cytosol; lum, lumenal) orientation to a specific site at the interface between the channel and lipid formed by both the Sec61p complex and the TRAM protein, another component of the transl ...
J. Mol. Evol., 54
... Type I signal peptidases (EC 3.4.21.89) are integral membrane proteins responsible for the removal of signal sequences from preproteins following protein translocation across a variety of membranes (Dalbey et al. 1997). Insight into the behavior of signal peptidase has come from the recent descripti ...
... Type I signal peptidases (EC 3.4.21.89) are integral membrane proteins responsible for the removal of signal sequences from preproteins following protein translocation across a variety of membranes (Dalbey et al. 1997). Insight into the behavior of signal peptidase has come from the recent descripti ...
LECT24 enz2
... immediately determine the weight of enzyme by knowing the activity. What if the enzyme is not pure? We then relate activity to mg of protein present. That measurement gives us the specific activity. What if the enzyme is pure? Then we can express activity as a turnover number. What’s that? Turnover ...
... immediately determine the weight of enzyme by knowing the activity. What if the enzyme is not pure? We then relate activity to mg of protein present. That measurement gives us the specific activity. What if the enzyme is pure? Then we can express activity as a turnover number. What’s that? Turnover ...
Modifications of a Nanomolar Cyclic Peptide
... these interactions with EphA4 may be dynamic, which is consistent with the observed SAR. To examine the importance of the observed salt bridge between the peptide N-terminus and Glu77 for EphA4 binding, we measured the binding affinity of APY-d3 for the EphA4 E77A mutant. Unexpectedly, the E77A mutati ...
... these interactions with EphA4 may be dynamic, which is consistent with the observed SAR. To examine the importance of the observed salt bridge between the peptide N-terminus and Glu77 for EphA4 binding, we measured the binding affinity of APY-d3 for the EphA4 E77A mutant. Unexpectedly, the E77A mutati ...
Adaptation and Protein Quality Control Under Metalloid
... for answering why cells behave like they do however – we also need knowledge of the physiological processes. Chapter 3 in this thesis deals with the mechanisms behind tellurite toxicity in yeast and chapter 4 concerns arseniteinduced protein aggregation. Why do certain proteins aggregate and how doe ...
... for answering why cells behave like they do however – we also need knowledge of the physiological processes. Chapter 3 in this thesis deals with the mechanisms behind tellurite toxicity in yeast and chapter 4 concerns arseniteinduced protein aggregation. Why do certain proteins aggregate and how doe ...
Chapter 10
... Proteins can be translocated into the ER either during their synthesis on membrane-bound ribosomes (cotranslational translocation) or after their translation has been completed on free ribosomes in the cytosol (posttranslational translocation). In mammalian cells, most proteins enter the ER cotransl ...
... Proteins can be translocated into the ER either during their synthesis on membrane-bound ribosomes (cotranslational translocation) or after their translation has been completed on free ribosomes in the cytosol (posttranslational translocation). In mammalian cells, most proteins enter the ER cotransl ...
Defining the anabolic window of opportunity
... studies directly assessing this question makes it all but impossible to make solid conclusions about the optimal timing. Moreover, it appears that the optimal timing of protein and/or amino acid ingestion may differ depending on the type of amino acid source, as well as concurrent ingestion of other ...
... studies directly assessing this question makes it all but impossible to make solid conclusions about the optimal timing. Moreover, it appears that the optimal timing of protein and/or amino acid ingestion may differ depending on the type of amino acid source, as well as concurrent ingestion of other ...
Quantitative Host Cell Protein Analysis Using Two
... followed by a final increase to 85% B in 2 min with a 2 min isocratic hold. Initial conditions were restored in 11 min and held for an additional 15 min to ensure column re-equilibration. The column temperature was maintained at 30 °C throughout and the flow rate at 0.3 μL min−1. Injection volume was ...
... followed by a final increase to 85% B in 2 min with a 2 min isocratic hold. Initial conditions were restored in 11 min and held for an additional 15 min to ensure column re-equilibration. The column temperature was maintained at 30 °C throughout and the flow rate at 0.3 μL min−1. Injection volume was ...
