Key concepts: Apoptosis Animal cells can activate an intracellular
... before there is any leakage of cytoplasmic contents. Apoptosis is mediated by proteolytic enzymes called caspases, which cleave specific intracellular proteins to help kill the cell. Caspases are present in all nucleated animal cells as inactive precursors. Initiator caspases are activated when brou ...
... before there is any leakage of cytoplasmic contents. Apoptosis is mediated by proteolytic enzymes called caspases, which cleave specific intracellular proteins to help kill the cell. Caspases are present in all nucleated animal cells as inactive precursors. Initiator caspases are activated when brou ...
Insights into membrane protein function from molecular modelling
... In most organisms, up to 30% of the genome encodes membrane proteins, which perform diverse tasks ranging from the uptake of nutrients to communication between cells via chemical or electrical signals. These proteins represent more than half of current therapeutic drug targets in humans, and are inv ...
... In most organisms, up to 30% of the genome encodes membrane proteins, which perform diverse tasks ranging from the uptake of nutrients to communication between cells via chemical or electrical signals. These proteins represent more than half of current therapeutic drug targets in humans, and are inv ...
11_Lecture_Presentation
... • Cells of different mating types locate each other via secreted factors specific to each type • A signal transduction pathway is a series of steps by which a signal on a cell’s surface is converted into a specific cellular response • Signal transduction pathways convert signals on a cell’s surface ...
... • Cells of different mating types locate each other via secreted factors specific to each type • A signal transduction pathway is a series of steps by which a signal on a cell’s surface is converted into a specific cellular response • Signal transduction pathways convert signals on a cell’s surface ...
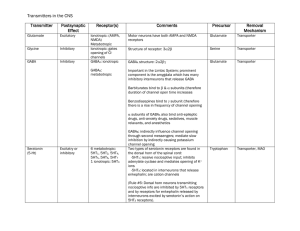
Transmitters in the CNS - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... enkephalin; are cation channels (Rule #6: Dorsal horn neurons transmitting nociceptive info are inhibited by 5HT1 receptors and by receptors for enkephalin released by interneurons excited by serotonin’s action on 5HT3 receptors). ...
... enkephalin; are cation channels (Rule #6: Dorsal horn neurons transmitting nociceptive info are inhibited by 5HT1 receptors and by receptors for enkephalin released by interneurons excited by serotonin’s action on 5HT3 receptors). ...
Slide 1
... protein modules that were first described in pleckstrin, the major protein kinase C substrate in platelets. PH domains have since been identified in several key regulatory proteins with characteristic structural features that include two orthogonal beta sheets that form a sandwich with an a helix at ...
... protein modules that were first described in pleckstrin, the major protein kinase C substrate in platelets. PH domains have since been identified in several key regulatory proteins with characteristic structural features that include two orthogonal beta sheets that form a sandwich with an a helix at ...
Protein Folding and Membrane Structure
... There are Multiple Levels at which Proteins Production is Controlled ...
... There are Multiple Levels at which Proteins Production is Controlled ...
Datasheet - Sigma
... The antiserum is affinity purified using affinity columns containing the appropriate amino acid sequence of the antigen. The antibody specifically detects GABAA receptor β3 subunit (protein with apparent molecular mass of 50-56 kDa) in rat brain membrane fractions. It has been used in immunoblotting ...
... The antiserum is affinity purified using affinity columns containing the appropriate amino acid sequence of the antigen. The antibody specifically detects GABAA receptor β3 subunit (protein with apparent molecular mass of 50-56 kDa) in rat brain membrane fractions. It has been used in immunoblotting ...
Mouse LIFR / CD118 Protein (His Tag)
... LIFR (leukemia inhibitory factor receptor) belongs to the family of cytokine receptors. LIFR forms a high-affinity receptor complex with gp130, which mediates the activity of LIF (leukemia inhibitory factor) and thus affects the differentiation, proliferation, and survival of a wide variety of cells ...
... LIFR (leukemia inhibitory factor receptor) belongs to the family of cytokine receptors. LIFR forms a high-affinity receptor complex with gp130, which mediates the activity of LIF (leukemia inhibitory factor) and thus affects the differentiation, proliferation, and survival of a wide variety of cells ...
control biological machines
... Alternating magnetic field induces alternating eddy currents in metal samples For nm particles: – f=1GHz (radiofrequency 109/s): – Radiofrequency magnetic field: RFMF ...
... Alternating magnetic field induces alternating eddy currents in metal samples For nm particles: – f=1GHz (radiofrequency 109/s): – Radiofrequency magnetic field: RFMF ...
research title proposal - Pontificia Universidad Javeriana, Cali
... Cali (Colombia), Tuesday January 13th, 2009 ...
... Cali (Colombia), Tuesday January 13th, 2009 ...
100 Marine organisms in somatostatin receptor scintillation proximity
... Glaxo Wellcome R&D, Gunnel’s Wood Road, Stevenage, SG12NY, England. Somatostatin is a small endogenous peptide first discovered for its ability to inhibit growth hormone secretion (1). It has been described as the “universal endocrine off switch” (2), and is now known to be widely distributed in the ...
... Glaxo Wellcome R&D, Gunnel’s Wood Road, Stevenage, SG12NY, England. Somatostatin is a small endogenous peptide first discovered for its ability to inhibit growth hormone secretion (1). It has been described as the “universal endocrine off switch” (2), and is now known to be widely distributed in the ...
