Document
... other proteins and help them fold/assemble properly (can be folding of one protein and assembly of multiple proteins). Heat shock protein story: Two major types: type I includes hsp70---bind and prevent misfolding of the substrate proteins (can also unfold proteins)---cytosol, chloroplast, mitochond ...
... other proteins and help them fold/assemble properly (can be folding of one protein and assembly of multiple proteins). Heat shock protein story: Two major types: type I includes hsp70---bind and prevent misfolding of the substrate proteins (can also unfold proteins)---cytosol, chloroplast, mitochond ...
PTM
... 1. Dealing with the N-terminal residue In bacteria, the N-terminal residue of the newlysynthesized protein is modified to remove the formyl group. The N-terminal methionine may also be ...
... 1. Dealing with the N-terminal residue In bacteria, the N-terminal residue of the newlysynthesized protein is modified to remove the formyl group. The N-terminal methionine may also be ...
organic molecules : proteins - Mr. Lesiuk
... longer they begin to twist into a spiral. (called an alpha helix). ...
... longer they begin to twist into a spiral. (called an alpha helix). ...
1 Signal Transduction, II G-proteins, Adenylate Cyclase, Protein
... domains - a helical domain with unclear function and the GTP domain. GTP binds in the center of the protein and GDP remains stuck in the active site upon hydrolysis. By comparing the structures of alpha bound to GTP or to GDP, three regions were identified whose conformation depends on which is boun ...
... domains - a helical domain with unclear function and the GTP domain. GTP binds in the center of the protein and GDP remains stuck in the active site upon hydrolysis. By comparing the structures of alpha bound to GTP or to GDP, three regions were identified whose conformation depends on which is boun ...
Gene Section AKAP9 (A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein (yotiao) 9)
... Note: Breakpoint in AKAP9-BRAF fusion is located within intron 8 of the gene. In this fusion, exons 1-8 of AKAP9 are fused with last 10 exons 9-18 of BRAF. In the fusion, AKAP9 lacks the centrosome binding domain and, as a result, the AKAP9-BRAF protein looses its cytoplasmic compartmentalization an ...
... Note: Breakpoint in AKAP9-BRAF fusion is located within intron 8 of the gene. In this fusion, exons 1-8 of AKAP9 are fused with last 10 exons 9-18 of BRAF. In the fusion, AKAP9 lacks the centrosome binding domain and, as a result, the AKAP9-BRAF protein looses its cytoplasmic compartmentalization an ...
Kinases
... even greater consequences for the phenotype. Gain, loss or modification of protein kinase genes could have far-reaching effects on fitness in a particular niche or host. Thus, it will be worthwhile to validate each case of species-specific variation, and look for biological significance. A promising ...
... even greater consequences for the phenotype. Gain, loss or modification of protein kinase genes could have far-reaching effects on fitness in a particular niche or host. Thus, it will be worthwhile to validate each case of species-specific variation, and look for biological significance. A promising ...
w12-proteins
... The direct detection and quantification of the proteins in a biological system o Can also assay protein “states” [post-translational modifications (PTMs), e.g. phosphorylation] o Provides high-confidence detection of proteins/validation of putative coding genes o Provides more accurate protein abu ...
... The direct detection and quantification of the proteins in a biological system o Can also assay protein “states” [post-translational modifications (PTMs), e.g. phosphorylation] o Provides high-confidence detection of proteins/validation of putative coding genes o Provides more accurate protein abu ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier
... shows the interaction of GTP-αs with adenylate cyclase (catalytic domains are mustard and ash). Adenylate cyclase then catalyzes the synthesis of the second messenger cyclic AMP (cAMP) from ATP. (C) Signaling is terminated when α hydrolyzes its bound GTP to GDP. In some signaling systems, GTP hydrol ...
... shows the interaction of GTP-αs with adenylate cyclase (catalytic domains are mustard and ash). Adenylate cyclase then catalyzes the synthesis of the second messenger cyclic AMP (cAMP) from ATP. (C) Signaling is terminated when α hydrolyzes its bound GTP to GDP. In some signaling systems, GTP hydrol ...
Practice Test MC and answers - Bremen High School District 228
... several organ systems, primarily under the influence of changing concentrations of estrogens and other steroid hormones. How can one hormone, such as estrogen, mediate so many effects? a. Estrogen is produced in very large concentration and therefore diffuses widely. b. Estrogen has specific recepto ...
... several organ systems, primarily under the influence of changing concentrations of estrogens and other steroid hormones. How can one hormone, such as estrogen, mediate so many effects? a. Estrogen is produced in very large concentration and therefore diffuses widely. b. Estrogen has specific recepto ...
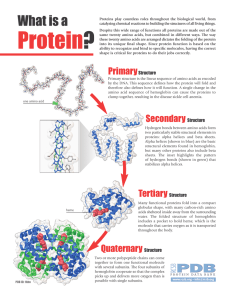
Protein?
... catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its uni ...
... catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its uni ...
Document
... Cryogenic protein storage and assessment of protein purity Flash freezing of protein for long term storage. Mass spectrometry and SDS-PAGE for determination of purity and molecular weight. Preparation of buffers for experiments in following weeks. ...
... Cryogenic protein storage and assessment of protein purity Flash freezing of protein for long term storage. Mass spectrometry and SDS-PAGE for determination of purity and molecular weight. Preparation of buffers for experiments in following weeks. ...
