* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
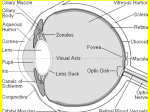
EAR • The ear is a sense organ for hearing and balance • Three main portions of ear – Outer Ear : containing air – Middle ear : containing air – Inner ear : containing fluid • Only mammals contain ear lobes Parts of ear Structure Function Pinna Fleshy part seen in the side of the head Passage which leads to the eadrum Direct sound waves in to the auditory canal Directs sound wave to he eardrum Auditory canal Parts of ear Structure Eardrum A thin membrane (tympanum) Function Vibrates when it receive the sound waves and passes the vibration to the ear ossicles Ear ossicles A chain of three small bones Magnify the sound vibrations and connecting the eardrum to the pass them on to the cochlea through oval window the oval window Oval window A thin membrane Transfers the sound vibrations from ear ossicles to the cochlea Round window A thin membrane below the oval window Help sound vibrations to pass through the cochlea Eustachian tube An air passage leading from the middle ear to the throat Helps to equalise the air pressure on each side of the eardrum Parts of ear Structure Function Cochlea A coiled tube with sensory cells and filled with fluid Changes sound vibrations into nervous impulses for transmission to the brain Auditory nerve A bundle of nerves connecting the cochlea to the brain Carries nervous impulses from the cochlea to the brain Semicircular canals Three canals containing a fluid which swirls when the head is moved Help the body to maintain balance Hearing Machanism Pinna- directs sound waves into the auditory canal Auditoty canal- directs sound waves to the eardrum Eardrum- vibrates at the same speed as the sound wave Ear-ossicles- magnify the sound vibrations and make the oval window vibrate at the same frequency Oval window- vibrates and makes the fluid in the cochlea vibrate Cochlea- changes the sound vibrations into nervous impulses Auditory nerve- transmits the nervous impulses from the cochlea to the brain The brain- interprets the nervous impulses as sounds Spot test 1. What’s the taste detected by the regions below? 2. State the 2 components which make up the central nervous system. 3. State the 2 types of nerves. 4. State 5 types of receptors in the skin and their function. 5. What’s the 2 factors which affect the sensitivity of the skin? 6. What’s function of the sweat glands in the skin? 7. What is mucus? 8. How can a common cold decrease our sense of smell? 9. Why is the sense of taste called a chemical sense?