Large number of receptors reduces cellular response time - Q-bio
... in simple models, this variability reduction does not interfere with the receptor specificity to ligands achieved by the Kinetic Proofreading mechanism. Thus cells can activate accurately in time and specifically to certain molecular signals. Keywords — spare receptors, kinetic proofreading, first p ...
... in simple models, this variability reduction does not interfere with the receptor specificity to ligands achieved by the Kinetic Proofreading mechanism. Thus cells can activate accurately in time and specifically to certain molecular signals. Keywords — spare receptors, kinetic proofreading, first p ...
The TNF and TNFR superfamilies
... that was able to kill cancer cells in mice. The TNF receptor (TNFR) led to the discovery of a superfamily of transmembrane proteins. There are 18 ligands and 28 receptors many of which are being targeted for therapeutic purposes. TNFR signaling is important for the immune response and FASL and APO2L ...
... that was able to kill cancer cells in mice. The TNF receptor (TNFR) led to the discovery of a superfamily of transmembrane proteins. There are 18 ligands and 28 receptors many of which are being targeted for therapeutic purposes. TNFR signaling is important for the immune response and FASL and APO2L ...
Shape matters in protein mobility within membranes - ICAM
... Lateral Brownian diffusion of proteins in lipid membranes has been predicted by Saffman and Delbrück to depend only on protein size and on the viscosity of the membrane and of the surrounding medium. Using a single-molecule tracking technique on two transmembrane proteins that bend the membrane diff ...
... Lateral Brownian diffusion of proteins in lipid membranes has been predicted by Saffman and Delbrück to depend only on protein size and on the viscosity of the membrane and of the surrounding medium. Using a single-molecule tracking technique on two transmembrane proteins that bend the membrane diff ...
Chapter 10 Intracellular Compartments and Transport
... A common pool of ribosomes is used to synthesize both the proteins that stay in the cytosol and those that are transported into membrane-enclosed organelles, including the ER ...
... A common pool of ribosomes is used to synthesize both the proteins that stay in the cytosol and those that are transported into membrane-enclosed organelles, including the ER ...
Chapter 16
... multi-docking protein known as the insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) perform this function (Fig. 16.12). The binding of signaling proteins either directly to the receptor or to IRS-1 allows them to be phosphorylated by the receptor. Some of these signaling proteins are involved in activation of t ...
... multi-docking protein known as the insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) perform this function (Fig. 16.12). The binding of signaling proteins either directly to the receptor or to IRS-1 allows them to be phosphorylated by the receptor. Some of these signaling proteins are involved in activation of t ...
cellular-communication-notes-1
... Used by cells to communicate to other cells a great distance away (but still in the same organism) One cell secrets a signal molecule (hormone) into the blood system (if an animal) or into the extracellular fluid (if a plant) The signal molecules travels throughout the body, most likely contacting n ...
... Used by cells to communicate to other cells a great distance away (but still in the same organism) One cell secrets a signal molecule (hormone) into the blood system (if an animal) or into the extracellular fluid (if a plant) The signal molecules travels throughout the body, most likely contacting n ...
Neuro Objectives 18
... Transduction: translating an extracellular stimulus to an intracellular signal Receptor potential: a graded potential generated in a sensory receptor cell Nature of stimulus: a. Nature: 5 major senses, chemo-, mechano-, and photoreceptors; a stimulus can be a combination of any of these and is not l ...
... Transduction: translating an extracellular stimulus to an intracellular signal Receptor potential: a graded potential generated in a sensory receptor cell Nature of stimulus: a. Nature: 5 major senses, chemo-, mechano-, and photoreceptors; a stimulus can be a combination of any of these and is not l ...
A One- or Two-Day Course for Your Campus on
... ligands, substrates, and drugs, and protein evolutionary conservation. Handson experience will be largely with molecules of each participant's choosing. Participants will learn easy methods for creating publication-quality molecular images, and how to put snapshots or rotating animations in Powerpoi ...
... ligands, substrates, and drugs, and protein evolutionary conservation. Handson experience will be largely with molecules of each participant's choosing. Participants will learn easy methods for creating publication-quality molecular images, and how to put snapshots or rotating animations in Powerpoi ...
No Slide Title
... -ER signals vary in amino acid sequence but each has at least 8 nonpolar amino acids -The binding pocket is a large hydrophobic pocket lined by methionines -methionines can accommodate sequences of different size and shape ...
... -ER signals vary in amino acid sequence but each has at least 8 nonpolar amino acids -The binding pocket is a large hydrophobic pocket lined by methionines -methionines can accommodate sequences of different size and shape ...
Answers to - Studentportalen
... normal cells. Suggest a point mutation that could cause this effect, and motivate your suggestion based on your knowledge of GPCR signaling. (3p) (9) Growth hormone is a small alpha helical protein. Explain how this asymmetric molecule binds to and activates growth hormone receptor. (3p) (10) Epider ...
... normal cells. Suggest a point mutation that could cause this effect, and motivate your suggestion based on your knowledge of GPCR signaling. (3p) (9) Growth hormone is a small alpha helical protein. Explain how this asymmetric molecule binds to and activates growth hormone receptor. (3p) (10) Epider ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).