Identification of the Amino Terminus of Neuronal Ca2
... VDCC a1 subunit constructs were co-expressed with the accessory a2-d and b2a subunits in Xenopus oocytes and mammalian (COS-7) cells. The a1Elong showed biophysical properties similar to those of rbEII; however, when G-protein modulation of expressed a1 subunits was induced by activation of co-expre ...
... VDCC a1 subunit constructs were co-expressed with the accessory a2-d and b2a subunits in Xenopus oocytes and mammalian (COS-7) cells. The a1Elong showed biophysical properties similar to those of rbEII; however, when G-protein modulation of expressed a1 subunits was induced by activation of co-expre ...
U5Word
... 4. The amino group transferred to kg (---> glu) is toxic when released as NH3 in GDH. This ammonia is detoxified by conversion to urea in the urea cycle (NH3 can be excreted). C. Regulation of AA Oxidation 1. GDH is inhibited by ATP and GTP and activated by ADP and GDP. MR: GDH + trnsam TCA ints ...
... 4. The amino group transferred to kg (---> glu) is toxic when released as NH3 in GDH. This ammonia is detoxified by conversion to urea in the urea cycle (NH3 can be excreted). C. Regulation of AA Oxidation 1. GDH is inhibited by ATP and GTP and activated by ADP and GDP. MR: GDH + trnsam TCA ints ...
Lecture 1 – Classification - LCQB
... The evolution of proteins is different from the evolution of organisms. It does not need to follow the evolutionary path of organismic reproduction. Rather, the evolution of proteins is directly related to improved , unaltered or diversified molecular functions, and the protein function is directly ...
... The evolution of proteins is different from the evolution of organisms. It does not need to follow the evolutionary path of organismic reproduction. Rather, the evolution of proteins is directly related to improved , unaltered or diversified molecular functions, and the protein function is directly ...
Posttranslational Protein Modiications in Plant
... for enzymes in primary metabolism (Calvin cycle, glycolysis, and respiration) and the C4 shuttle accommodating photosynthesis in C4 plants (Table III). As will be evident, most of these classic examples involve regulation by (de)phosphorylation, reversible formation of disulfide bonds involving thior ...
... for enzymes in primary metabolism (Calvin cycle, glycolysis, and respiration) and the C4 shuttle accommodating photosynthesis in C4 plants (Table III). As will be evident, most of these classic examples involve regulation by (de)phosphorylation, reversible formation of disulfide bonds involving thior ...
Lecture 1 – Classification - LCQB
... The TIM barrel has a central cylinder or barrel of β-sheet formed from 8 parallel βstrands. ...
... The TIM barrel has a central cylinder or barrel of β-sheet formed from 8 parallel βstrands. ...
Posttranslational Protein Modiications in Plant
... for enzymes in primary metabolism (Calvin cycle, glycolysis, and respiration) and the C4 shuttle accommodating photosynthesis in C4 plants (Table III). As will be evident, most of these classic examples involve regulation by (de)phosphorylation, reversible formation of disulfide bonds involving thior ...
... for enzymes in primary metabolism (Calvin cycle, glycolysis, and respiration) and the C4 shuttle accommodating photosynthesis in C4 plants (Table III). As will be evident, most of these classic examples involve regulation by (de)phosphorylation, reversible formation of disulfide bonds involving thior ...
Are Hydrophobins and/or Non-Specific Lipid Transfer Proteins
... that these adducts correspond to glucose units that were covalently bound upon the protein via Maillard-reaction. The Maillard-reaction is a well known non-enzymatic reaction which can form covalent linkages between reducing sugars and protein-free amino groups and is preferred by high-temperature t ...
... that these adducts correspond to glucose units that were covalently bound upon the protein via Maillard-reaction. The Maillard-reaction is a well known non-enzymatic reaction which can form covalent linkages between reducing sugars and protein-free amino groups and is preferred by high-temperature t ...
Although ABA is mainly made in the leaves and the root cap, all
... ABA-induced Ca2+ increase is mediated by second messengers, IP3 and cADPR. cADPR has been shown to induce cytosolic Ca2+ increase and stomatal closure in Commelina guard cells (Leckie et al., 1998). Also in tomato hypocotyls cells, microinjected cADPR induced ABA-inducible gene expression that can ...
