Audition
... Frequency Theory states that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a tone, thus enabling us to sense its pitch. Sound Frequency ...
... Frequency Theory states that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a tone, thus enabling us to sense its pitch. Sound Frequency ...
Chapter 11 Section 1
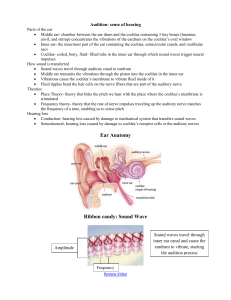
... the spiral-shaped structure that is filled with liquid and contains tiny hair cells – When these hairs vibrate they send a signal to the auditory nerve which takes the signal to the brain for decoding and interpretation. – When a person experiences hearing loss is is usually because these hairs have ...
... the spiral-shaped structure that is filled with liquid and contains tiny hair cells – When these hairs vibrate they send a signal to the auditory nerve which takes the signal to the brain for decoding and interpretation. – When a person experiences hearing loss is is usually because these hairs have ...
Notes
... • cause some of us to get seasick when the head, body and eyes undergo motional disturbances. • The three little bones of the air-filled middle ear which are attached to the eardrum, excite vibrations in the cochlea, the liquid-filled inner ear. ...
... • cause some of us to get seasick when the head, body and eyes undergo motional disturbances. • The three little bones of the air-filled middle ear which are attached to the eardrum, excite vibrations in the cochlea, the liquid-filled inner ear. ...
Y8_Sound_summary - Ralph Thoresby School
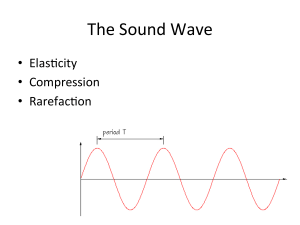
... The height of the wave is called the amplitude. The loudness of a sound depends on the amplitude. Louder notes have more energy and the wave has a bigger amplitude. ...
... The height of the wave is called the amplitude. The loudness of a sound depends on the amplitude. Louder notes have more energy and the wave has a bigger amplitude. ...
Hearing part I
... The lever system of the bony ossicle ossicles are arranged in such a manner that they function as a series of levers handle of the malleus is about 1.3 times that of long process of the incus increases the force of movement of the stapes about 1.3 times Both mechanisms amplify the sound pressure at ...
... The lever system of the bony ossicle ossicles are arranged in such a manner that they function as a series of levers handle of the malleus is about 1.3 times that of long process of the incus increases the force of movement of the stapes about 1.3 times Both mechanisms amplify the sound pressure at ...
bats2
... Sound is wave of rarefaction and compression has speed 330m/s, c = f * l wavelength l - determines whether objects will reflect or diffract sound frequency f intensity measured ...
... Sound is wave of rarefaction and compression has speed 330m/s, c = f * l wavelength l - determines whether objects will reflect or diffract sound frequency f intensity measured ...
Review Quiz #3: Sensation and Perception
... 9. The __________________________ occurs when two or more alternating blinking lights create the appearance of movement. 10. _________________________ are distance cues of visual perception which include relative size, relative motion and texture gradient. _________________________ are depth cues wh ...
... 9. The __________________________ occurs when two or more alternating blinking lights create the appearance of movement. 10. _________________________ are distance cues of visual perception which include relative size, relative motion and texture gradient. _________________________ are depth cues wh ...
The Auditory Sense: Hearing
... • The most common form of deafness • Caused when the three inner bones (Malleus, Incus, Stapes) of the ear fuse • Can be treated through hearing aids ...
... • The most common form of deafness • Caused when the three inner bones (Malleus, Incus, Stapes) of the ear fuse • Can be treated through hearing aids ...
noise induced hearing loss
... Using two ears to localise a sound source is called spatial or binaural localisation. This is based on three acoustic cues received by the ears: 1.Interaural intensity differences 2.Interaural time differences 3.The effects of the pinnae ...
... Using two ears to localise a sound source is called spatial or binaural localisation. This is based on three acoustic cues received by the ears: 1.Interaural intensity differences 2.Interaural time differences 3.The effects of the pinnae ...
A.P. Psychology 4 (D)
... Different frequencies vibrate in different places of the cochlea Problem: low-pitched sounds not localized ...
... Different frequencies vibrate in different places of the cochlea Problem: low-pitched sounds not localized ...
PsychSim 5: THE AUDITORY SYSTEM Name: Kiet
... What are the four tasks of the auditory system? 1. pick up stimulus energy from the world around us 2. change that energy into a pattern of neural impulses. 3. carry those impulses to the proper locations in the brain. 4. process the information contained in the pattern of impulses so that the sti ...
... What are the four tasks of the auditory system? 1. pick up stimulus energy from the world around us 2. change that energy into a pattern of neural impulses. 3. carry those impulses to the proper locations in the brain. 4. process the information contained in the pattern of impulses so that the sti ...
Y8_Sound_Key Words - Ralph Thoresby School
... less strong than in solids. The particles can move past each other in a liquid. ...