MCB Lecture 2 – Amino Acids and Proteins
... H-bond per every 2 AA. Has a lot of Proline and Glycine. Tertiary Structure – 3-dimensional structure based on non-covalent interactions (Van der Waals, H-Bonding, Electrostatic Interactions) and covalent bonds (Cys-Cys bond – disulfide bond) o Protein Domain – a tertiary structure where different s ...
... H-bond per every 2 AA. Has a lot of Proline and Glycine. Tertiary Structure – 3-dimensional structure based on non-covalent interactions (Van der Waals, H-Bonding, Electrostatic Interactions) and covalent bonds (Cys-Cys bond – disulfide bond) o Protein Domain – a tertiary structure where different s ...
GoMap
... databases) and GO terms with evidence -link to BLAST search results • Have GO term assignment linked to InterProScan, in the meantime, link hits to GO via mapping file • Use EC number mappings if your protein hits an enzyme ...
... databases) and GO terms with evidence -link to BLAST search results • Have GO term assignment linked to InterProScan, in the meantime, link hits to GO via mapping file • Use EC number mappings if your protein hits an enzyme ...
Pharmacology
... which activate G_ protein , so that GTP replaced GDP on α_ subunit * β&γ interaet with other ion channel * these effectors change the concentration of 2_ messenger which are responsible for further action in the cell * activation of adenyl cyclase by α _ GTP sub unit production of c_ AMP (2_massenge ...
... which activate G_ protein , so that GTP replaced GDP on α_ subunit * β&γ interaet with other ion channel * these effectors change the concentration of 2_ messenger which are responsible for further action in the cell * activation of adenyl cyclase by α _ GTP sub unit production of c_ AMP (2_massenge ...
Cytokines
... Bind receptors, alter gene expression Can bind the secreting cell (autocrine) Can bind another cell close by (paracrine) Few cases bind another cell far away (endocrine) Very low Kd receptors (10-10-10-12 M) Cytokines regulate immune responses ...
... Bind receptors, alter gene expression Can bind the secreting cell (autocrine) Can bind another cell close by (paracrine) Few cases bind another cell far away (endocrine) Very low Kd receptors (10-10-10-12 M) Cytokines regulate immune responses ...
PROTEASE SWITCHES: PATHWAYS TO INFLAMMATION AND PAIN
... Activated neuropeptide receptors and PARs interact with -arrestins at the plasma membrane, which uncouple receptors from heterotrimeric G-proteins to mediate desensitization, and couple receptors to clathrin and AP2 to mediate endocytosis. -arrestins also recruit MAP kinases to receptors in endoso ...
... Activated neuropeptide receptors and PARs interact with -arrestins at the plasma membrane, which uncouple receptors from heterotrimeric G-proteins to mediate desensitization, and couple receptors to clathrin and AP2 to mediate endocytosis. -arrestins also recruit MAP kinases to receptors in endoso ...
from_Bi_150_molbiol
... the tRNA synthetase translates the genetic code, because it contacts (a) the amino acid ...
... the tRNA synthetase translates the genetic code, because it contacts (a) the amino acid ...
2. Purification of WDR77
... the interacting WD40 repeat domain -containing protein WDR77 to determine specific substrates. Furthermore, the WD40 domain containing protein WDR77 has been shown to interact specifically with histone H2A. However, the dependence of the interaction between WDR77 and modified histone H2A has not bee ...
... the interacting WD40 repeat domain -containing protein WDR77 to determine specific substrates. Furthermore, the WD40 domain containing protein WDR77 has been shown to interact specifically with histone H2A. However, the dependence of the interaction between WDR77 and modified histone H2A has not bee ...
Problem Set Chapter 15
... different heterotrimeric G proteins are activated in each cell type adenylyl cyclase is activated in some cells and inactivated in others. an enzyme that is activated in all three cell types is capable of catalyzing glycogen breakdown, smooth muscle relaxation, and cardiac muscle contraction. ...
... different heterotrimeric G proteins are activated in each cell type adenylyl cyclase is activated in some cells and inactivated in others. an enzyme that is activated in all three cell types is capable of catalyzing glycogen breakdown, smooth muscle relaxation, and cardiac muscle contraction. ...
Gene Section LTA (Lymphotoxin-A) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... The soluble form of TNFb is usually a homotrimer with a relative molecular mass of 60 to 70 kDa, whereas the membrane form of TNFb is a heteromeric complex with lymphotoxin b (TNFc, LTb, TNFSF3). The human TNFb shares 35% identity and 50% homology in amino acid sequence with the human TNFa. The biol ...
... The soluble form of TNFb is usually a homotrimer with a relative molecular mass of 60 to 70 kDa, whereas the membrane form of TNFb is a heteromeric complex with lymphotoxin b (TNFc, LTb, TNFSF3). The human TNFb shares 35% identity and 50% homology in amino acid sequence with the human TNFa. The biol ...
Chapter 5 – Proteins and Amino Acids
... D. Protein Recommendations and Nitrogen Balance 1. Protein on Food Labels 2. Nitrogen Balance Protein in Foods A. Protein Quality 1. Digestibility 2. Amino Acid Composition 3. High-Quality Proteins 4. Complementary Proteins B. Protein Sparing Nutrition in Practice – Vegetarian Diets A. Are vegetaria ...
... D. Protein Recommendations and Nitrogen Balance 1. Protein on Food Labels 2. Nitrogen Balance Protein in Foods A. Protein Quality 1. Digestibility 2. Amino Acid Composition 3. High-Quality Proteins 4. Complementary Proteins B. Protein Sparing Nutrition in Practice – Vegetarian Diets A. Are vegetaria ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).