... ABA-induced Ca2+ increase is mediated by second messengers, IP3 and cADPR. cADPR has been shown to induce cytosolic Ca2+ increase and stomatal closure in Commelina guard cells (Leckie et al., 1998). Also in tomato hypocotyls cells, microinjected cADPR induced ABA-inducible gene expression that can ...
Protein structure is conceptually divided into four levels of organization
... (b) A view from the top of the barrel of the active site of the enzyme RuBisCo (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase), which is involved in CO2 fixation in plants. A substrate analog (red) binds across the barrel with the two phosphate groups, P1 and P2, on opposite sides of the pocket. A number of cha ...
... (b) A view from the top of the barrel of the active site of the enzyme RuBisCo (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase), which is involved in CO2 fixation in plants. A substrate analog (red) binds across the barrel with the two phosphate groups, P1 and P2, on opposite sides of the pocket. A number of cha ...
Plant–pathogen interactions: what is proteomics telling us?
... overcome plant defences and to establish successful colonization of the host plant. Five secretion systems (types I–V) have been reported in bacteria, which are distinguished by their constituent proteins [14]. The main secretion system used by pathogenic bacteria during infection is the type III se ...
... overcome plant defences and to establish successful colonization of the host plant. Five secretion systems (types I–V) have been reported in bacteria, which are distinguished by their constituent proteins [14]. The main secretion system used by pathogenic bacteria during infection is the type III se ...
ZRII ACHIEVE™ PRODUCT INFORMATION
... Soy is naturally high in protein, rich in complex carbohydrates, high in fiber, and free of lactose, making it a good protein choice for many people. Achieve uses only soy protein from certified non-GMO soybeans, which means our soy is free of genetically modified organisms. Soy also has an impressi ...
... Soy is naturally high in protein, rich in complex carbohydrates, high in fiber, and free of lactose, making it a good protein choice for many people. Achieve uses only soy protein from certified non-GMO soybeans, which means our soy is free of genetically modified organisms. Soy also has an impressi ...
Beta Proteins - Two Important Folds : BCH 622 Worksheet
... Residues 110-136 (View3) are a long alpha helix (how many turns? __________ ) which forms the primary contact with the other subunit in the dimer. Residues 137-208 are the DNAbinding domain, a small open-face sandwich antiparallel beta sheet (View4). The pair of helices at residues 170-190 and their ...
... Residues 110-136 (View3) are a long alpha helix (how many turns? __________ ) which forms the primary contact with the other subunit in the dimer. Residues 137-208 are the DNAbinding domain, a small open-face sandwich antiparallel beta sheet (View4). The pair of helices at residues 170-190 and their ...
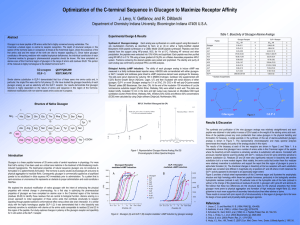
Levy APS - Indiana University Bloomington
... substitution but to a more modest degree. Most notably, the amino acids that border these four residues were relatively insensitive to substitution and support the report that this region of glucagon is prone to alpha-helix formation (4). The directional changes in bioactivity at the two receptors w ...
... substitution but to a more modest degree. Most notably, the amino acids that border these four residues were relatively insensitive to substitution and support the report that this region of glucagon is prone to alpha-helix formation (4). The directional changes in bioactivity at the two receptors w ...
Regulation of phospholipase D activity, membrane targeting and
... regulator of both constitutive and agonist-promoted intracellular vesicle trafficking [1,2]. Several recent reviews discuss the structure, regulation and functions of PLD. This short article focuses on the role of phosphoinositides as regulators of yeast and mammalian PLD activity and function and, ...
... regulator of both constitutive and agonist-promoted intracellular vesicle trafficking [1,2]. Several recent reviews discuss the structure, regulation and functions of PLD. This short article focuses on the role of phosphoinositides as regulators of yeast and mammalian PLD activity and function and, ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).