... less strong than in solids. The particles can move past each other in a liquid. ...
THE AUDITORY SYSTEM (p.1) 1. The Sound Stimulus a waveform
... a waveform of different pressures (usually air, could be water, etc.) of less to more to less to more, etc. compressed air/water molecules (lower to higher to lower to higher air/water pressure waves) frequency of the waveforms = # compressions/second = Hertz = Hz corresponds to pitch (greater frequ ...
... a waveform of different pressures (usually air, could be water, etc.) of less to more to less to more, etc. compressed air/water molecules (lower to higher to lower to higher air/water pressure waves) frequency of the waveforms = # compressions/second = Hertz = Hz corresponds to pitch (greater frequ ...
Slide 1
... Slowly insert the speculum to a depth of 1.0 to 1.5 cm (1/2 inch). Note discharge, scaling, excessive redness, lesions, foreign bodies, and cerumen. Inspect the tympanic membrane for landmarks, color, contour, and perforations. ...
... Slowly insert the speculum to a depth of 1.0 to 1.5 cm (1/2 inch). Note discharge, scaling, excessive redness, lesions, foreign bodies, and cerumen. Inspect the tympanic membrane for landmarks, color, contour, and perforations. ...
Spatial Hearing
... to be admitted to a school for airline pilots. For being accepted, they must have very good spatial-hearing capabilities. This is necessary, among other reasons, because they have to respond correctly to signals from auditory displays in the cockpit. Outline a battery of perceptual tests which could ...
... to be admitted to a school for airline pilots. For being accepted, they must have very good spatial-hearing capabilities. This is necessary, among other reasons, because they have to respond correctly to signals from auditory displays in the cockpit. Outline a battery of perceptual tests which could ...
Module 13 Hearing - Northside Middle School
... Middle ear transmits the vibrations through the piston into the cochlea in the inner ear Vibrations cause the cochlea’s membrane to vibrate fluid inside of it Fluid ripples bend the hair cells on the nerve fibers that are part of the auditory nerve Theories Place Theory- theory that links th ...
... Middle ear transmits the vibrations through the piston into the cochlea in the inner ear Vibrations cause the cochlea’s membrane to vibrate fluid inside of it Fluid ripples bend the hair cells on the nerve fibers that are part of the auditory nerve Theories Place Theory- theory that links th ...
Interaural Time Difference
... Information about Distance • Differing effect of short distance (i.e., within arms length) v. longer distances • Short distances are dramatically influenced by interaural level differences (ILD) ...
... Information about Distance • Differing effect of short distance (i.e., within arms length) v. longer distances • Short distances are dramatically influenced by interaural level differences (ILD) ...
Hearing
... Relative discrimination of signals on the basis of intensity and frequency depends in part on interactions between these two dimensions. A common measure is the just-noticeable difference (JND). JND is the smallest difference or change along a stimulus dimension that can just be detected 50% o ...
... Relative discrimination of signals on the basis of intensity and frequency depends in part on interactions between these two dimensions. A common measure is the just-noticeable difference (JND). JND is the smallest difference or change along a stimulus dimension that can just be detected 50% o ...
The Sound Wave - Professor Buss
... 300 Hz to 3 kHz (most energy) Speech 20 to 80 Hz Low Bass 80 to 320 Hz Upper Bass 320 to 2,560 Hz Midrange 2,560 to 5,120 Hz Upper Midrange 2.5k to ...
... 300 Hz to 3 kHz (most energy) Speech 20 to 80 Hz Low Bass 80 to 320 Hz Upper Bass 320 to 2,560 Hz Midrange 2,560 to 5,120 Hz Upper Midrange 2.5k to ...
скачати - ua
... When we think of hearing, most only consider the outer ear. In reality, the inner ear is the part that does all of the work. The outer ear works as a reverse megaphone, which collects the sounds that we hear and brings them into the inner part of the ear. Ears are located on either side of the head ...
... When we think of hearing, most only consider the outer ear. In reality, the inner ear is the part that does all of the work. The outer ear works as a reverse megaphone, which collects the sounds that we hear and brings them into the inner part of the ear. Ears are located on either side of the head ...
Sensory systems: II. Auditory
... the I.D. (~.2 m; frequency greater than ~ 1,700 Hz). Differences in time of arrival at the two ears Is unambiguous only when wavelengths are greater than 1/2 the I.D. (~.1 m; frequency less than about 3,400 Hz). ...
... the I.D. (~.2 m; frequency greater than ~ 1,700 Hz). Differences in time of arrival at the two ears Is unambiguous only when wavelengths are greater than 1/2 the I.D. (~.1 m; frequency less than about 3,400 Hz). ...
Human hearing Physical Characteristics Physical characteristics
... Small displacement over large area becomes large displacement over small area Hall, Musical Acoustics, 3rd Ed. ...
... Small displacement over large area becomes large displacement over small area Hall, Musical Acoustics, 3rd Ed. ...