The Human Ear - AP Psychology
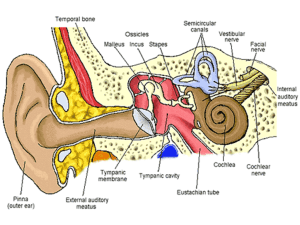
... • The eustachian tube is a selective valve that allows air to enter behind the sealed eardrum. The eustachian tube connects the back of the nose to the middle ear. Air can pass from the back of the nose to the middle ear through the eustachian tube (see diagram above). The eustachian tube replaces t ...
... • The eustachian tube is a selective valve that allows air to enter behind the sealed eardrum. The eustachian tube connects the back of the nose to the middle ear. Air can pass from the back of the nose to the middle ear through the eustachian tube (see diagram above). The eustachian tube replaces t ...
Hearing
... Conduction Hearing Loss Hearing loss caused by damage to the mechanical system that conducts sound waves to the cochlea. Problems with the eardrum or three bones of the middle ear. Sensorineural Hearing Loss Hearing loss caused by damage to the cochlea’s receptor cells or to the auditory nerves; als ...
... Conduction Hearing Loss Hearing loss caused by damage to the mechanical system that conducts sound waves to the cochlea. Problems with the eardrum or three bones of the middle ear. Sensorineural Hearing Loss Hearing loss caused by damage to the cochlea’s receptor cells or to the auditory nerves; als ...
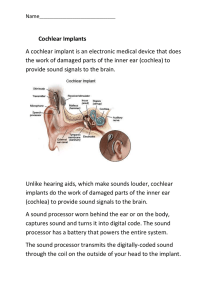
Cochlear Implants
... The implant converts the digitally-coded sound into electrical impulses and sends them along the electrode array placed in the cochlea (the inner ear). The implant's electrodes stimulate the cochlea's hearing nerve, which then sends the impulses to the brain where they are interpreted as sound. 1. T ...
... The implant converts the digitally-coded sound into electrical impulses and sends them along the electrode array placed in the cochlea (the inner ear). The implant's electrodes stimulate the cochlea's hearing nerve, which then sends the impulses to the brain where they are interpreted as sound. 1. T ...
TWO Sense Organs in ONE
... • 1. The EAR is really TWO Sense Organs in ONE. It not only detects Sound Waves, it also senses the Position of the HEAD, whether it is STILL, MOVING IN A STRAIGHT LINE, OR ROTATING. • 2. Sound is nothing more than Vibrations in the Air around us. • 3. Deep LOW-PITCHED Sounds result from slow vibrat ...
... • 1. The EAR is really TWO Sense Organs in ONE. It not only detects Sound Waves, it also senses the Position of the HEAD, whether it is STILL, MOVING IN A STRAIGHT LINE, OR ROTATING. • 2. Sound is nothing more than Vibrations in the Air around us. • 3. Deep LOW-PITCHED Sounds result from slow vibrat ...
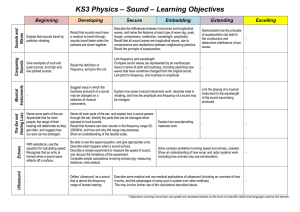
Sound - Townley Grammar School
... Complete simple calculations involving echoes (eg. measuring distances, time delays). ...
... Complete simple calculations involving echoes (eg. measuring distances, time delays). ...
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers
... Frequency Theory states that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a tone, thus enabling us to sense its pitch. Sound Frequency ...
... Frequency Theory states that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a tone, thus enabling us to sense its pitch. Sound Frequency ...
Sounds Waves
... volunteer tell which is higher. Repeat this for 4 different trials. Beat interference: Set box to 440 Hz and listen to sound, change from sound to beats and slowly turn dial down to 430 and record what happens (only one speaker is changing its frequency) Resonance: Tap the tuning fork and listen to ...
... volunteer tell which is higher. Repeat this for 4 different trials. Beat interference: Set box to 440 Hz and listen to sound, change from sound to beats and slowly turn dial down to 430 and record what happens (only one speaker is changing its frequency) Resonance: Tap the tuning fork and listen to ...
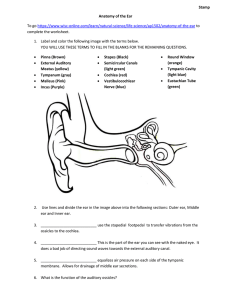
File
... 8. ___________________________ funnels and amplifies sound toward the eardrum. 9. ___________________________ are the sense organs for equilibrium and balance. Hair cells within the canals perceive balance and position in space both aid in balance and have nothing to do with hearing. 10. ___________ ...
... 8. ___________________________ funnels and amplifies sound toward the eardrum. 9. ___________________________ are the sense organs for equilibrium and balance. Hair cells within the canals perceive balance and position in space both aid in balance and have nothing to do with hearing. 10. ___________ ...
