a. asthenosphere b. lithosphere c. mesosphere d. outer core e. inner
... ____ 2. A substance composed of two or more elements is a(n) a. mix. c. compound. b. amalgam. d. complex. 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ ...
... ____ 2. A substance composed of two or more elements is a(n) a. mix. c. compound. b. amalgam. d. complex. 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ ...
Drawing the Earth
... Directions: You will be creating a representation of the Earth, its layers (structural and compositional) and spheres. You have three (3) options: 1. Work with a group (3-4) and make a large poster 2. Work individually or with a partner and create a smaller drawing (8.5 x 11) 3. Create a layered “bo ...
... Directions: You will be creating a representation of the Earth, its layers (structural and compositional) and spheres. You have three (3) options: 1. Work with a group (3-4) and make a large poster 2. Work individually or with a partner and create a smaller drawing (8.5 x 11) 3. Create a layered “bo ...
6th Grade Earth Science – Inside Earth Vocabulary 1. crust – the
... made of iron and nickel which spins as the earth rotates and creates a magnetic field and the north & south poles on earth 9. compass – an instrument composed of a small, light-weight magnet called a needle, that is balanced on a frictionless bearing 10. continental drift – the hypothesis that the c ...
... made of iron and nickel which spins as the earth rotates and creates a magnetic field and the north & south poles on earth 9. compass – an instrument composed of a small, light-weight magnet called a needle, that is balanced on a frictionless bearing 10. continental drift – the hypothesis that the c ...
Dangerous Earth
... the Earth is made of a thin, rigid sheet called the lithosphere, which is broken into pieces called plates. The lithosphere is made up of the crust and the upper part of the mantle. Underneath the lithosphere is a thin zone within the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because of radioactive decay dee ...
... the Earth is made of a thin, rigid sheet called the lithosphere, which is broken into pieces called plates. The lithosphere is made up of the crust and the upper part of the mantle. Underneath the lithosphere is a thin zone within the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because of radioactive decay dee ...
PHYSICAL GEOLOGY
... the formation of minerals and rocks, weathering, erosion, earthquakes, and crustal deformation. Lecture 3 hours. Laboratory 3 hours. Total 6 hours per week. GENERAL COURSE PURPOSE This is an introductory course in geology that is intended to meet the needs of the student pursuing a career in earth o ...
... the formation of minerals and rocks, weathering, erosion, earthquakes, and crustal deformation. Lecture 3 hours. Laboratory 3 hours. Total 6 hours per week. GENERAL COURSE PURPOSE This is an introductory course in geology that is intended to meet the needs of the student pursuing a career in earth o ...
Earth`s Systems Study Guide 1. Name the four parts of Earth`s
... 6. What is the importance of seismic waves? Describe what seismic waves can tell us. ...
... 6. What is the importance of seismic waves? Describe what seismic waves can tell us. ...
Quiz
... _____ 1. What is the layer directly beneath Earth’s crust called? a. oceanic crust c. outer core b. inner core d. mantle _____ 2. Because of intense pressure, the inner core of Earth is a. liquid. c. solid. b. gaseous. d. plastic. _____ 3. Which of the following gives evidence for plate tectonics? a ...
... _____ 1. What is the layer directly beneath Earth’s crust called? a. oceanic crust c. outer core b. inner core d. mantle _____ 2. Because of intense pressure, the inner core of Earth is a. liquid. c. solid. b. gaseous. d. plastic. _____ 3. Which of the following gives evidence for plate tectonics? a ...
Outline General Geology 2011
... - Minerals: Building Blocks of Rocks: 1. Composition and structures of minerals 2. Physical properties of minerals 3. Mineral groups 4. Silicate minerals - Rocks: Materials of the Lithosphere 1. Rock cycle 2. Igneous rocks 3. Physical weathering 4. Chemical weathering 5. Sedimentary rocks 6. Metamor ...
... - Minerals: Building Blocks of Rocks: 1. Composition and structures of minerals 2. Physical properties of minerals 3. Mineral groups 4. Silicate minerals - Rocks: Materials of the Lithosphere 1. Rock cycle 2. Igneous rocks 3. Physical weathering 4. Chemical weathering 5. Sedimentary rocks 6. Metamor ...
