ch 13 PPT File
... 1. Fossils found on one continent were similar to fossils found on another continent. 2. Mountain layers seem to continue from one continent to another. 3. Glacier deposits were found at the equator where glaciers can not exist. ...
... 1. Fossils found on one continent were similar to fossils found on another continent. 2. Mountain layers seem to continue from one continent to another. 3. Glacier deposits were found at the equator where glaciers can not exist. ...
Changing Earth 1
... in which most rock is hot enough to flow in convection currents; Earth’s thickest layer. ...
... in which most rock is hot enough to flow in convection currents; Earth’s thickest layer. ...
Earth Science Name Web Inquiry—Plate Tectonics/Earth`s Interior
... Web Inquiry—Plate Tectonics/Earth’s Interior ...
... Web Inquiry—Plate Tectonics/Earth’s Interior ...
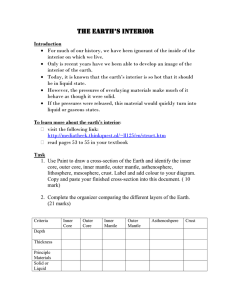
The Earth`s Interior
... The Earth’s Interior Introduction For much of our history, we have been ignorant of the inside of the interior on which we live. Only is recent years have we been able to develop an image of the interior of the earth. Today, it is known that the earth’s interior is so hot that it should be in ...
... The Earth’s Interior Introduction For much of our history, we have been ignorant of the inside of the interior on which we live. Only is recent years have we been able to develop an image of the interior of the earth. Today, it is known that the earth’s interior is so hot that it should be in ...
Lesson 1 - Earth`s Interior
... evidence to learn about Earth’s interior: direct evidence from rock samples and indirect evidence from seismic waves. Rocks from inside Earth give geologists clues about Earth’s structure. To study Earth’s interior, geologists also study seismic waves. When earthquakes occur, they produce seismic wa ...
... evidence to learn about Earth’s interior: direct evidence from rock samples and indirect evidence from seismic waves. Rocks from inside Earth give geologists clues about Earth’s structure. To study Earth’s interior, geologists also study seismic waves. When earthquakes occur, they produce seismic wa ...
journey 05 - Auburn High School
... The study of seismic waves allows scientists to “see” inside the earth. Scientists have discovered that seismic waves • refract • reflect • change velocity • and become absorbed by various parts of the Earth’s interior ...
... The study of seismic waves allows scientists to “see” inside the earth. Scientists have discovered that seismic waves • refract • reflect • change velocity • and become absorbed by various parts of the Earth’s interior ...
Chapter12 EarthsInterior
... Source of magnetism • the convection currents in outer liquid core produce electric currents and any electric field is associated with a magnetic field. ...
... Source of magnetism • the convection currents in outer liquid core produce electric currents and any electric field is associated with a magnetic field. ...
Plate Tectonics
... basins. Gas and dust from large volcanoes can change the atmosphere. The solid crust of the earth—including both the continents and the ocean basins— consists of separate plates that ride on a denser, hot, gradually deformable layer of the earth. The crust sections move very slowly, pressing against ...
... basins. Gas and dust from large volcanoes can change the atmosphere. The solid crust of the earth—including both the continents and the ocean basins— consists of separate plates that ride on a denser, hot, gradually deformable layer of the earth. The crust sections move very slowly, pressing against ...
Plate Tectonic Notes: Lab Science 9
... I can explain how gravity is responsible for the rising and sinking of material in the mantle. I can define convection currents. ...
... I can explain how gravity is responsible for the rising and sinking of material in the mantle. I can define convection currents. ...
Interior of Earth
... interior of the Earth was composed of different material to the crust. We now differentiate the interior into two types of mantle (asthenosphere and lower mantle) and two types of core (outer and inner). The key to measuring the size of each of these regions is the study of seismic waves. ...
... interior of the Earth was composed of different material to the crust. We now differentiate the interior into two types of mantle (asthenosphere and lower mantle) and two types of core (outer and inner). The key to measuring the size of each of these regions is the study of seismic waves. ...
Grade 7 Science Unit 4: The Earth`s Crust
... 3. Anaxagoras: Greek who believed that volcanic eruptions were caused by great winds within the earth. ...
... 3. Anaxagoras: Greek who believed that volcanic eruptions were caused by great winds within the earth. ...
Grade 7 Science Unit 4: The Earth’s Crust
... 3. Anaxagoras: Greek who believed that volcanic eruptions were caused by great winds within the earth. ...
... 3. Anaxagoras: Greek who believed that volcanic eruptions were caused by great winds within the earth. ...
7Unit4Slideshow7
... 3. Anaxagoras: Greek who believed that volcanic eruptions were caused by great winds within the earth. ...
... 3. Anaxagoras: Greek who believed that volcanic eruptions were caused by great winds within the earth. ...
The Planet Oceanus
... (b) If the density, or rigidity, of Earth increased evenly with depth, seismic wave velocity would increase with depth, and the waves would bend smoothly upward toward the surface. (c) If Earth were layered inside, some seismic waves would be reflected at the boundaries between layers while others w ...
... (b) If the density, or rigidity, of Earth increased evenly with depth, seismic wave velocity would increase with depth, and the waves would bend smoothly upward toward the surface. (c) If Earth were layered inside, some seismic waves would be reflected at the boundaries between layers while others w ...
geography2
... The shape, height, and arrangement Of landforms in a particular place. Topography ...
... The shape, height, and arrangement Of landforms in a particular place. Topography ...
Assignment - 1
... analyses, rock samples, volcanoes and seismic waves provided a better understanding of the earth structure. The current interpretation of the earth structure comprises three major layers; crust, mantle and core. Crust is divided into oceanic and continental portions. The dynamic interaction between ...
... analyses, rock samples, volcanoes and seismic waves provided a better understanding of the earth structure. The current interpretation of the earth structure comprises three major layers; crust, mantle and core. Crust is divided into oceanic and continental portions. The dynamic interaction between ...
Vocabulary 1 - Cobb Learning
... Ab/abs: from; away; off Absent—not present Abdicate—to give up formally (a throne, etc.) ...
... Ab/abs: from; away; off Absent—not present Abdicate—to give up formally (a throne, etc.) ...
Structure of the Earth
... composition similar to peridotite – Two parts • Mesosphere (lower mantle) • Asthenosphere or upper mantle ...
... composition similar to peridotite – Two parts • Mesosphere (lower mantle) • Asthenosphere or upper mantle ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.