Pitch - Department of Psychology
... No such separation of sounds sources on sensory surface Sources combine to equally stimulate ear receptors ...
... No such separation of sounds sources on sensory surface Sources combine to equally stimulate ear receptors ...
Psychoacoustics - University of Limerick
... the outer, middle and inner ear • Sound waves travel down the auditory canal and cause the ear drum to vibrate. • The main function of the ossicles is the efficient transfer of sound waves from air to the fluids of the cochlea. • The ossicles of the middle ear vibrate in response to tympanic membran ...
... the outer, middle and inner ear • Sound waves travel down the auditory canal and cause the ear drum to vibrate. • The main function of the ossicles is the efficient transfer of sound waves from air to the fluids of the cochlea. • The ossicles of the middle ear vibrate in response to tympanic membran ...
Show Me Science Advanced
... 2. Students should understand that sound waves travel in a given direction until an outside force or object disrupts its motion and reflects it, and that sound can travel through different mediums, including solids, liquids, and gases. 3. Explain how the human ear works, interpreting sound waves and ...
... 2. Students should understand that sound waves travel in a given direction until an outside force or object disrupts its motion and reflects it, and that sound can travel through different mediums, including solids, liquids, and gases. 3. Explain how the human ear works, interpreting sound waves and ...
The Special Senses
... ossicles (three tiny bones – malleus/hammer, incus/anvil, & stapes/stirrup) which transmit sound to the inner ear • Eustachian tube connects to pharynx, allowing air pressure to equalize on both side of the eardrum; can be blocked by infections ...
... ossicles (three tiny bones – malleus/hammer, incus/anvil, & stapes/stirrup) which transmit sound to the inner ear • Eustachian tube connects to pharynx, allowing air pressure to equalize on both side of the eardrum; can be blocked by infections ...
Sound Localisation - University of Limerick
... overlap of vibration patterns on the BM – for small delay times between masker and signal • fatigue in the auditory nerve or higher centres – reduces the response to the signal after the masker • The auditory processes underlying forward and backward masking are not well understood ...
... overlap of vibration patterns on the BM – for small delay times between masker and signal • fatigue in the auditory nerve or higher centres – reduces the response to the signal after the masker • The auditory processes underlying forward and backward masking are not well understood ...
2320Lecture7
... of sound: • very high and very low frequencies must have more energy (higher dB) to be heard • greatest sensitivity (lowest detection threshold) is between 1000 hz to 5000hz ...
... of sound: • very high and very low frequencies must have more energy (higher dB) to be heard • greatest sensitivity (lowest detection threshold) is between 1000 hz to 5000hz ...
Document
... dissipated by the round window. • When hair cells are stimulated, action potentials are triggered that pass down axons of the auditory nerve—a branch of cranial nerve VIII. ...
... dissipated by the round window. • When hair cells are stimulated, action potentials are triggered that pass down axons of the auditory nerve—a branch of cranial nerve VIII. ...
Audition Outline - Villanova University
... – www.neurophys.wisc.edu/~ychen/auditory/animation/animationmain.html ...
... – www.neurophys.wisc.edu/~ychen/auditory/animation/animationmain.html ...
The anatomy of the hearing process involves the external, middle
... sound aid and residual hearing to develop oral communication skills. The oral approach emphasizes the use of amplified sound and residual hearing but also may employ lipreading, reading and writing, motokinesthetic speech training (feeling an individual’s face and reproducing breath and voice patter ...
... sound aid and residual hearing to develop oral communication skills. The oral approach emphasizes the use of amplified sound and residual hearing but also may employ lipreading, reading and writing, motokinesthetic speech training (feeling an individual’s face and reproducing breath and voice patter ...
Lecture 20: The Auditory System: Aniruddha Das
... Most natural sounds – speech, animal calls, music – have complex mixtures of frequencies (think of a piano chord, hitting a number of keys simultaneously). The frequencies in natural sounds also constantly change (prosody in language; trills in bird song) Sounds carry precise timing information. Thi ...
... Most natural sounds – speech, animal calls, music – have complex mixtures of frequencies (think of a piano chord, hitting a number of keys simultaneously). The frequencies in natural sounds also constantly change (prosody in language; trills in bird song) Sounds carry precise timing information. Thi ...
What are some practical ways we use sound energy?
... that is lined with receptors that respond to sound The receptors are tiny hair cells that shake back and forth in response to sound waves When they shake, the hair cells create nerve impulses which go to the brain along the auditory nerve ...
... that is lined with receptors that respond to sound The receptors are tiny hair cells that shake back and forth in response to sound waves When they shake, the hair cells create nerve impulses which go to the brain along the auditory nerve ...