Foundation 1 - Discovering Astronomy
... Earth is the only terrestrial planet to have a significant magnetic field! To have a significant magnetic field, the planet must: 1. Be a fast rotator- Earth takes 24 hours to rotate 2. Liquid metallic interior- Earth has outer molten iron core ...
... Earth is the only terrestrial planet to have a significant magnetic field! To have a significant magnetic field, the planet must: 1. Be a fast rotator- Earth takes 24 hours to rotate 2. Liquid metallic interior- Earth has outer molten iron core ...
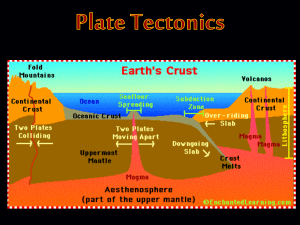
Plate Techtonics
... Earthquake – Violent movement of the earth along faults Seismograph – measures the intensity of earthquakes Focus – the point in the earth where an earthquake begins Epicenter – the point on the surface above the focus of an earthquake ...
... Earthquake – Violent movement of the earth along faults Seismograph – measures the intensity of earthquakes Focus – the point in the earth where an earthquake begins Epicenter – the point on the surface above the focus of an earthquake ...
Lithosphere #2
... Core- Made mostly of metals, iron and nickel; consists of 2 parts, outer core (molten) and inner core (solid); movement of outer core creates magnetic field, and is composed of iron. ...
... Core- Made mostly of metals, iron and nickel; consists of 2 parts, outer core (molten) and inner core (solid); movement of outer core creates magnetic field, and is composed of iron. ...
ASTRONOMY 161
... Continuing convection in the asthenosphere causes plates to move relative to each other. The study of plate motion is called plate tectonics. The motion of continents was first suspected by Sir Francis Bacon (17th cent). Best known for leading the scientific revolution with his new 'observation and ...
... Continuing convection in the asthenosphere causes plates to move relative to each other. The study of plate motion is called plate tectonics. The motion of continents was first suspected by Sir Francis Bacon (17th cent). Best known for leading the scientific revolution with his new 'observation and ...
Physical Layers of Earth
... The oceanic crust is thinner than the continental crust. Oceanic crust is also denser than continental crust ...
... The oceanic crust is thinner than the continental crust. Oceanic crust is also denser than continental crust ...
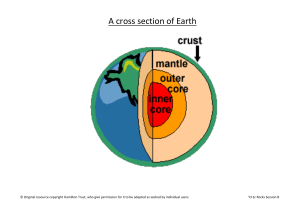
Earth Surfaces Chapter 1 Study Guide The inner core is . (A
... 15. Mantle material rises in convection currents because heated materials N. conduction become ____________ dense. (U-Y) 16. When geologists study Earth’s interior, they rely on ________ methods O. indirect such as seismic waves to study layers. (K-O) 17. When sun warms your face it is a form of hea ...
... 15. Mantle material rises in convection currents because heated materials N. conduction become ____________ dense. (U-Y) 16. When geologists study Earth’s interior, they rely on ________ methods O. indirect such as seismic waves to study layers. (K-O) 17. When sun warms your face it is a form of hea ...
Naked Science Colliding Continents
... What will Earth look like in 250 million years? Explore the powerful forces deep below the Earth's surface that rip apart vast landmasses and smash them together, creating everything from tsunamis and earthquakes to mountains and canyons. Watch the documentary and answer the following questions (you ...
... What will Earth look like in 250 million years? Explore the powerful forces deep below the Earth's surface that rip apart vast landmasses and smash them together, creating everything from tsunamis and earthquakes to mountains and canyons. Watch the documentary and answer the following questions (you ...
Cross section of the Earth
... layer of red-hot solid rocks; some of these rocks are so soft that they ooze about and can blast out of cracks in the crust, as lava. The layer under the mantle is called the Outer Core. It is made of liquid iron and nickel. Special movement in this section is responsible for the Earth’s magnetic ...
... layer of red-hot solid rocks; some of these rocks are so soft that they ooze about and can blast out of cracks in the crust, as lava. The layer under the mantle is called the Outer Core. It is made of liquid iron and nickel. Special movement in this section is responsible for the Earth’s magnetic ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.